Cartoon – Unmitigated Disaster Spin


https://www.axios.com/coronavirus-lessons-other-countries-24794264-1653-4500-922c-7f1c66efa011.html
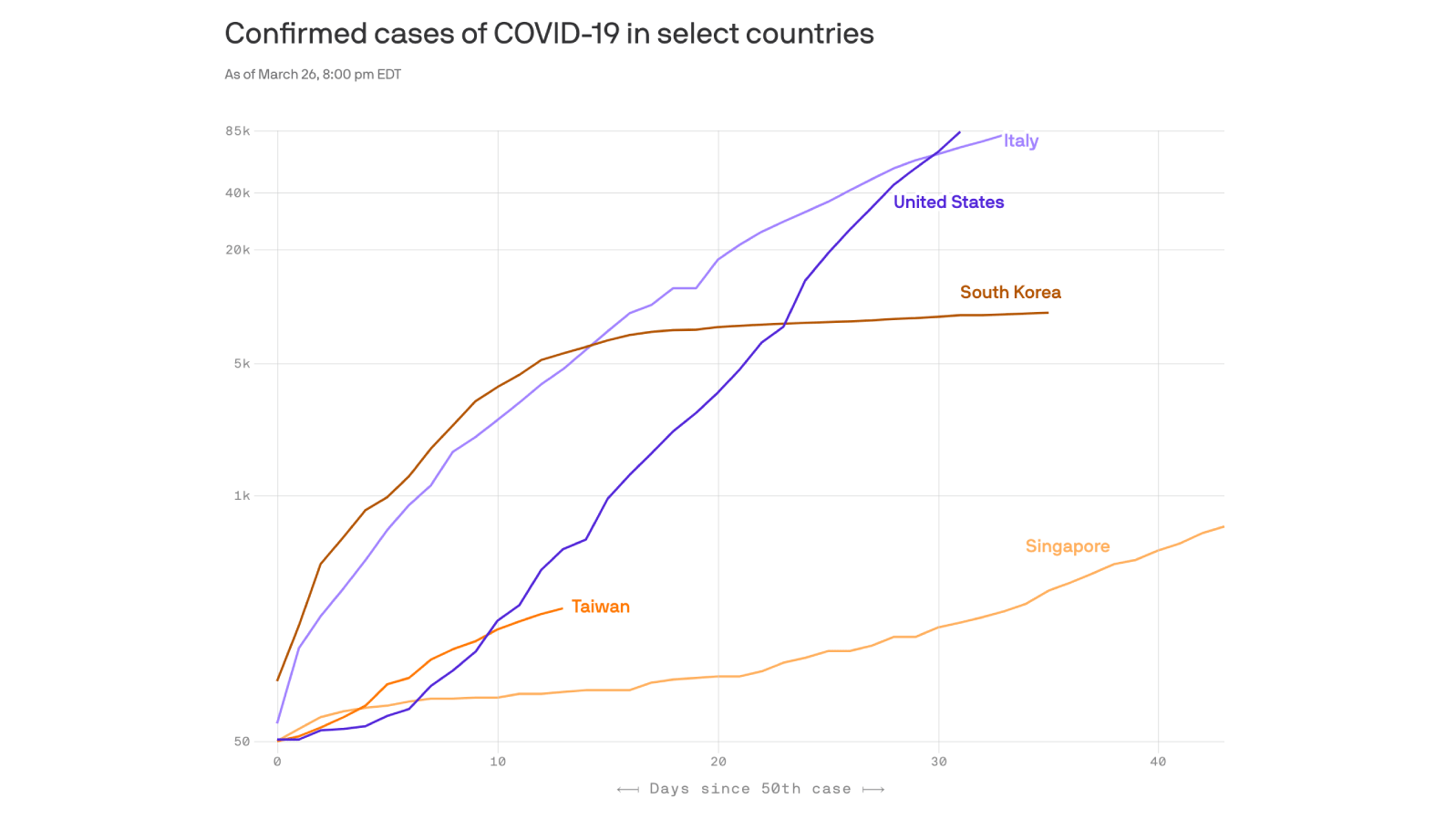
The countries that have most successfully fended off the novel coronavirus have mainly done it with a combination of new technology and old-school principles.
Why it matters: There’s a lot the U.S. can learn from the way other countries have handled this global pandemic — although we may not be able to apply those lessons as quickly as we’d like.
The big picture: A handful of Asian countries, including South Korea, Singapore and Taiwan, have succeeded where the U.S. and Europe have failed.
The bad news: It’s too late for the U.S. to simply do what worked in those countries. We’ve already made too many mistakes.
As a new infection begins to spread, you want to quickly test the people who might have it, and quarantine the ones who do. Then you want to figure out who else they might have infected, and test those people, and quarantine the ones who are indeed sick. This process gets repeated.
This test-and-trace process is nothing new. It’s the standard playbook. South Korea, Singapore and Taiwan just executed it a lot better than the United States.
Next time a mysterious virus starts spreading abroad, better testing and a much faster response will be imperative.
Singapore has gotten pretty draconian with its track-and-trace process.
That might be too Big Brother for the U.S., but a voluntary version of it might work — we already consent to a whole lot of location tracking for much less important ends.
Taiwan, meanwhile, aided its coronavirus response by making better use of data it already had. It quickly merged its immigration and health care databases, giving authorities a real-time view of who was getting sick and where they had traveled.
Public communication is one of the big things Italy — a leading example of what not to do — got wrong.
Singapore, by contrast, came out early with a clear message: This was going to be bad for a while, and people needed to stick together and do their part.
The U.S., so far, looks a lot more like Italy.
The U.S. can’t go back in time to get things right at the beginning. So we can’t match the success of places like South Korea.
The bottom line: “If we had got on top of this thing two months ago, America would look very, very different,” Ashish Jha, director of Harvard’s Global Health Institute, said in a recent interview with the New Yorker.

With news this weekend that the coronavirus is poised to become a global pandemic and that China covered up early evidence of its spread, I was pleased to see an article from Ashley Fuoco Antonelli of the Advisory Board’s Daily Briefing revisiting a four-year-old post of mine. Kristina Daugirdas (my wife) and I had just taught a class on global outbreaks, and we pulled together a list of recurring patterns.
Fuoco Antonelli goes through that list and carefully shows how each of them maps pretty well onto what we’ve seen so far with the coronavirus. Here’s a taste:
Bagley’s 2016 list features several recurring themes that center on governments’ responses to disease outbreaks. For instance, three themes that he highlighted are:
- “Governments are typically unprepared, disorganized, and resistant to taking steps necessary to contain infectious diseases, especially in their early phases”;
- “Public officials are reluctant to publicize infections for fear of devastating the economy”; and
- “Local, state, federal, and global governing bodies are apt to point fingers at one another over who’s responsible for taking action. Clear lines of authority are lacking.”
Each of those themes certainly holds true today. Media outlets have reported that China was slow to report the new coronavirus outbreak and implement measures to contain it. And some observers have questioned whether Chinese officials downplayed the outbreak’s severity.
For example, the New York Times‘s Li Yuan writes that, as the first cases of the virus emerged, officials “insisted that it was controlled and treatable,” and “the [Chinese] government took pains to keep up appearances.” For example, she notes, “[T]wo days before Wuhan told the world about the severity of the outbreak, it hosted a potluck banquet attended by more than 40,000 families so the city could apply for a world record for most dishes served at an event.”
Media reports also have highlighted complications and conflict between local and central officials in China regarding what information could be shared with the public. For instance, the Wall Street Journal‘s Josh Chin writes that Wuhan Mayor Zhou Xianwang has cited rules set by leaders in Beijing for “limit[ing] what he could disclose about the threat posed by the pathogen.”
As I told Fuoco Antonelli, there’s a sense that we’ve seen this movie before, and history offers us resources for thinking about how this is likely to play out. That may explain why some of the best writing on the virus has come from historians of infectious disease—including in particular my colleague Howard Markel, who has criticized the Chinese authorities for their heavy-handed quarantine.
I wanted to close by flagging Ashish Jha’s recent post at the Health Affairs Blog. Ashish takes an early look at the American response and closes with a look toward the future:
Here is the bottom line: we need to be doing more. This outbreak, under the best of circumstances, is going to cost countries around the world tens of billions of U.S. dollars and American businesses possibly many billions more. Yet we spend a fraction of that each year on vaccine platforms, research on viruses, and capacity-building for rapid vaccine production. Firefighting is always more expensive than fire prevention. In a highly connected world, with climate change upon us, novel disease outbreaks that become global is the new normal.
Indeed, if history teaches us anything, it’s that outbreaks of novel infectious diseases have always been normal. Even so, we’re almost never ready. History teaches us that too.






