https://www.bloomberg.com/news/features/2018-08-22/priced-out-of-health-insurance-americans-rig-their-own-safety-nets

Consumers frustrated by high costs are bypassing the bureaucracy with patchwork plans.
When their son Sky was born four years ago, Lindsie and Chris Bergevin were hit with a big surprise: $7,000 in bills for the birth that their health plan didn’t cover. Sky was two when the couple jettisoned their medical insurance, which helped them eventually pay off the debt.
Now that they’re ready to have a second child, they’re not going back to their old coverage, with its premiums of more than $350 a month. Instead, they’ve patched together an alternative through a religious group and a primary-care doctor whom they can visit anytime for a monthly fee.
“I was so jaded with the whole health-care insurance situation,” Lindsie, 35, says. “I just didn’t want to deal with it.”
The Bergevins, who rent a snug little house near downtown Boise, Idaho, are joining a small but growing number of Americans rigging their own medical safety nets. They’re frustrated by the high costs, opaque pricing, and maddening bureaucracy of health insurance.
In their quest for a different way, they’re meeting doctors like Julie Gunther who are also fed up. These physicians have opted to reject insurance, instead charging patients directly in return for more personalized care.
“I like to think we can protect people in vulnerable moments where they’re going to get lost like a widget,” Gunther said, “because they’re not a widget for us.”
We Want to Hear Your Insurance Story:
Bloomberg News wants to hear about being uninsured in America in 2018 and what it means to you.
Please click here to tell us your story.
Bloomberg News is following people who are uninsured in a year-long effort to tell the story of Americans struggling to afford the rising costs of health care, and the financial and medical trade-offs they make.
No reliable data exist on how many people are replacing insurance with arrangements like the Bergevins’, but the trend appears to be gaining momentum.
The number of people joining so-called health-care sharing ministries—religion-based cost-sharing plans—rose 74 percent from 2014 to 2016, according to the latest Internal Revenue Service data. An alliance for the groups said that more than 1 million people now participate in such programs. Similarly, primary-care clinics like the one Julie Gunther started in 2014 have grown to almost 900 from just a handful in the early 2000s, according to the Direct Primary Care Coalition, a trade group for the clinics.
The number of people without traditional insurance is expected to increase. The Trump Administration lifted the Affordable Care Act’s penalty for those who go without insurance, while also encouraging the growth of lightly regulated products such as short-term health plans. Proponents of Obamacare fear the administration’s actions will draw healthy people out of the ACA marketplaces, raising costs for those who remain.
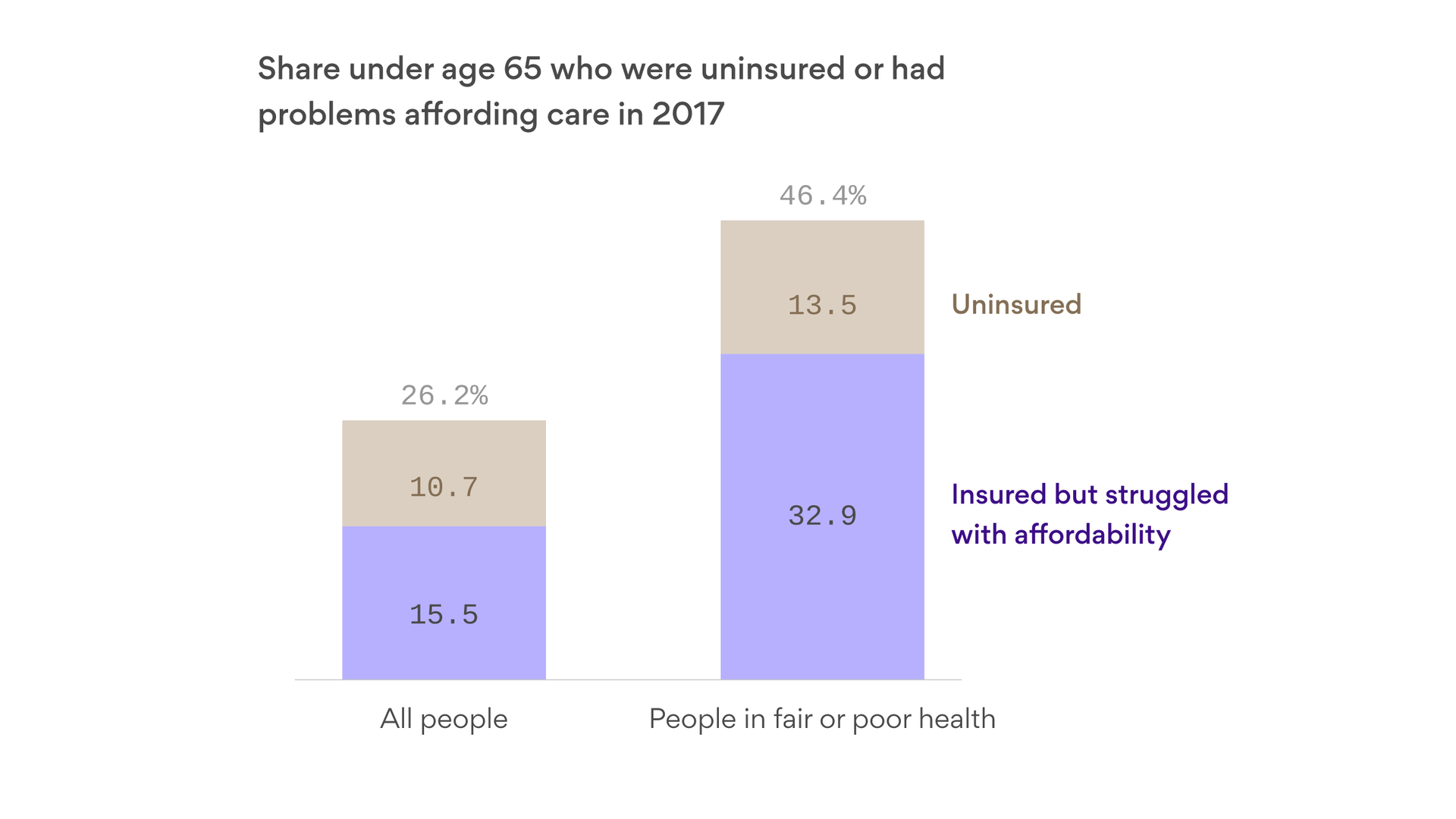
Though the ACA expanded coverage to 19 million Americans, some of those gains are reversing. About 28 million remain uninsured. A study by the Kaiser Family Foundation, a health-research nonprofit, determined that most uninsured families simply found health insurance too expensive.
The Bergevins are one of those families.
Lindsie is a freelance graphic designer who focuses on clients in the craft industry. Chris, 34, is a supervisor at the auto shop the Bergevins jointly own with another couple. Though the business is growing, things were tight enough that Chris didn’t draw a salary until last summer. Last year, the couple took home from $40,000 to $50,000, after taxes.
In 2014, when Lindsie was pregnant with Sky, the couple still had coverage through her job at the Idaho Statesman newspaper.
A calculator on her Aetna health plan’s website estimated the Bergevins would need to pay about $3,000 or $4,000 out-of-pocket for Sky’s birth. When the total bill came, the sum for prenatal care, hospital costs, anesthesia, and other care was triple the estimate.
They were still paying off Sky’s birth in 2016 when Lindsie had surgery to remove her tonsils and correct a deviated septum, leaving them with several thousands of dollars more in bills.
She put the sum on a CareCredit medical credit card and is paying $300 each month toward that debt.
As the couple thought more about it, maintaining their coverage made little sense. They were falling deeper into medical debt, despite having insurance which itself cost thousands of dollars a year. In 2016, Lindsie left her newspaper job to devote herself full-time to her thriving freelance design business—and they went uninsured.
“I couldn’t justify it,” she says. The cheapest policy she could find through the Affordable Care Act, she recalls, was $547 a month—more than half the family’s $875 monthly rent at the time. It had a high deductible that could leave them with out-of-pocket costs of more than $10,000.
“If something were to happen to us, we would have been in trouble,” she acknowledges. To hedge, the couple bought an inexpensive accident policy from Aflac that would cover some costs from an injury if, for example, Chris hurt himself working.
A friend told them about a small primary-care clinic called SparkMD less than a mile from their house. The doctors didn’t accept insurance. Instead, they charged a monthly fee of $130 per family. That allowed visits as needed without any limits. When Lindsie went to check it out, a physician began with an in-depth conversation about the family’s health.
“It was amazing. She sat down with me for an hour and talked about everything,” Lindsie says.
Gunther, the Bergevins’ new physician, had long wanted to be a family doctor in her hometown. Working for a large hospital system, though, she was soon chafing under a bureaucracy that seemed to make too many of her clinical decisions for her, down to what tools and equipment she could use. Even worse, Gunther was paid based on her volume of patients and services billed.
She saw patients in 15-minute intervals and says she felt like a factory line worker. She’d later joke that she spent longer waiting in line for her morning coffee than she did with a patient.
“I was saying ‘I’m sorry’ all the time,” Gunther, 42, recalls. “I’m sorry I’m late, I’m sorry this didn’t get called in, I’m sorry this got forgotten, I’m sorry they didn’t give me the message.”
Burned out, she quit her job in 2014 and started her own practice. She borrowed about $200,000 to renovate an old red-brick law office on a leafy corner of downtown Boise, a few blocks from one of the city’s big hospital campuses.
Along with a nurse practitioner and a small office staff, she cares for about 600 patients. A typical primary-care doctor carries at least double or triple that load. More than half of Gunther’s patients have health insurance, often in high-deductible plans. Others are small business owners like the Bergevins. Most are disenchanted with the health-care system.
Last year, Lindsie Bergevin had a bad fever and what she described as “the worst pain I think I ever had in my head.” She called Gunther at 9:30 p.m. on a Saturday. Gunther met her at the clinic 15 minutes later. “She’s like, ‘Girl, you have a double ear infection, and the worst I’ve ever seen.’”
Bergevin walked out with an antibiotic and says that if Gunther hadn’t seen her, she would’ve gone to the emergency room, which could have resulted in a bill for hundreds or thousands of dollars.
Gunther tells her patients that belonging to her practice is not a replacement for having health insurance.
“There’s a whole bunch of things I can’t take care of,” Gunther says. “If you’re not standing upright, or bleeding doesn’t stop, do not call me.”
In April, knowing that they wanted to conceive this year, the Bergevins paid to join a Christian nonprofit called Liberty HealthShare. Organizations like Liberty, sometimes called faith-based plans, help like-minded members share some medical costs. To join, members must pledge to adhere to Christian principles. They are required to make fixed payments each month, and the money is disbursed to cover health-care needs for other families.
Though health-sharing ministries function like insurance in some ways, they aren’t regulated by states, don’t have capital requirements to protect against large losses and don’t have to adhere to rules about minimum benefits. They decline to cover medical expenses that result from behavior they deem immoral. They won’t pay medical costs for a drunk driver in a car crash, for example, or for contraception.
There are other restrictions too: Liberty limits coverage of pre-existing conditions for up to three years, according to its guidelines. Members can also get bounced for “failure to fully disclose known or suspected pre-existing condition information” when they join. Those limits are part of the reason why they’re cheaper—and potentially riskier.
The Bergevins originally expected to pay $450 per month for Liberty. Because Lindsie is overweight, they pay a surcharge of $80 per month—a fee regulated insurers are barred from charging. When they joined, their plan had an “annual unshared amount”—the equivalent of a deductible—of $1,500. Two months later, they learned that amount would increase to $2,250. Lindsie wasn’t thrilled, but she calls it “a ton cheaper than a typical deductible.” And on the plus side, Liberty would reimburse them for some of the cost of membership in SparkMD.
In early June, Lindsie sat at her kitchen table with a stack of medical bills going back four years. Sky ran in from the living room, where Dr. Seuss cartoons played on the TV, looking for dessert before he finished his dinner.
The Bergevins’ improvised plan has pros and cons. They didn’t have to pay premiums for almost two years while they were uninsured, easing their finances significantly while their businesses grew. They love the personalized care they get from Gunther. And their costs for having another child should be capped at a lower level under the Liberty plan.
But between Liberty and SparkMD, the Bergevins pay more than they did for health coverage through Lindsie’s old job, and, she estimates, about as much as Obamacare insurance would cost. The family is still exposed to considerable risk. Liberty caps reimbursements at $1 million—a limit that insurance companies can’t impose. They have two friends who have had cancer, and, Chris says, “a million’s definitely not enough.”
The Bergevins have their fingers crossed that their choices will allow them to expand their family without incurring the kind of debt that Sky’s birth and Lindsie’s surgery left them with. But they know their improvised approach isn’t for everyone.
“It’s not like I’m trying to say, just go without insurance,” Lindsie says. “You have to find something that’s going to work for you.”