The Protecting Access to Medicare Act (PAMA)
Congress passed the Protecting Access to Medicare Act (PAMA) in 2014 to help safeguard Medicare beneficiaries’ access to needed health services, including laboratory tests. Unfortunately, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has taken a flawed and misguided approach to PAMA implementation. As a result of the Department’s actions, seniors will face an estimated $670 million in cuts to critical lab services this year alone, leaving the health of 57 million Medicare beneficiaries hanging in the balance.
PAMA cuts will be particularly burdensome to the most vulnerable seniors, such as those in skilled nursing facilities, those managing chronic conditions, and seniors living in medically underserved communities. The American Clinical Laboratory Association has raised significant concerns about the impact of Medicare lab cuts on seniors and their access to lifesaving diagnostics and lab services.
Learn more about the harm posed by these cuts on seniors here. Read the lawsuit ACLA has filed against HHS here.
WHAT’S AT STAKE
In 2016, seniors enrolled in Medicare received an average of
16 individual lab tests per year
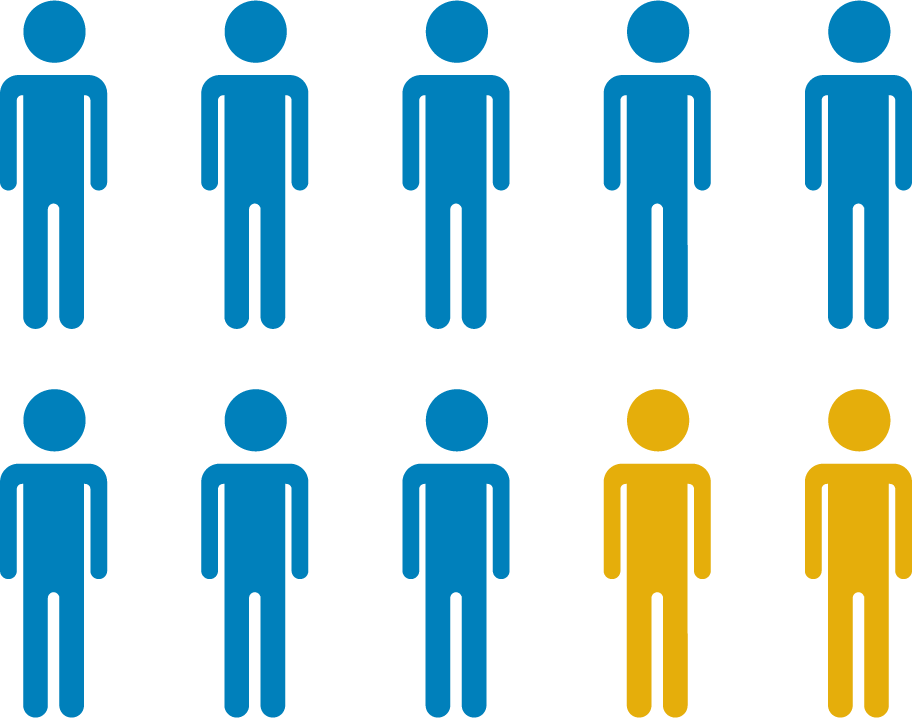

80% of seniors
have at least one chronic disease and 77% have at least two—successful disease monitoring and management requires reliable access to routine testing

1 million
seniors are living in assisted living or skilled nursing homes

3.5 million
homebound seniors
rely on skilled home health care services

An estimated
10 million
seniors live in rural areas
LACK OF ACCESS TO LAB TESTS
can result in undiagnosed conditions, lack of treatment for sick patients, and the failure to monitor and treat chronic conditions before they become worse—
resulting in a decline in overall health and longevity.
The PAMA cuts will also have a broad impact on laboratories across the country. Those that will face the brunt of the cuts are the very labs and providers that are uniquely positioned to provide services—like house-calls, 24-hour emergency STAT testing, and in-facility services at skilled nursing facilities—that are particularly important to seniors who are more likely to be homebound, managing multiple chronic conditions, or living in rural areas that are medically underserved.


