THE PROGNOSIS
New Census Bureau data on the number of uninsured Americans is either a testament to the resiliency of the Affordable Care Act or a sign that President Trump’s anti-ACA rhetoric and policies are starting to work.
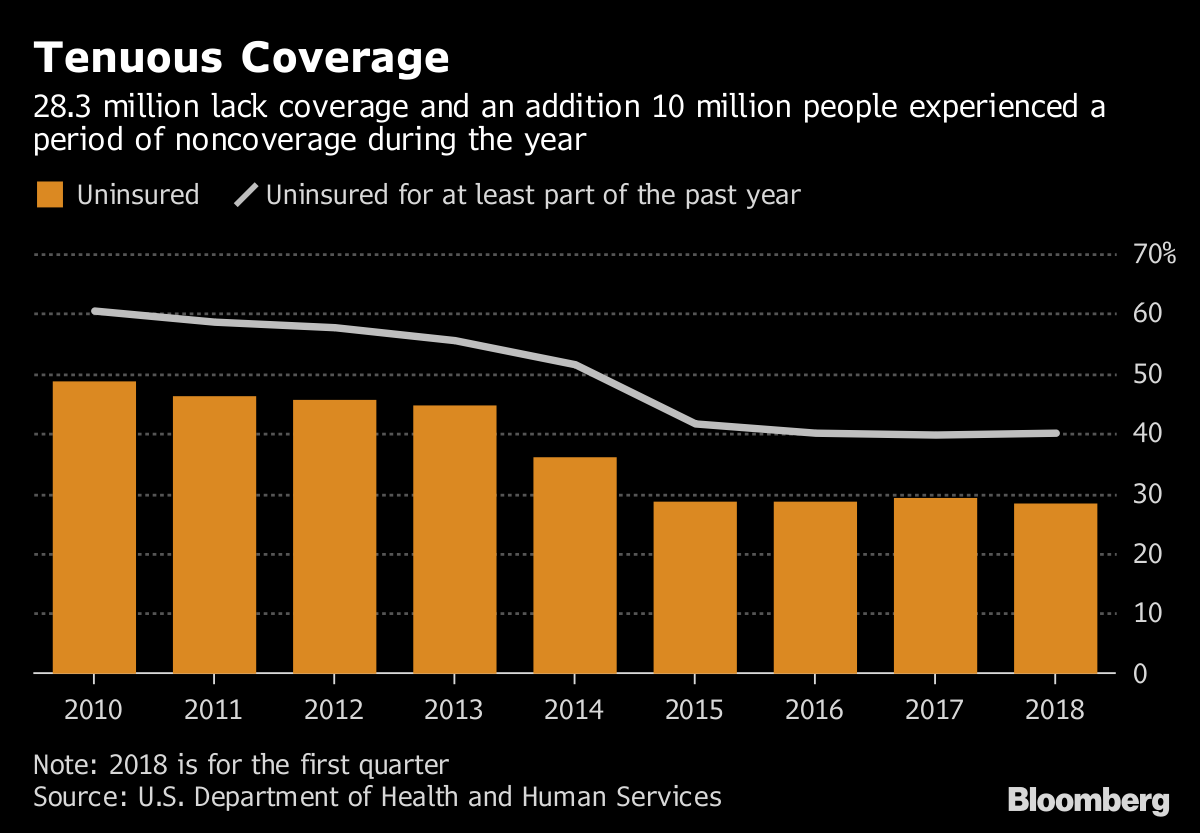
As our colleague Jeff Stein reported Wednesday, there was a slight uptick in the number of Americans without health insurance in 2017 compared to 2016, even though that number essentially remained statistically flat. Still, the fact that uninsured rate went up at all, by about 400,000 people, marks the first time since the ACA’s implementation that the uninsured rate didn’t drop.
Supporters of the ACA worry the news marks the beginning of a trend, especially when some of Trump administration policies intended to circumvent the ACA go into effect next year.
Ahead of open enrollment last year, the Trump administration dramatically decreased funding for any Obamacare outreach or advertising, limited resources for “navigators” who help people find an insurance plan, and shortened the window for people to sign up for insurance from three months to six weeks in states that use a federally run marketplace.
“Even with all of that, health coverage stayed steady. But at the same time, we’d like to see further progress in the rate of the uninsured,” said Judith Solomon of the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
It’s part of a pattern to weaken the 2010 health-care law known as Obamacare. After the GOP Congress failed to repeal and replace the ACA last summer, the Trump administration moved to dilute the law in other ways: including signing off on a plan to eliminate the individual mandate penalty next year; allowing individuals to buy skimpier, short-term health plans without certain coverage requirements under Obamacare; and seeking to allow states to put conditions on Medicaid coverage.
Some of the most prominent health care organizations in the country came together this morning to voice their disapproval of those short-term plans — including the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, the American Heart Association, Planned Parenthood Federation of America, the National Women’s Law Center, the , American Academy of Family Physicians, the American Academy of Pediatrics and Families USA.
“The Administration’s decision to expand short-term health plans will leave cancer patients and survivors with higher premiums and fewer insurance options,” said Dr. Gwen Nichols, chief medical officer of the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society.
The groups’ statements, compiled and released by Sen. Tammy Baldwin (D-Wis.), are in support of the senator’s effort to have Congress rescind the White House regulation. Nearly every Democratic senator has signed a resolution of disapproval to overturn it.
The census data reflects trends that started last year, when the administration’s policies had yet to be implemented. Fourteen states saw their uninsured populations rise in 2017. The only three states that didn’t see a spike in that number were New York, California and Louisiana. The first two aren’t surprising given those states’ robust efforts to enroll their own residents, while Louisiana expanded Medicaid in June 2016 so its decrease represents those low-income individuals who now have government coverage.
Medicaid expansion in most of the 33 states and D.C. that have done so under the ACA has predictably decreased the number of people without coverage. The uninsured rate last year in states with an expanded Medicaid program was 6.6 percent compared to 12.2 percent in non-expansion states — a gap that has only continued to grow since 2013.
To be fair, as Larry Levitt, senior vice president at the Kaiser Family Foundation, pointed out on Twitter: the uninsured rate started leveling off before the Trump administration started its work. But Levitt suggested the uninsured rate may really rise in 2019 when elimination of the individual mandate penalty takes effect. Moreover, states are increasingly taking the White House up on its suggestion to add work requirements to their Medicaid programs — in just the first three months of it being implemented in Arkansas, more than 4,000 people were jettisoned from the rolls for failure to comply.
Matthew Fiedler, a health-policy expert at the Brookings Institution, agreed with Levitt’s assessment, noting that the bulk of the people who were uninsured pre-ACA have already been enrolled in the program. He contended that if policy had remained static, there would likely have been a modest decline instead of similar increase in the uninsured rate — though not a dramatic one. The real effects, he said, of the Trump administration’s efforts to chip away at the ACA are still to come.
“I don’t think the right takeaway is that none of the policy changes will have a negative effect. I think they will going forward, we just haven’t seen that yet,” he said. “I think if your goal is to evaluate the ACA, I think the right takeaway is that there was a lot of progress, but more policy progress to be made.”
Of course, Democrats and Republicans have disparate views on how to get there. Democrats are now pushing for a public option or a universal health care system in which the government would foot the bill for many health-care costs. A lot of them feel the ACA “got us roughly 40 percent there and established a framework for lawmakers to make that progress going forward,” Fiedler said. That’s why we’re now seeing so many Democratic candidates and lawmakers embracing some iteration of a “Medicare for all” program.
Republicans still criticize the ACA as vast government overreach and are vowing they will take another stab at repealing it should they maintain the congressional majorities after the November midterms.
“We made an effort to fully repeal and replace ObamaCare and we’ll continue,” Vice President Pence said while campaigning for Baldwin’s opponent, Leah Vukmir, if the GOP performs well in the midterms.
One additional interesting data point from the census is ages at which there was the greatest increases or decreases in the uninsured rate. As highlighted in the chart above, rates of those without insurance rose at ages 18 and 19 — when children are no longer eligible for the Children’s Health Insurance Program; and for those between ages 25 and 26 — when children no longer qualify for their parents’ insurance. The uninsured rate dropped, however, for those aged 64 and 65 — when adults are eligible for Medicare.
The greatest spike in those without insurance was documented for 26 year olds. That’s likely because young adults are typically healthier and feel less urgency to pay for insurance when they lose coverage under their family’s plan.
As noted by the New York Times’ Margot Sanger Katz on Twitter, these stats show just how crucial government programs and laws have been in providing health coverage to Americans: