
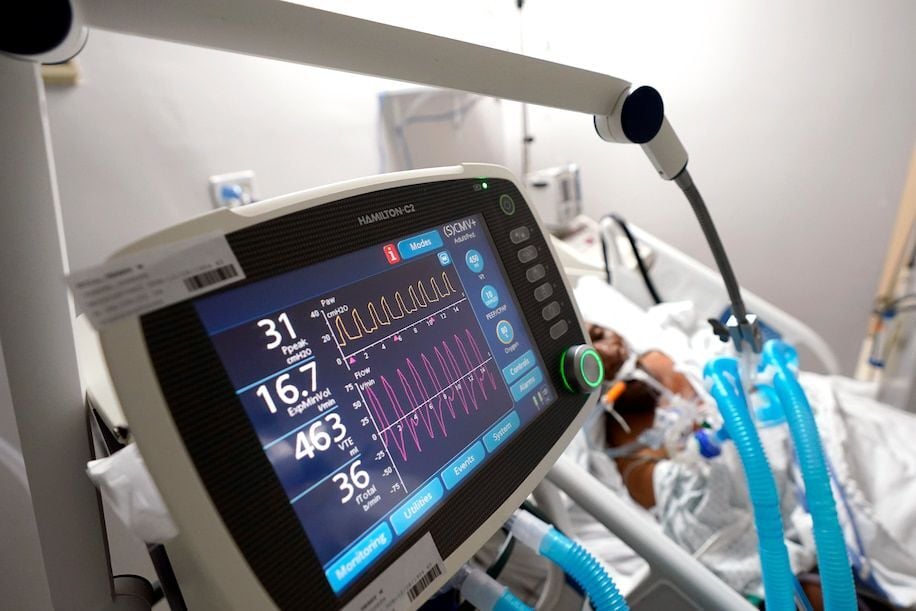
The latest statistics, as of July 10, show COVID-19-related deaths in U.S. are just under 1,000 per day nationally, which is down from a peak average of about 2,000 deaths per day in April. However, cases are once again rising very substantially, which is worrisome as it may indicate that substantial increases in COVID-19 deaths could follow. How do these numbers compare to deaths of other causes? Ron Fricker, statistician and disease surveillance expert from Virginia Tech, explains how to understand the magnitude of deaths from COVID-19.
As a disease surveillance expert, what are some of the tools you have to understand the deaths caused by a disease?
Disease surveillance is the process by which we try to understand the incidence and prevalence of diseases across the country, often with the particular goal of looking for increases in disease incidence. The challenge is separating signal from noise, by which I mean trying to discern an increase in disease incidence (the signal) from the day-to-day fluctuations in that disease (the noise). The hope is to identify any increase as quickly as possible so that medical and public health professionals can intervene and try to mitigate the disease’s effects on the population.
A critical tool in this effort is data. Often disease data is collected and aggregated by local and state public health departments and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention from data that is reported by doctors and medical facilities. Surveillance systems then use this data and a variety of algorithms to attempt to find a signal amidst the noise.
Early on, many people pointed out that the flu has tens of thousands of deaths a year, and so COVID-19 didn’t seem so bad. What’s wrong with that comparison?
The CDC estimates the average number of flu-related deaths since 2010-11 is around 36,000 per year. This varies from a low of 12,000 deaths in 2011-12 to a high of 61,000 deaths in 2017-18. Thus, the number of COVID-19 deaths to date is three to four times greater than the annual average number of flu-related deaths over the past decade; it is 10 times larger when compared to the 2010-11 flu season but only about twice as large compared to 2017-18.
To make this a fair comparison, note that seasonal influenza mostly occurs over a few months, usually in late fall or early winter. So, the time periods are roughly comparable, with most of the COVID-19-related deaths occurring since late March. However, COVID-19 does not appear to be seasonal, and fatalities are a lagging measure because the time from infection to death is weeks if not months in duration, so the multiples in the previous paragraph will be greater by the end of the year.
Furthermore, while death rates have been coming down from a peak of more than 2,700 on April 21, 2020, the United States is now averaging just under 1,000 deaths per day as of July 10, and given the dramatic increase in cases of late, we should expect the fatality rate to further rise. For example, the University of Washington’s IHME model currently predicts slightly more than 208,000 COVID-19-related deaths by November 1.
So, by any comparison, the COVID-19 death rate is significantly higher than the seasonal influenza death rate.
What are some comparisons that could provide some context in understanding the scale of deaths caused by COVID-19?
As of this writing, more than 130,000 people have died of COVID-19, and that total could grow to 200,000 or more by fall. Those numbers are so big, they’re hard to grasp.
Michigan Stadium in Ann Arbor is the largest football stadium in the United States. It holds 107,420 people, so no football stadium in the country is large enough to hold everyone who has died from COVID-19 thus far. By the time bowl season comes along, assuming we have a football season this year, the number of COVID-19 fatalities will likely exceed the capacity of the Rose and Cotton bowl stadiums combined.
The state of Wyoming has a population of slightly less than 600,000 people, so it’s the equivalent of one out of every five people in that state dying in the last four months. By this fall, the COVID-19 death total will be the equivalent of fully one-third of the people in Wyoming dying.
The populations of Grand Rapids, Michigan; Huntsville, Alabama; and Salt Lake City, Utah are each just over 200,000 people. Imagine if everyone in one of those cities died over the course of six months. That’s what COVID-19 may look like by fall.
How do COVID-19 deaths compare to chronic diseases like cancer or heart disease?
Today, COVID-19 ranks as the sixth leading cause of death in the United States, following heart disease, cancer, accidents, lower chronic respiratory diseases and stroke. Heart disease is the leading cause, with just over 647,000 Americans dying from it each year. Alzheimer’s disease, formerly the sixth largest cause of death, kills just over 121,000 people per year. If the University of Washington IHME model’s current prediction of COVID-19-related deaths comes to pass, COVID-19 will be the third leading cause of death in the United States by the end of the year.
The American Cancer Society estimates that in 2020 there will be an estimated 1.8 million new cancer cases diagnosed and 606,520 cancer deaths in the United States. Lung cancer is estimated to kill about 135,000 people in the US in 2020, so the number of COVID-19 deaths is currently equivalent and will exceed it soon. Of course, it is important to note that the COVID-19 deaths have occurred in about the past four months while the number of lung cancer deaths is for a year. So, COVID-19 deaths are occurring at roughly three times the rate of lung cancer deaths.
What are some historical comparisons that you think are useful in understanding the scale of deaths from COVID-19?
The 1918 influenza pandemic was similar in some ways to the current pandemic and different in other ways. One key difference is the age distribution of deaths, where COVID-19 is concentrated among older adults while the the 1918 pandemic affected all ages. In my state of Virginia, only 8% of the people who died in the 1918 pandemic were more than 50 years old, compared to more than 97% for COVID-19.
The CDC estimates that the 1918 pandemic resulted in about 675,000 deaths in the United States, so slightly more than five times the current number of COVID-19 deaths. In October of 1918, the worst month for the influenza pandemic, about 195,000 people died – well more than all who have died so far from COVID-19.
As with any historical comparison, there are important qualifiers. In this case, the influenza pandemic started in early 1918 and continued well into 1919, whereas COVID-19 deaths are for about one-third of a year (March through June). However, today the United States’ population is about three times the size of the population in 1918. These two factors roughly “cancel out,” and so it is reasonable to think about the 1918 epidemic being about five times worse than COVID-19, at least thus far.
In comparison to past wars, the U.S. has now had more deaths from COVID-19 than all the combat-related deaths in all the wars since the Korean War, including the Vietnam War and Operations Desert Shield and Desert Storm. In World War II there were 291,557 combat casualties. So the number of people who have died from COVID-19 thus far is about 45% of the WWII combat casualties. By the fall, it could be more than 70%.
Finally, note that the number of confirmed and probable deaths from COVID-19 in New York City (23,247 on July 10, 2020) is more than eight times the number who died in the 9/11 attack (2,753).


.png)





CAMBRIDGE – Aristotle was right. Humans have never been atomized individuals, but rather social beings whose every decision affects other people. And now the COVID-19 pandemic is driving home this fundamental point: each of us is morally responsible for the infection risks we pose to others through our own behavior.
In fact, this pandemic is just one of many collective-action problems facing humankind, including climate change, catastrophic biodiversity loss, antimicrobial resistance, nuclear tensions fueled by escalating geopolitical uncertainty, and even potential threats such as a collision with an asteroid.
As the pandemic has demonstrated, however, it is not these existential dangers, but rather everyday economic activities, that reveal the collective, connected character of modern life beneath the individualist façade of rights and contracts.
Those of us in white-collar jobs who are able to work from home and swap sourdough tips are more dependent than we perhaps realized on previously invisible essential workers, such as hospital cleaners and medics, supermarket staff, parcel couriers, and telecoms technicians who maintain our connectivity.
Similarly, manufacturers of new essentials such as face masks and chemical reagents depend on imports from the other side of the world. And many people who are ill, self-isolating, or suddenly unemployed depend on the kindness of neighbors, friends, and strangers to get by.
The sudden stop to economic activity underscores a truth about the modern, interconnected economy: what affects some parts substantially affects the whole. This web of linkages is therefore a vulnerability when disrupted. But it is also a strength, because it shows once again how the division of labor makes everyone better off, exactly as Adam Smith pointed out over two centuries ago.
Today’s transformative digital technologies are dramatically increasing such social spillovers, and not only because they underpin sophisticated logistics networks and just-in-time supply chains. The very nature of the digital economy means that each of our individual choices will affect many other people.
Consider the question of data, which has become even more salient today because of the policy debate about whether digital contact-tracing apps can help the economy to emerge from lockdown faster.
This approach will be effective only if a high enough proportion of the population uses the same app and shares the data it gathers. And, as the Ada Lovelace Institute points out in a thoughtful report, that will depend on whether people regard the app as trustworthy and are sure that using it will help them. No app will be effective if people are unwilling to provide “their” data to governments rolling out the system. If I decide to withhold information about my movements and contacts, this would adversely affect everyone.
Yet, while much information certainly should remain private, data about individuals is only rarely “personal,” in the sense that it is only about them. Indeed, very little data with useful information content concerns a single individual; it is the context – whether population data, location, or the activities of others – that gives it value.
Most commentators recognize that privacy and trust must be balanced with the need to fill the huge gaps in our knowledge about COVID-19. But the balance is tipping toward the latter. In the current circumstances, the collective goal outweighs individual preferences.
But the current emergency is only an acute symptom of increasing interdependence. Underlying it is the steady shift from an economy in which the classical assumptions of diminishing or constant returns to scale hold true to one in which there are increasing returns to scale almost everywhere.
In the conventional framework, adding a unit of input (capital and labor) produces a smaller or (at best) the same increment to output. For an economy based on agriculture and manufacturing, this was a reasonable assumption.
But much of today’s economy is characterized by increasing returns, with bigger firms doing ever better. The network effects that drive the growth of digital platforms are one example of this. And because most sectors of the economy have high upfront costs, bigger producers face lower unit costs.
One important source of increasing returns is the extensive experience-based know-how needed in high-value activities such as software design, architecture, and advanced manufacturing. Such returns not only favor incumbents, but also mean that choices by individual producers and consumers have spillover effects on others.
The pervasiveness of increasing returns to scale, and spillovers more generally, has been surprisingly slow to influence policy choices, even though economists have been focusing on the phenomenon for many years now. The COVID-19 pandemic may make it harder to ignore.
Just as a spider’s web crumples when a few strands are broken, so the pandemic has highlighted the risks arising from our economic interdependence. And now California and Georgia, Germany and Italy, and China and the United States need each other to recover and rebuild. No one should waste time yearning for an unsustainable fantasy.