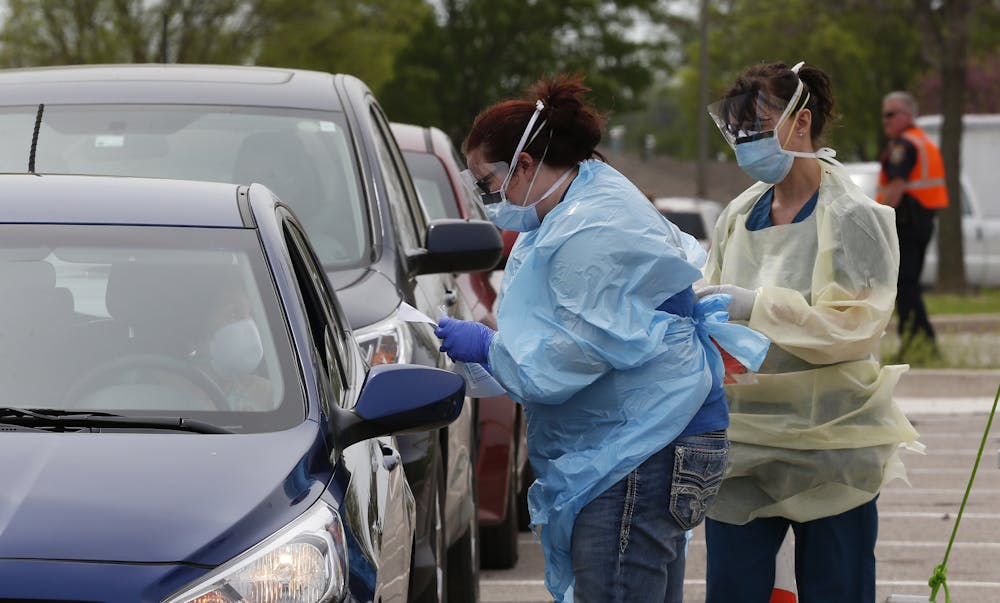
For many people in the U.S., getting tested for COVID-19 is a struggle. In Arizona, testing sites have seen lines of hundreds of cars stretching over a mile. In Texas and Florida, some people were waiting for five hours for free testing.
The inconvenience of these long waits alone discourages many people from getting tested. With the surge in cases, many public testing sites have been reaching maximum capacity within hours of opening, leaving many people unable to get tested for days. Those that do get tested often face a week-long wait to get their test results.
Every person who isn’t tested could be spreading COVID-19 unknowingly. These overstretched testing programs are a weak link in the U.S. pandemic response.
I study public health policy to combat infectious disease epidemics. The key to overcoming this pandemic is to slow transmission of the virus by preventing contagious people from infecting others. A widespread quarantine would accomplish this, but is economically and socially burdensome. Testing offers a way to identify contagious people so they can be isolated to prevent the spread of the disease. This is especially important for COVID-19 because an estimated 40% or more of all people infected with SARS-CoV-2 have few or no symptoms so testing is the only way to identify them.
Some states are doing much better than others. But as a whole, the U.S. is falling far short of the amount of testing needed to control the pandemic. What are the challenges the U.S. is facing? And what is the way forward?
Testing should be free, easy, fast and accurate
The ultimate goal of testing is for everyone, regardless of symptoms, to know at all times whether they are infected with the coronavirus. To achieve this level of testing, tests should be free, very easy to perform and provide accurate results quickly.
Ideally, free COVID-19 tests would be delivered to everyone directly. The tests would be simple to perform – like a saliva test – and would give a perfectly accurate result within minutes. Everyone could test themselves weekly or anytime they were going to be in close contact with other people.
In this ideal scenario, most, if not all, contagious people would be detected before they could spread the virus to others. And because of the rapid results, there would be no burden of quarantining between doing the test and getting the result.
Researchers are working on better-quality tests, but access is a problem of infrastructure, not science. Right now, nowhere in the U.S. comes close to meeting surging demand for testing.

One of the worst cases: Texas
The difficulty of getting a COVID-19 test varies by state, but currently, people in Texas face some of the biggest obstacles, which results in far fewer tests being done than is needed to control the pandemic.
First, Houston – which is experiencing a surge in cases – and many testing sites across the state recommend or offer testing only to people who have symptoms, were exposed to a COVID-19 case or are a member of a high-risk group.
Even people recommended for testing still face challenges. It is possible to request an appointment for a free COVID-19 test, but testing facilities can handle only so many patients a day and testing slots fill up quickly. Even if someone gets an appointment, they may face an hours-long wait at the testing site.
Finally, public health experts recommend that people who may have been exposed to COVID-19 should quarantine at home for 14 days or until they receive a negative test result. In Texas, patients are supposed to get results through an online portal in three to five days, but many labs have been taking seven to nine days to return results. These long delays mean people face a much higher burden of quarantining while waiting for results.
All of these challenges make it clear that Texas is simply not testing enough people to keep the spread of COVID-19 in check.
To gauge the success of COVID-19 testing programs, epidemiologists use a measure called test positivity. This is simply the percentage of tests that come back positive. The lower the test positivity, the better, because that means very few cases are going undetected. A high test-positivity rate is usually a sign that only the sickest people are getting tested and many cases are being missed.
The World Health Organization guidelines say that if more than 1 out of 20 COVID-19 tests comes back positive – a test positivity of more than 5% – this is an indication that a lot of cases are not diagnosed and the epidemic is not under control.
Texas currently has a test-positivity of around 16%, which means that a lot of infected people are not getting tested and may be unknowingly spreading the disease.

One of the best cases: New Mexico
In stark contrast to Texas is New Mexico, which has one of the strongest testing programs in the U.S.
First, public health officials there encourage everyone to get tested for COVID-19 regardless of symptoms or exposure. The state has also prohibited health providers from charging patients for tests. People seeking a test have the option to walk in or to make an appointment ahead of time, whichever is more convenient.
All of this relatively good access to testing has resulted in one of the highest per capita testing rates in the country, at over 20,000 tests per 100,000 people, and a test-positivity rate of around 4%. New Mexico’s testing program is diagnosing a relatively high proportion of cases despite the state experiencing a recent surge.
New Mexico still has room for improvement. Long lines, wait times and limited capacity are becoming more common as cases surge, but the foundation of a strong testing program has helped the state cope with the increase in cases.
The big-picture problems
The pre-pandemic infectious disease testing capabilities in the U.S. are clearly unable to meet the current demand. A nationwide response is needed, and there are three things that Congress, the federal government and local governments can do to help ensure COVID-19 tests will be easy to get, fast and accurate.
First, Congress can provide funding to stimulate the testing supply chain, scale up existing testing programs and promote innovation in test development.
Second, governments can improve the management and coordination of testing programs to more efficiently use existing resources.
And third, innovative testing methods that reduce the need for lab capacity – like paper-strip tests and pooled testing – need be approved and implemented more quickly.
Every little improvement in testing capabilities means more COVID-19 cases can be caught before the virus is transmitted. And slowing the spread of the virus is the key to overcoming the pandemic.



