
A vaccine would be the ultimate weapon against the coronavirus and the best route back to normal life. Officials like Dr. Anthony S. Fauci, the top infectious disease expert on the Trump administration’s coronavirus task force, estimate a vaccine could arrive in at least 12 to 18 months.
The grim truth behind this rosy forecast is that a vaccine probably won’t arrive any time soon. Clinical trials almost never succeed. We’ve never released a coronavirus vaccine for humans before. Our record for developing an entirely new vaccine is at least four years — more time than the public or the economy can tolerate social-distancing orders.
But if there was any time to fast-track a vaccine, it is now. So Times Opinion asked vaccine experts how we could condense the timeline and get a vaccine in the next few months instead of years.
Here’s how we might achieve the impossible.
Normally, researchers need years to secure funding, get approvals and study results piece by piece. But these are not normal times.
There are already at least 254 therapies and 95 vaccines related to Covid-19 being explored.
“If you want to make that 18-month timeframe, one way to do that is put as many horses in the race as you can,” said Dr. Peter Hotez, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine.
Despite the unprecedented push for a vaccine, researchers caution that less than 10 percent of drugs that enter clinical trials are ever approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
The rest fail in one way or another: They are not effective, don’t perform better than existing drugs or have too many side effects.
Fortunately, we already have a head start on the first phase of vaccine development: research. The outbreaks of SARS and MERS, which are also caused by coronaviruses, spurred lots of research. SARS and SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19, are roughly 80 percent identical, and both use so-called spike proteins to grab onto a specific receptor found on cells in human lungs. This helps explain how scientists developed a test for Covid-19 so quickly.
There’s a cost to moving so quickly, however. The potential Covid-19 vaccines now in the pipeline might be more likely to fail because of the swift march through the research phase, said Robert van Exan, a cell biologist who has worked in the vaccine industry for decades. He predicts we won’t see a vaccine approved until at least 2021 or 2022, and even then, “this is very optimistic and of relatively low probability.”
And yet, he said, this kind of fast-tracking is “worth the try — maybe we will get lucky.”
The next step in the process is pre-clinical and preparation work, where a pilot factory is readied to produce enough vaccine for trials. Researchers relying on groundwork from the SARS and MERS outbreaks could theoretically move through planning steps swiftly.
Sanofi, a French biopharmaceutical company, expects to begin clinical trials late this year for a Covid-19 vaccine that it repurposed from work on a SARS vaccine. If successful, the vaccine could be ready by late 2021.
As a rule, researchers don’t begin jabbing people with experimental vaccines until after rigorous safety checks.
They test the vaccine first on small batches of people — a few dozen during Phase 1, then a few hundred in Phase 2, then thousands in Phase 3. Months normally pass between phases so that researchers can review the findings and get approvals for subsequent phases.
But “if we do it the conventional way, there’s no way we’re going to be reaching that timeline of 18 months,” said Akiko Iwasaki, a professor of immunobiology at Yale University School of Medicine and an investigator at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
There are ways to slash time off this process by combining several phases and testing vaccines on more people without as much waiting.
Last week the National Academy of Sciences showed an overlapping timeline, describing it as moving at “pandemic speed.”
It’s here that talk of fast-tracking the timeline meets the messiness of real life: What if a promising vaccine actually makes it easier to catch the virus, or makes the disease worse after someone’s infected?
That’s been the case for a few H.I.V. drugs and vaccines for dengue fever, because of a process called vaccine-induced enhancement, in which the body reacts unexpectedly and makes the disease more dangerous.
Researchers can’t easily infect vaccinated participants with the coronavirus to see how the body behaves. They normally wait until some volunteers contract the virus naturally. That means dosing people in regions hit hardest by the virus, like New York, or vaccinating family members of an infected person to see if they get the virus next. If the pandemic subsides, this step could be slowed.
“That’s why vaccines take such a long time,” said Dr. Iwasaki. “But we’re making everything very short. Hopefully we can evaluate these risks as they occur, as soon as possible.”
This is where the vaccine timelines start to diverge depending on who you are, and where some people might get left behind.
If a vaccine proves successful in early trials, regulators could issue an emergency-use provision so that doctors, nurses and other essential workers could get vaccinated right away — even before the end of the year. Researchers at Oxford announced this week that their coronavirus vaccine could be ready for emergency use by September if trials prove successful.
So researchers might produce a viable vaccine in just 12 to 18 months, but that doesn’t mean you’re going to get it. Millions of people could be in line before you. And that’s only if the United States finds a vaccine first. If another country, like China, beats us to it, we could wait even longer while it doses its citizens first.
You might be glad of that, though, if it turned out that the fast-tracked vaccine caused unexpected problems. Only after hundreds or thousands are vaccinated would researchers be able to see if a fast-tracked vaccine led to problems like vaccine-induced enhancement.
“It’s true that any new technology comes with a learning curve,” said Dr. Paul Offit, the director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “And sometimes that learning curve has a human price.”
Once we have a working vaccine in hand, companies will need to start producing millions — perhaps billions — of doses, in addition to the millions of vaccine doses that are already made each year for mumps, measles and other illnesses. It’s an undertaking almost unimaginable in scope.
Companies normally build new facilities perfectly tailored to any given vaccine because each vaccine requires different equipment. Some flu vaccines are produced using chicken eggs, using large facilities where a version of the virus is incubated and harvested. Other vaccines require vats in which a virus is cultured in a broth of animal cells and later inactivated and purified.
Those factories follow strict guidelines governing biological facilities and usually take around five years to build, costing at least three times more than conventional pharmaceutical factories. Manufacturers may be able to speed this up by creating or repurposing existing facilities in the middle of clinical trials, long before the vaccine in question receives F.D.A. approval.
“They just can’t wait,” said Dr. Iwasaki. “If it turns out to be a terrible vaccine, they won’t distribute it. But at least they’ll have the capability” to do so if the vaccine is successful.
The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation says it will build factories for seven different vaccines. “Even though we’ll end up picking at most two of them, we’re going to fund factories for all seven, just so that we don’t waste time,” Bill Gates said during an appearance on “The Daily Show.”
In the end, the United States will have the capacity to mass-produce only two or three vaccines, said Vijay Samant, the former head of vaccine manufacturing at Merck.
“The manufacturing task is insurmountable,” Mr. Samant said. “I get sleepless nights thinking about it.”
Consider just one seemingly simple step: putting the vaccine into vials. Manufacturers need to procure billions of vials, and billions of stoppers to seal them. Sophisticated machines are needed to fill them precisely, and each vial is inspected on a high-speed line. Then vials are stored, shipped and released to the public using a chain of temperature-controlled facilities and trucks. At each of these stages, producers are already stretched to meet existing demands, Mr. Samant said.
It’s a bottleneck similar to the one that caused a dearth of ventilators, masks and other personal protective equipment just as Covid-19 surged across America.
If you talk about vaccines long enough, a new type of vaccine, called Messenger RNA (or mRNA for short), inevitably comes up. There are hopes it could be manufactured at a record clip. Mr. Gates even included it on his Time magazine list of six innovations that could change the world. Is it the miracle we’re waiting for?
Rather than injecting subjects with disease-specific antigens to stimulate antibody production, mRNA vaccines give the body instructions to create those antigens itself. Because mRNA vaccines don’t need to be cultured in large quantities and then purified, they are much faster to produce. They could change the course of the fight against Covid-19.
“On the other hand,” said Dr. van Exan, “no one has ever made an RNA vaccine for humans.”
Researchers conducting dozens of trials hope to change that, including one by the pharmaceutical company Moderna. Backed by investor capital and spurred by federal funding of up to $483 million to tackle Covid-19, Moderna has already fast-tracked an mRNA vaccine. It’s entering Phase 1 trials this year and the company says it could have a vaccine ready for front-line workers later this year.
“Could it work? Yeah, it could work,” said Dr. Fred Ledley, a professor of natural biology and applied sciences at Bentley University. “But in terms of the probability of success, what our data says is that there’s a lower chance of approval and the trials take longer.”
The technology is decades old, yet mRNA is not very stable and can break down inside the body.
“At this point, I’m hoping for anything to work,” said Dr. Iwasaki. “If it does work, wonderful, that’s great. We just don’t know.”
The fixation on mRNA shows the allure of new and untested treatments during a medical crisis. Faced with the unsatisfying reality that our standard arsenal takes years to progress, the mRNA vaccine offers an enticing story mixed with hope and a hint of mystery. But it’s riskier than other established approaches.
Imagine that the fateful day arrives. Scientists have created a successful vaccine. They’ve manufactured huge quantities of it. People are dying. The economy is crumbling. It’s time to start injecting people.
But first, the federal government wants to take a peek.
That might seem like a bureaucratic nightmare, a rubber stamp that could cost lives. There’s even a common gripe among researchers: For every scientist employed by the F.D.A., there are three lawyers. And all they care about is liability.
Yet F.D.A. approvals are no mere formality. Approvals typically take a full year, during which time scientists and advisory committees review the studies to make sure that the vaccine is as safe and effective as drug makers say it is.
While some steps in the vaccine timeline can be fast-tracked or skipped entirely, approvals aren’t one of them. There are horror stories from the past where vaccines were not properly tested. In the 1950s, for example, a poorly produced batch of a polio vaccine was approved in a few hours. It contained a version of the virus that wasn’t quite dead, so patients who got it actually contracted polio. Several children died.
The same scenario playing out today could be devastating for Covid-19, with the anti-vaccination movement and online conspiracy theorists eager to disrupt the public health response. So while the F.D.A. might do this as fast as possible, expect months to pass before any vaccine gets a green light for mass public use.
At this point you might be asking: Why are all these research teams announcing such optimistic forecasts when so many experts are skeptical about even an 18-month timeline? Perhaps because it’s not just the public listening — it’s investors, too.
“These biotechs are putting out all these press announcements,” said Dr. Hotez. “You just need to recognize they’re writing this for their shareholders, not for the purposes of public health.”
What if It Takes Even Longer Than the Pessimists Predict?
Covid-19 lives in the shadow of the most vexing virus we’ve ever faced: H.I.V. After nearly 40 years of work, here is what we have to show for our vaccine efforts: a few Phase 3 clinical trials, one of which actually made the disease worse, and another with a success rate of just 30 percent.
Researchers say they don’t expect a successful H.I.V. vaccine until 2030 or later, putting the timeline at around 50 years.
That’s unlikely to be the case for Covid-19, because, as opposed to H.I.V., it doesn’t appear to mutate significantly and exists within a family of familiar respiratory viruses. Even still, any delay will be difficult to bear.
But the history of H.I.V. offers a glimmer of hope for how life could continue even without a vaccine. Researchers developed a litany of antiviral drugs that lowered the death rate and improved health outcomes for people living with AIDS. Today’s drugs can lower the viral load in an H.I.V.-positive person so the virus can’t be transmitted through sex.
Therapeutic drugs, rather than vaccines, might likewise change the fight against Covid-19. The World Health Organization began a global search for drugs to treat Covid-19 patients in March. If successful, those drugs could lower the number of hospital admissions and help people recover faster from home while narrowing the infection window so fewer people catch the virus.
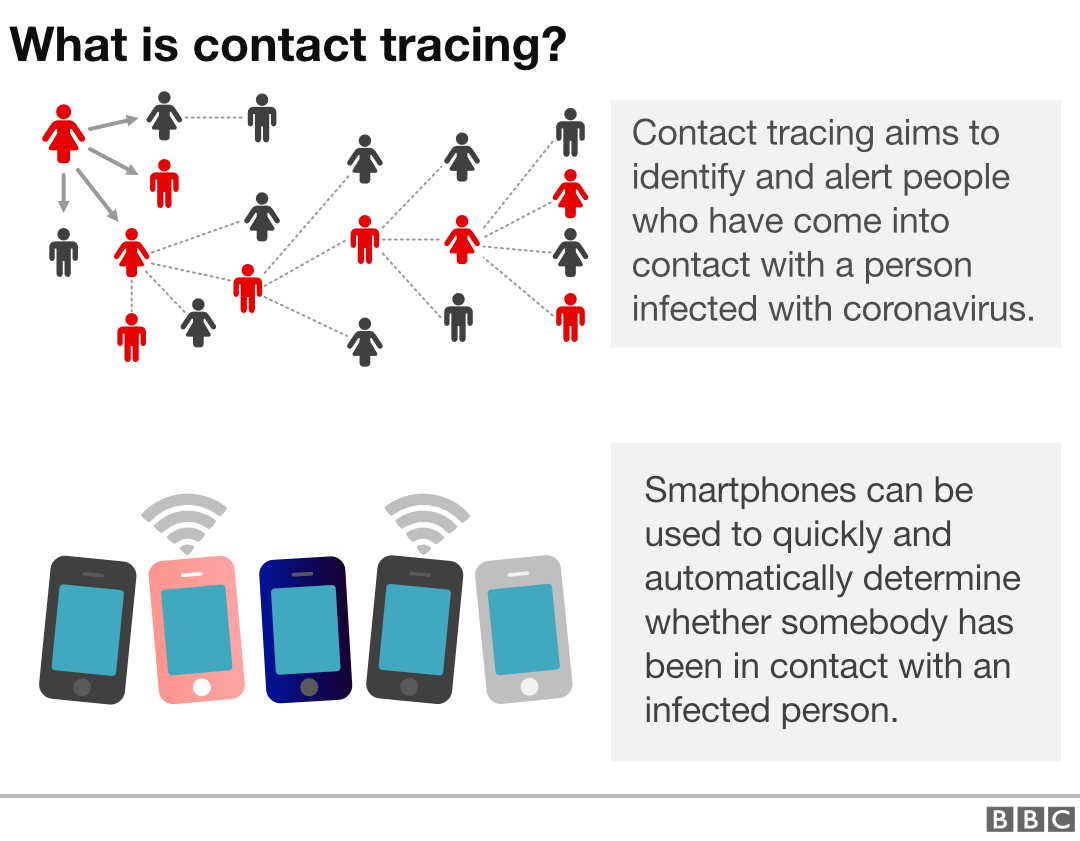
Combine that with rigorous testing and contact tracing — where infected patients are identified and their recent contacts notified and quarantined — and the future starts looking a little brighter. So far, the United States is conducting fewer than half the number of tests required and we need to recruit more than 300,000 contact-tracers. But other countries have started reopening following exactly these steps.
If all those things come together, life might return to normal long before a vaccine is ready to shoot into your arm.









%2Farc-anglerfish-washpost-prod-washpost%2FEAJ46XUOLMI6VEZCUKPHL374SM.jpg&w=908)


