https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/hospital-management-administration/2017-the-year-that-was-10-things-for-healthcare-executives-to-note-as-they-head-into-2018.html

Disruption got real. Hospital-insurer negotiations heated up. Activist shareholders shook up legacy hospital operators. Healthcare and the government failed to effectively communicate. These and six other trends that shaped the year in healthcare — and the lessons executives can take from them into 2018.
1. Disruption got real. After years of speculation about who or what would become the “Uber of healthcare,” the tectonic plates of the industry shifted substantially in the past year — and there’s reason to believe this will only continue in 2018. A number of mergers illustrate the blurring line between healthcare and other industries, such as retail and insurance. Consider the combinations of CVS and Aetna or Optum and DaVita and Surgical Care Affiliates. As for what’s to come, Apple and Amazon have both shown interest in expanding their healthcare footprint. In fact, just last month, we reported Amazon was in talks to move into the EHR space.
Executive’s takeaway: Executives grew skeptical of the term ‘disruptor’ when it was used as generously as it was circa 2011-2016. But now disruption is actually unfolding at a rapid clip, and executives are paying close attention to who/what poses the greatest threat to their business models.
2. Hospital-insurer negotiations heated up. Previously, a health system and a commercial insurer occasionally hit a snag in the contract negotiation process, resulting in a dispute palpable enough to consumers that it warranted headlines. These impasses generally lasted a matter of weeks before outside pressure drove the parties to compromise. The nature of these conflicts has since changed. This past year brought regular coverage of strained provider-payer talks. In fact, we now do a weekly compilation of payer-provider disputes and resolutions to stay abreast of these conflicts as they occur and subside. In 2017, we saw lawmakers intervene in payer-provider disputes, a health system executive’s meant-to-be-private email about an insurance company go public, and a children’s hospital go out of network with a commercial insurer — affecting 10,000 kids.
Executive’s takeaway: Health system executives are growing increasingly vocal with their thoughts about commercial insurers. In the past, executives took great lengths to observe discretion in these relationships. Now the gloves are off — or at least one is. We’re sure we haven’t seen the worst of a payer-provider dispute yet, but the number we see on a weekly basis, and their tone, indicates that disputes are both more frequent and more serious than in years past.
3. Investments in value-based care, once a somewhat safe bet, became debatable. In a final rule issued in November, CMS officially canceled the hip fracture and cardiac bundled payment programs and rolled back some mandatory requirements in the Comprehensive Care for Joint Replacement Model. This will continue to have a ripple effect on payers, providers and health system strategy. For hospitals and health systems that made significant investments to support excellence under the program, this news is difficult to take — especially since no investment is made lightly amid thin margins. Although CMS says it is still committed to value-based care as a concept, the mandatory nature of the bundles program acted as a pedal-to-the-metal force that made hospitals act. Since commercial payers follow Medicare, the fate of the program will likely influence the adoption of bundles among private insurers, too.
Executive’s takeaway: Most all executives tell us they want to be on the leading edge, not bleeding edge, of value-based care. Without a “do it or lose it” approach to bundles, the industry lost a major impetus toward value-based care, in which many health systems and physicians would take the plunge together. Providers have never had a clearly paved path for their “journey toward value-based care.” At best, it was a dirt trail. Now it could be compared to a dirt trail covered in snow. This leaves executives questioning the value of their current and future investments in value-based care.
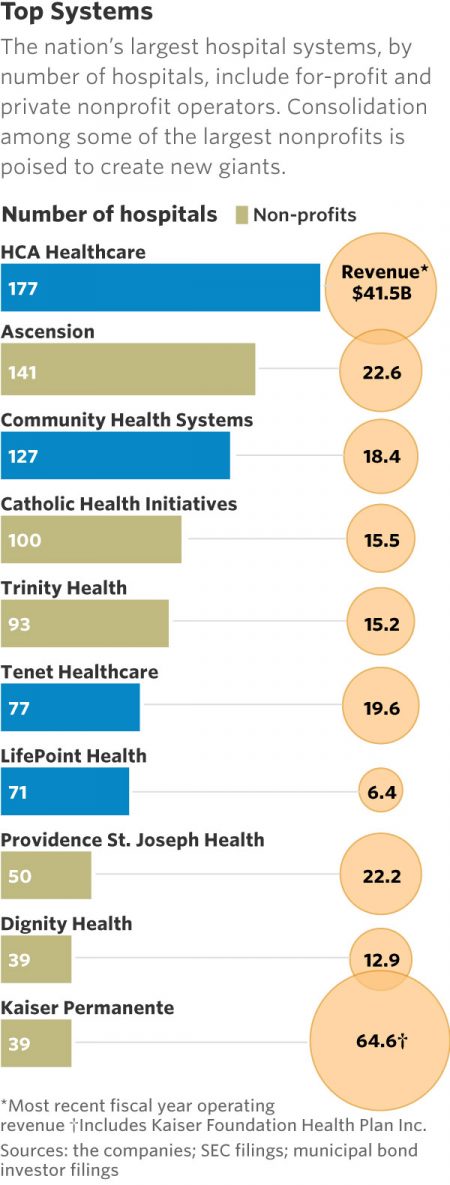
4. Big systems want bigger. Just when you thought you had a handle on what a “big” health system looked like in the United States, a few major players rewrote (or are attemping to rewrite) the playbook. After more than a year of talks, Catholic Health Initiatives and Dignity Health signed a definitive agreement in December to create a 139-hospital, $28.4 billion health system. Soon after came reports of St. Louis-based Ascension and Renton, Wash.-based Providence St. Joseph discussing a merger, which would result in a 191-hospital, $44.8 billion operation. Although both of these deals trail Oakland, Calif.-based Kaiser Permanente and its nearly $65 billion in revenue, they illustrate how the composition of nonprofit American health systems is continuing to change from local and regional entities to corporate national networks. For example, if Ascension and Providence combine, they will outsize the largest for-profit health system today — Nashville, Tenn.-based HCA Healthcare — which includes 177 hospitals in 20 states and Britain.
Executive’s takeaway: Executives may want to reevaluate the oft-spoken phrase “all healthcare is local” in light of 2017’s M&A activity. Hospitals will continue to serve as economic engines in their respective communities, but the organization of health systems is moving in a direction where they are viewed as ubiquitous brands as opposed to regional hubs for health. For example, San Francisco-based Dignity and Englewood, Colo.-based CHI are basing the corporate headquarters for their new enterprise in Chicago. Ascension and Providence would have footprints in 27 states if they merge.
5. Many health systems that were new players in the health plan business got out of it. Provider-sponsored health plans always carried a great amount of risk. Of the 37 health plans launched by hospitals and health systems since 2010, only four were found profitable in 2015, according to research published this past year by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. As major health insurers reduced their individual coverage options and rolled back from the public exchanges this year, we also saw several health systems decide to scale back or shut down their health plans. New Hyde Park, N.Y.-based Northwell Health shared plans in August to wind down its health insurance business, CareConnect, over the next year. Dayton, Ohio-based Premier Health is selling its health plan to Evolent Health, a Washington, D.C.-based value-based care platform. Louisville, Ky.-based Baptist Health plans to shut down its health plan operation in 2018. Late last year, Dallas-based Tenet Healthcare revealed plans to scale back its insurance business in 2017 after officials attributed lukewarm earnings to its health plan business.
Executive’s takeaway: When even the big five health insurers — so well-equipped with analytic tools, data, infrastructure, utilization management experience and risk analysis talent — have a difficult time accounting for risk, it is not surprising many green health systems made their move for the door this past year. This is not an opportune time for health systems with little experience managing risk to build or buy a health plan.
6. Activist shareholders shook up legacy hospital operators. Board room issues within the major for-profit hospital operators are typically opaque, but 2017 brought a rash of investor-prompted activity that resulted in ousted CEOs, overhauled boards of directors, poison pills and new governance rules. Tenet Healthcare underwent significant change in 2017 under intense pressure from its largest shareholder, Glenview Capital Management. When two Tenet board members, both employed by Glenview, resigned over what they described as “irreconcilable differences,” they made it known that Glenview would possibly “evaluate other avenues” to be a constructive owner of Tenet on or after Sept. 1. By Aug. 31, Tenet announced it would replace CEO Trevor Fetter, “refresh” the composition of its board of directors and implement a short-term shareholder rights plan. Mr. Fetter resigned in October, before a successor was named, after 14 years with the system. In August, an investor in Franklin, Tenn.-based Community Health Systems called for the resignationof CEO Wayne Smith, who has led the 127-hospital system since 1997, over what the investor described as missteps in strategy resulting in financial trouble for the system. At this time, Mr. Smith still holds his job, but CHS may be bracing for more investor activity. Chinese billionaire Tianqiao Chen has gradually been ramping up his stock in the hospital operator since 2016. At time of publication, he holds nearly 23 percent of CHS stock. Finally, directors of HCA Healthcare made a change in late 2017 to allow established investors to participate in the board seat nomination process, a move made in response to an activist investor.
Executive’s takeaway: The fact that two of the largest U.S. for-profit hospital operators faced calls for CEO resignations in 2017 is part of a sweeping trend across industries in which activist investors start campaigns for change by targeting top management. Between January and May 2017, activist shareholders were responsible for ousting CEOs at three high-profile S&P 500 companies — American International Group, CSX and Arconic, according to The Wall Street Journal. Investors were attempting to oust six other CEOs in the same time frame. It’s worth noting that CEOs feel the heat at the launch of campaigns versus as a last resort. The WSJ characterized this trend as “a new level of aggressiveness for a group already known for its bold actions.”
7. As the average health system C-suite grew, a few systems reduced administrative roles. While the number of practicing physicians in the U.S. grew 150 percent between 1975 and 2010, the number of healthcare administrators increased 3,200 percent in the same period. Yet in 2017, we saw a few major health systems go against the grain and not only lay off administrators, but eliminate their roles completely. In June, Houston-based MD Anderson Cancer Center eliminated executive vice president roles and gave senior vice presidents more focused areas of responsibility. Valley Medical Center, part of Seattle-based UW Medicine, got rid of the COO position in May, and Charleston, S.C.-based Roper St. Francis did the same in August. In December, San Diego-based Scripps Health shared plans to eliminate the CEO position in its four hospitals in favor of a regional CEO model.
Executive’s takeaway: This past year contained several isolated incidents in which executive or administrative jobs were not immune from the financial pressures mounting on hospitals and health systems. There is reason to believe “right-sizing” (or at least reducing) administrative staffing at health systems will continue throughout 2018. Chris Van Gorder, president and CEO of Scripps Health, recently shared that layoffs at the system will likely include administrative and leadership roles while the system continues to hire caregivers. His reasoning, an excerpt of which follows, is applicable to many health systems today: “Healthcare is changing rapidly with huge growth in ambulatory care and reduced utilization of inpatient hospitals — and given the elimination of the individual mandate under the Affordable Care Act, the uninsured will once again be growing nationally. … We’ve got to shift our organizational structures around to be able to deal with the new world of healthcare delivery, find ways of lowering our costs significantly. If we don’t, we will not be able to compete.”
8. Healthcare and the government failed to effectively communicate. In 2017, the opportunities for the Trump administration, Congress and healthcare leaders to convene about healthcare legislation and policy came and went. CEOs from the five largest nonprofit health systems in the country took pen to paper, urging President Donald Trump and Congress to meet with them and exchange ideas. In the end, the closest thing we saw to healthcare reform in 2017 were bills — the American Health Care Act, Better Care Reconciliation Act of 2017 (or Skinny Repeal package), the Graham-Cassidy healthcare bill — that received significant opposition from major healthcare stakeholders, which are not historically liberal. Yet even an avalanche of nays from the American Medical Association, American Hospital Association, Federation of American Hospitals, American Psychiatric Association, Association of American Medical Colleges and several other groups did not sway Congress. All but three Republican Senators voted to pass the Skinny Repeal package, illustrating how the bipartisan nature of our political process is overriding expertise and informed lawmaking.
Executive’s takeaway: A bipartisan approach is the most effective way when attempting to redesign a $3 trillion industry that influences life-or-death decisions. These efforts also require input from a variety of seasoned healthcare experts who can challenge ideas, anticipate repercussions and identify blind spots. This holds true no matter which party holds control of the White House, Congress or both. Although healthcare stakeholders and government officials did not productively connect in 2017, health system leaders must persist in their attempts to influence public policy and exercise greater creativity in their advocacy efforts. Strategies that worked in the past can no longer be counted on in 2018 and beyond.
9. Fed up, nurses walked off the job. While nurses’ strikes are not a novel event, there is a reason many demanded wider attention and transcended local business news to become national headlines. The most noteworthy strike of the year took place July 12, when approximately 1,200 nurses at Boston-based Tufts Medical Center began a 24-hour strike — the first nursing strike Boston saw in 31 years. Roughly 120 miles from Boston, approximately 800 nurses at Berkshire Medical Center in Pittsfield, Mass., participated in a one-day strike in October. Across the country in California, nurses organized rallies and protests at more than 20 Kaiser Permanente sites to protest what they called inadequate staffing levels. In September, nurses and other hospital personnel unionized with SEIU walked off their jobs at Riverside University Health System – Medical Center in Moreno Valley, Calif., for three days. The county footed the $1.5 million bill for temporary replacement nurses for those 72 hours. Speaking of a bill, Minneapolis-based Allina Health tallied the costs of two 2016 strikes — one lasting six weeks — called by the Minnesota Nurses Association. The system put the figure in the ballpark of $149 million, which anchored Allina’s operating loss of $30 million for fiscal year 2016.
Executive’s takeaway: Although it is tempting to reduce labor strikes to events fueled by local market forces and politics, hospital and health system executives should pause and consider that striking nurses’ arguments — that they are expected to work demanding jobs with too few staff, resulting in unsafe conditions, high stress and burnout — is a description that applies to many, if not most, U.S. hospitals. Gender dynamics may also yield greater influence on administrator-nurse affairs in the coming year. As the nation comes to terms with troubling events that went unaddressed after women’s claims and voices were not met with the attention they deserved, health system executive teams are wise to change the approach taken in years past and pay closer attention to the female-dominated field of nursing. As one representative with the MNA told The Nation: “[Management is] a male institution thinking they can snub 1,200 women and pretend their opinions about healthcare don’t count.”
10. The year healthcare became very, extremely, incredibly difficult. Was any component of healthcare ever easy? Those who have spent years in the industry would say no. Yet 2017 was the year in which officials and lawmakers reminded the American public that healthcare is complicated. While true, this narrative functioned as a sound bite to normalize Congressional dysfunction.
Executive’s takeaway: What’s concerning here is whether this throwaway statement will make its way from Capitol Hill to hospital board rooms, executive offices, clinician lounges and medical school lecture halls and, over time, nurture a climate that fosters and condones inaction. It is unproductive to constantly point out the complicated nature of healthcare and/or bask in this acknowledgement. To do so is not the behavior of an effective leader. It goes without saying that healthcare is complicated. Healthcare is also necessary, expensive, life-saving, honorable, slow, inaccessible, urgent, flawed, and never going away. What are you doing to make it better?