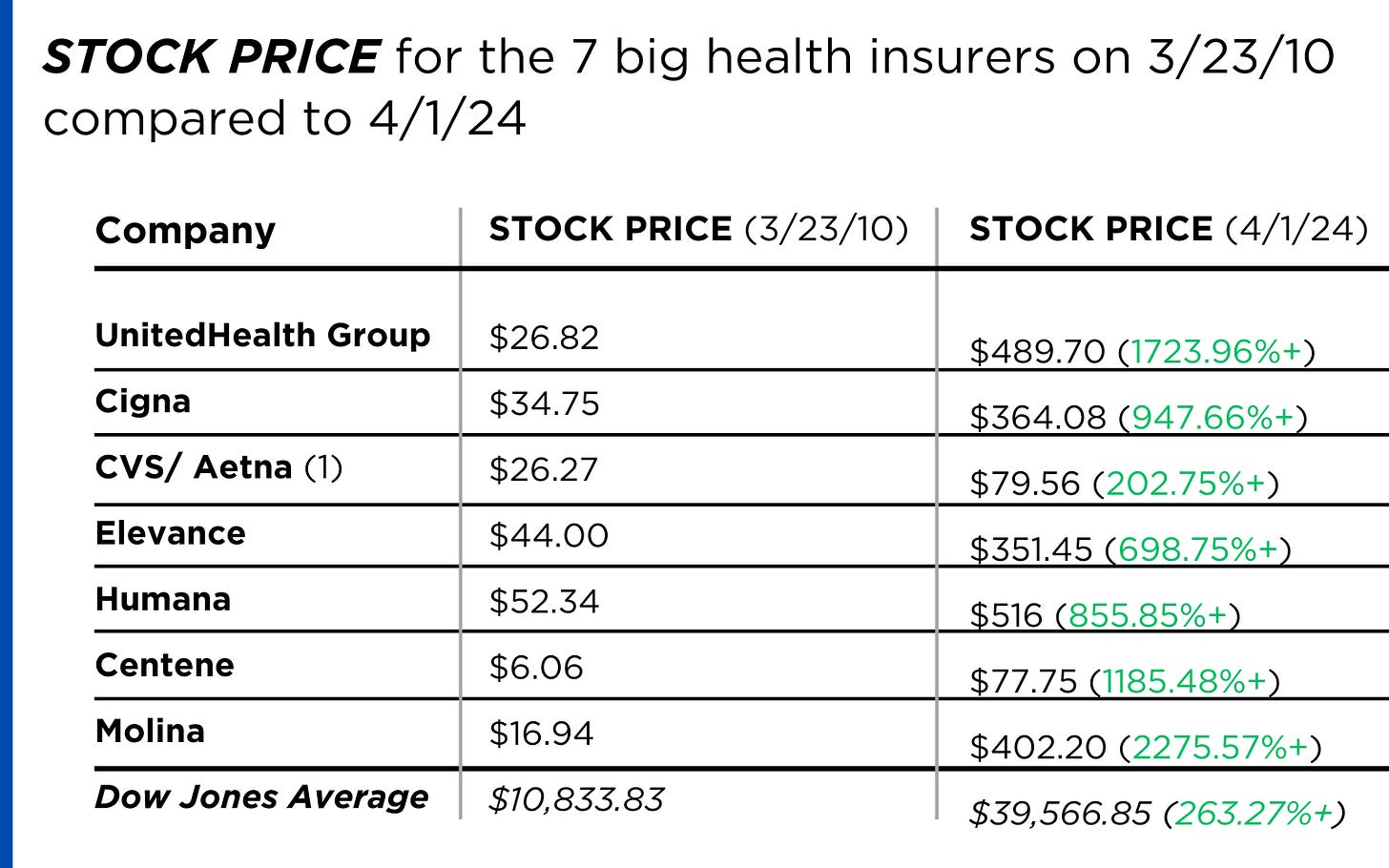
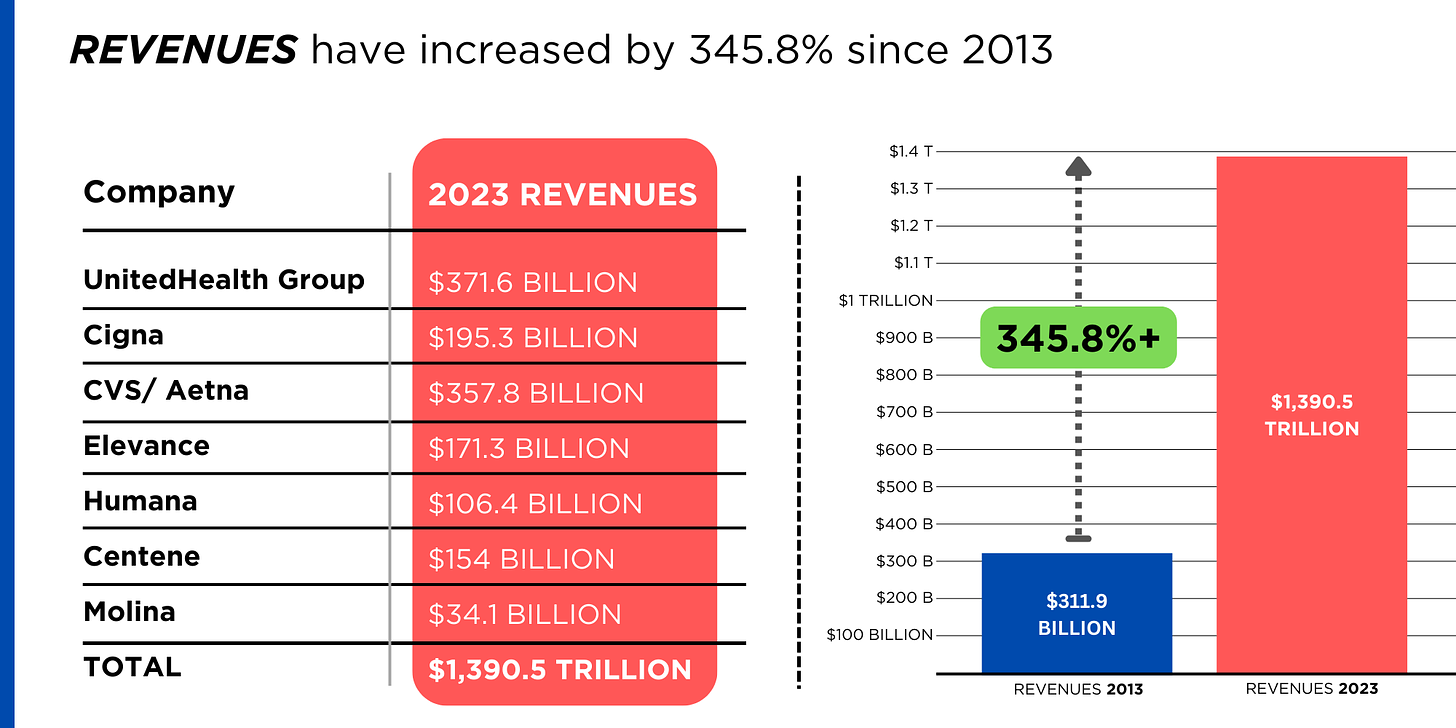
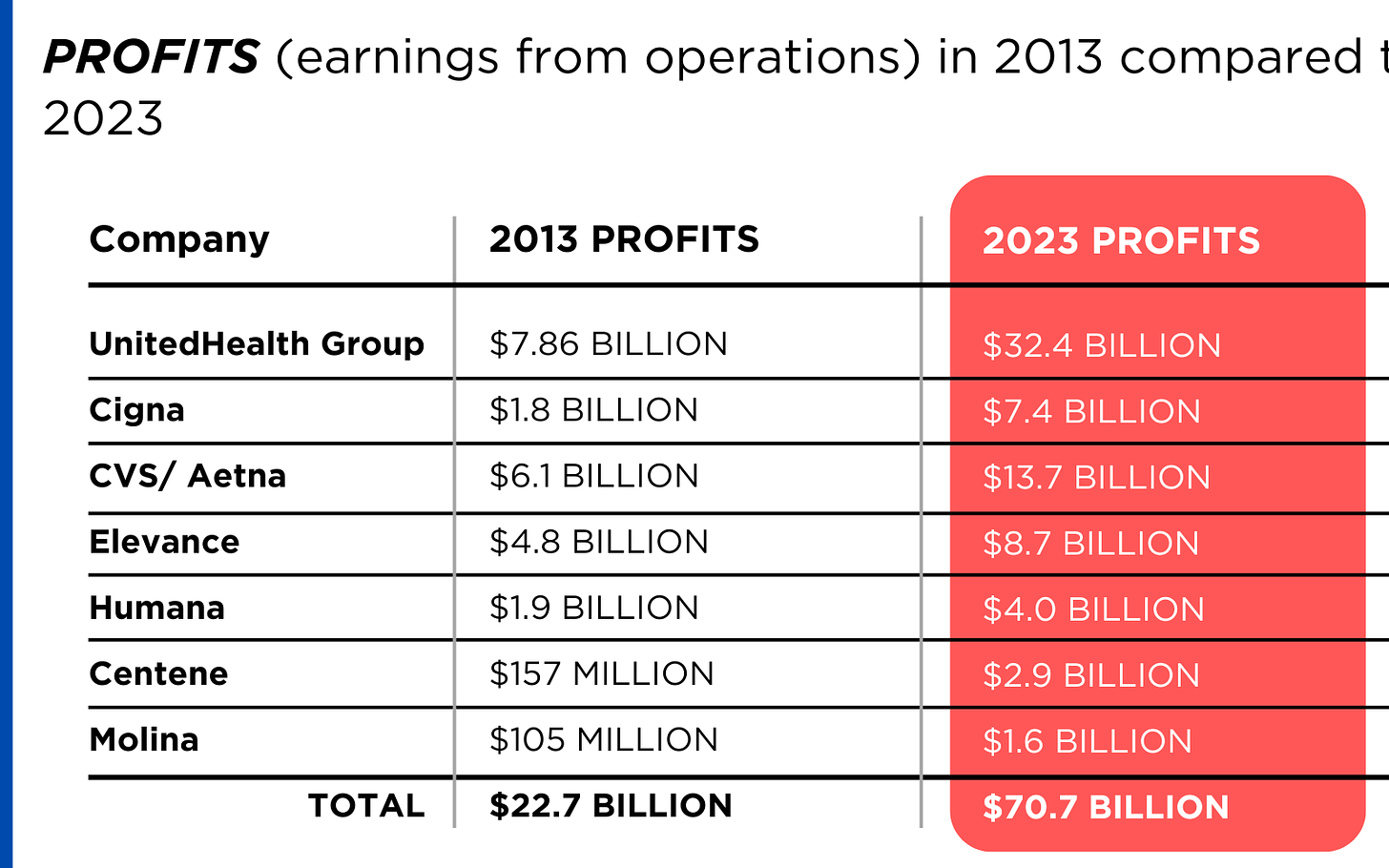
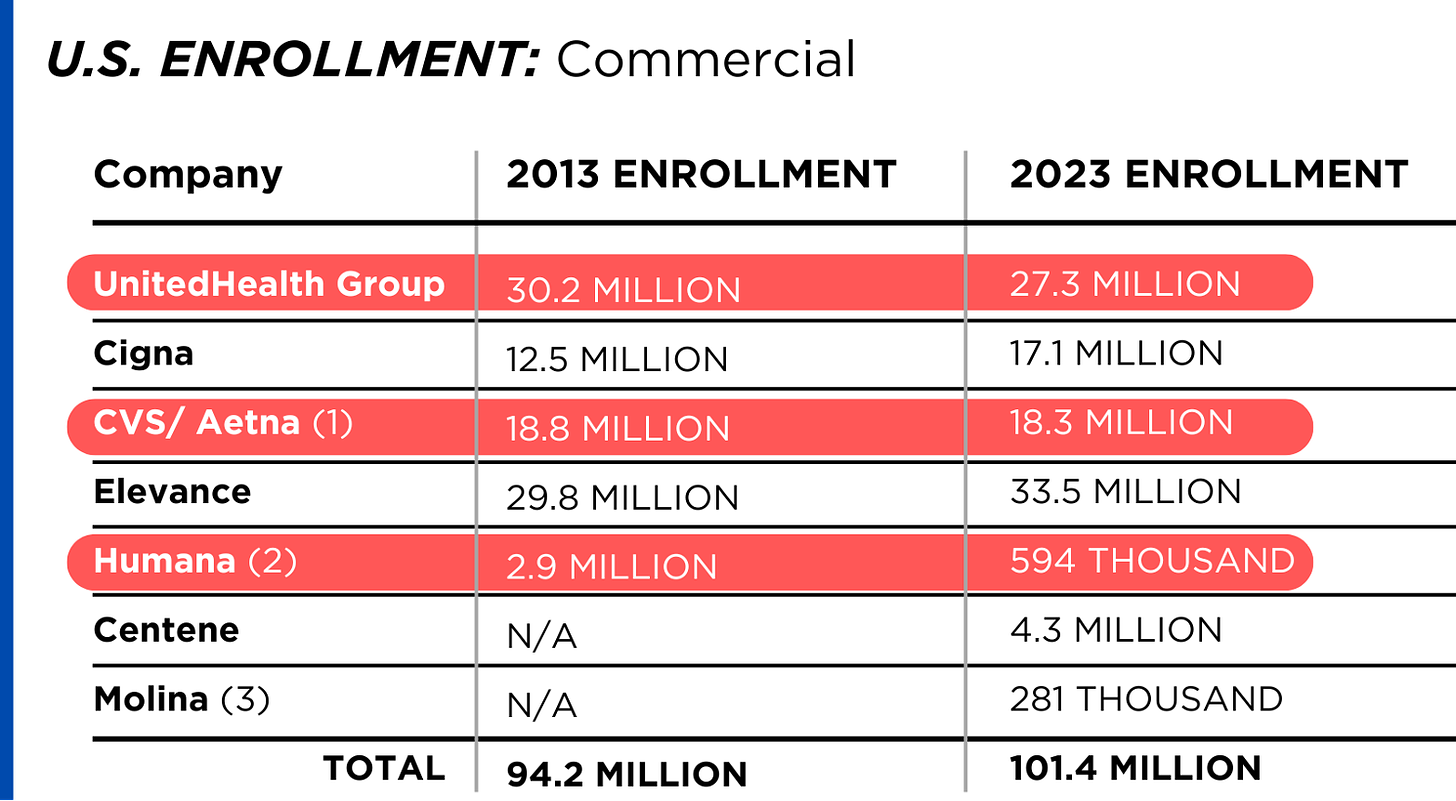
https://www.yahoo.com/lifestyle/spotlight-health-insurance-companies-patients-014648180.html
After UnitedHealthcare CEO Brian Thompson, left, was killed and Anthem released a controversial anesthesia policy, people shared their stories of insurance woes. (UnitedHealth Group via AP, Getty)
On Wednesday, Brian Thompson, the chief executive of UnitedHealthcare, was fatally shot in midtown Manhattan in what police are calling a “pre-meditated, preplanned, targeted attack.” Days before, Anthem Blue Cross Blue Shield said in a note to providers that it would limit anesthesia coverage in some states if a surgery or procedure exceeded a set time limit (the policy, set to go into effect in February, was swiftly reversed following an uproar).
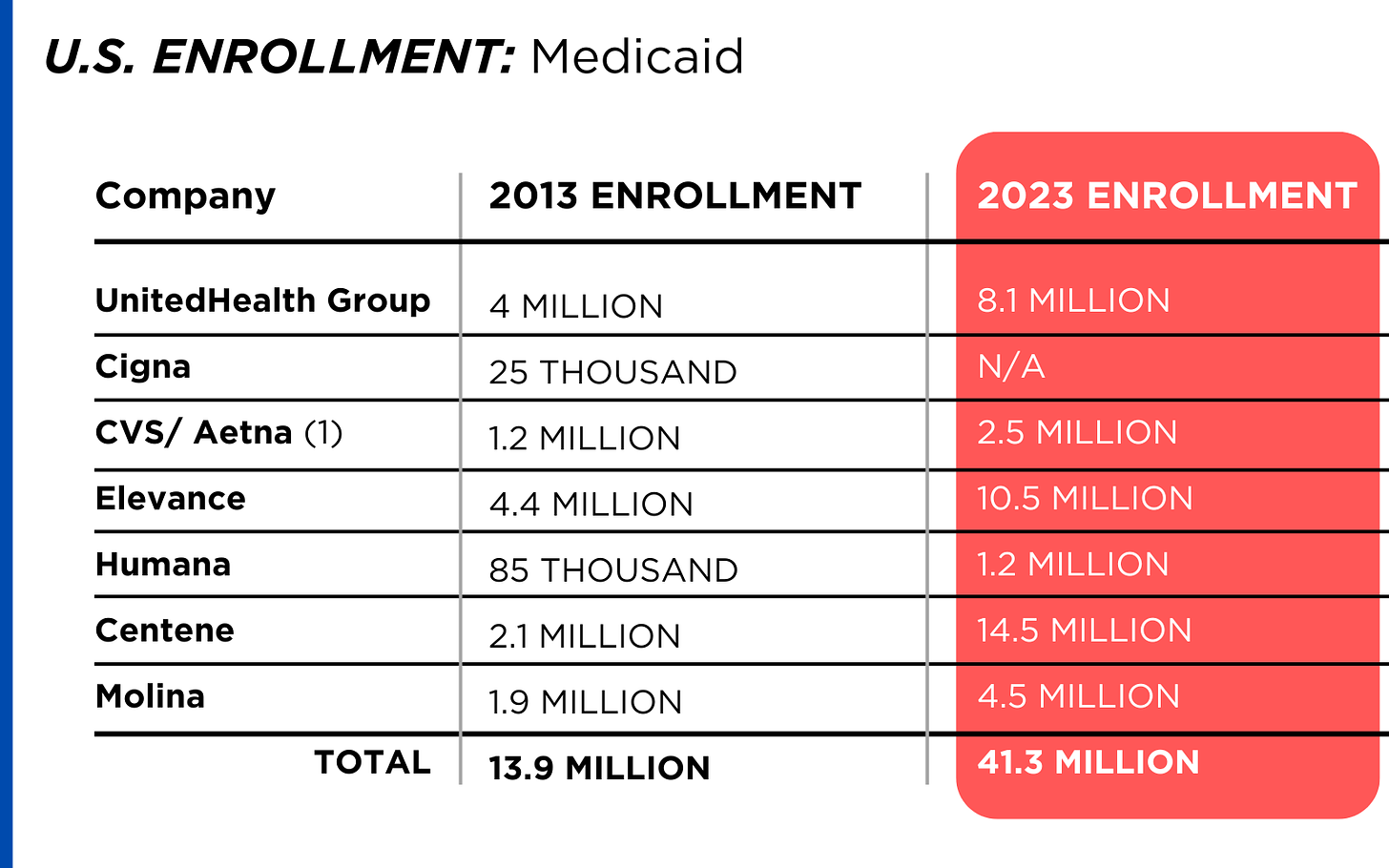
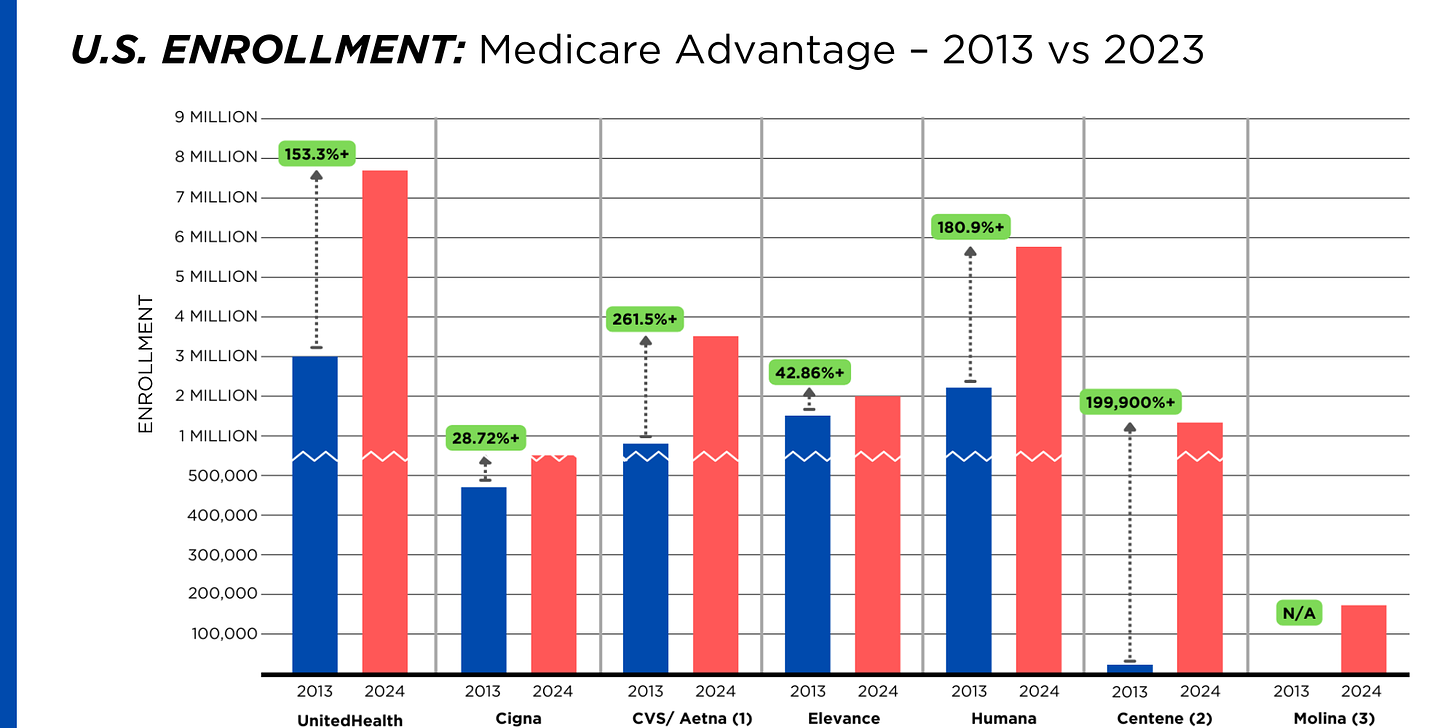
The U.S. health care insurance system relies on private insurance, which covers 200 million Americans, and government-run programs.
Americans receive coverage through their employers, government programs like Medicaid or Medicare or by purchasing it themselves — often at a high cost. Even when an individual is covered by insurance, medical coverage can be expensive, with co-pays, deductibles and premiums adding up. Going to an out-of-network provider for care (which can be done unintentionally, for example if you are taken by ambulance to a hospital) can lead to exorbitant bills.
And then there’s the fact that, according to data from state and federal regulators, insurers reject about one in seven claims for treatment.
And most people don’t push back — a study found that only 0.1% of denied claims under the Affordable Care Act, a law designed to make health insurance more affordable and prevent coverage denials for pre-existing conditions, are formally appealed. This leaves many people paying out of pocket for care they thought was covered — or skipping treatment altogether.
For many, the cost of life-saving care is too high, and medical debt is the No. 1 cause of bankruptcy in America.
That is to say nothing of the emotional labor of navigating the complex system. With Thompson’s killing and the Anthem policy, there’s been widespread response with a similar through line: a pervasive contempt for the state of health insurance in the United States. The most illustrative reactions, though are the personal ones, the tales of denied claims, battles with insurance agents, delayed care, filing for bankruptcy and more.
‘We sat in the hospital for three days’
Jessica Alfano, a content creator who goes by @monetizationmom, shared her story on TikTok about battling an insurance company while her one-year-old child was in the hospital with a brain tumor. When her daughter needed to have emergency surgery at a different hospital was outside their home state, UnitedHealthcare allegedly refused to approve the transfer via ambulance to New York City. She also couldn’t drive her daughter to the hospital as the insurance company told them they would not cover her at the next hospital if they left the hospital by their own will and did not arrive by ambulance. “I vividly remember being on the phone with UnitedHealthcare for days and days — nine months pregnant about to give birth alone — while my other baby was sitting in a hospital room,” she said.
‘Excruciating pain’
While pregnant, Allie, who posts on TikTok as @theseaowl44, went to the hospital in “excruciating pain,” she said in a video. After initially being sent home by a doctor who said she was having pain from a urinary tract infection and the baby sitting on her bladder, she returned to the hospital to learn she was suffering from appendicitis. She was sent to a bigger hospital in St. Louis, where she had emergency surgery. Her son survived the surgery but died the next day after she delivered him.
About 45 minutes later, Allie suffered a pulmonary embolism and had to have an emergency dilation and curettage (D&C) to remove the placenta, nearly dying in the process. It was after all of this that she learned she had been sent to a hospital that was out of network. “We ended up with a bill from the hospital that was more than what we paid for the home that we live in, and it was going to take probably, I don’t know, 20 to 30 years to pay off this hospital bill,” Allie said. “We opted to have to file bankruptcy, but not before I exhausted every appeal with [insurance company] Cigna — I wrote letters, I spilled my heart out, I talked on the phone, I explained our situation and our story, thinking surely someone would understand this was not my fault.
On the third and final appeal, because they only allow you three, Cigna’s appeal physician told me, point blank, it was my fault that when I was dying from a ruptured appendix in the ER, that I didn’t check and make sure that the hospital I was being sent to by ambulance was in my insurance network.”
Hundreds of similar stories are being told, but the comments section on these videos paints a picture in itself. “I wear leg braces and walk with crutches as a paraplegic and they tried to deny my new leg braces and only approve me a wheelchair. They wanted to take my ability to WALK away,” commented TikToker @ChickWithSticks.
“Perfectly healthy pregnancy, until it wasn’t,” TikToker Meagan Pitts shared. “NICU stay was covered by my insurance, the neonatologist group contracted by the NICU: Denied. I’m sorry, what?”
Another wrote that her son was born with a congenital heart defect and needed open heart surgery. “My husband changed jobs & we switched to UHC,” she wrote. “They DENIED my son’s cath lab intervention!”
‘The most stressful time of my life’
One Redditor, @Sweet_Nature_7015, wrote that they struggled with UnitedHealthcare when they and their husband were in a “terrible car accident” that was the other driver’s fault. Since United Healthcare only covered two days in the hospital, the Redditor wrote that the case manager tried to find a way to “kick him out of the hospital” — but since their husband was in a coma, he was unable to be discharged safely. “The stress of being told — your health insurance isn’t covering this anymore, we have to discharge your husband — while he’s in a freaking coma and on a ventilator, etc, rediculous [sic],” they wrote. “I have to sign some papers to give up all of my husband’s benefits via his job – which included his life insurance that he had paid into, so we lost that. This allowed him to be covered by Medicaid. I can’t even put into words how much stress UHC caused on top of my husband (and my) health issues in the most stressful time of my life.”
The kicker, they wrote, was that years later the couple was awarded a court settlement from the other driver in the accident — and “UHC rolled up to the court and took the entire settlement money as their payment for those two days in the hospital they had paid for.”
‘I’m one of the lucky ones’
On the same thread, Redditor @sebastorio wrote that they went to the emergency room for an eye injury, which their doctor said could have resulted in a loss of sight. “UHC denied my claim, and I paid $1,400 out of pocket,” they said. “I’m one of the lucky ones. Can’t imagine how people would feel if that happened for critical or life-saving care.”
‘Constant stream of hostile collection calls’
Redditor @colonelcatsup opened up about their experience with insurance while having a baby, writing that they went into premature labor while insured under one company but that at midnight, their insurance switched to United Healthcare. “I gave birth in the morning. My daughter was two months early and was in the NICU for weeks so the bill was over $80,000 and United refused to pay it, saying it wasn’t their responsibility,” they wrote. “In addition to dealing with a premature baby, I had a constant stream of hostile collection calls and mail from the hospital for 18 months. My credit took a hit.”
Eventually, their employer hired an attorney to fight UHC, and the insurance company eventually paid. “I will never forgive them for the added stress hanging over me for the first year and a half of my child’s life,” they wrote.
‘Debt or death’
On Substack, on which she posted an excerpt from her Instagram, author Bess Kalb also recounted her experience with health insurance coverage when she was bleeding during her pregnancy and was asked by an EMT what insurance she had before deciding whether they would go to the nearest hospital. When her husband said to take Kalb to the hospital, despite not knowing the insurance implications, their bill was more than $10,000.https://www.instagram.com/p/DDNphXCp3Qu/embed/captioned/?cr=1&v=12
“The private insurance industry forces millions of Americans to choose between debt or death,” Kalb wrote. “Often, ghoulishly, the outcome is both. If I were worried about an ambulance out of coverage, I would have waited at home or waited in traffic for an hour to cross Los Angeles to get to my doctor’s office and sat in the waiting room bleeding out and perhaps would not be here to write this, and neither would my son.”