
HIGHLIGHTS
- Big Insurance revenues and profits have increased by 300% and 287% respectively since 2012 due to explosive growth in the companies’ pharmacy benefit management (PBM) businesses and the Medicare replacement plans they call Medicare Advantage.
- The for-profits now control more than 80% of the national PBM market and more than 70% of the Medicare Advantage market.
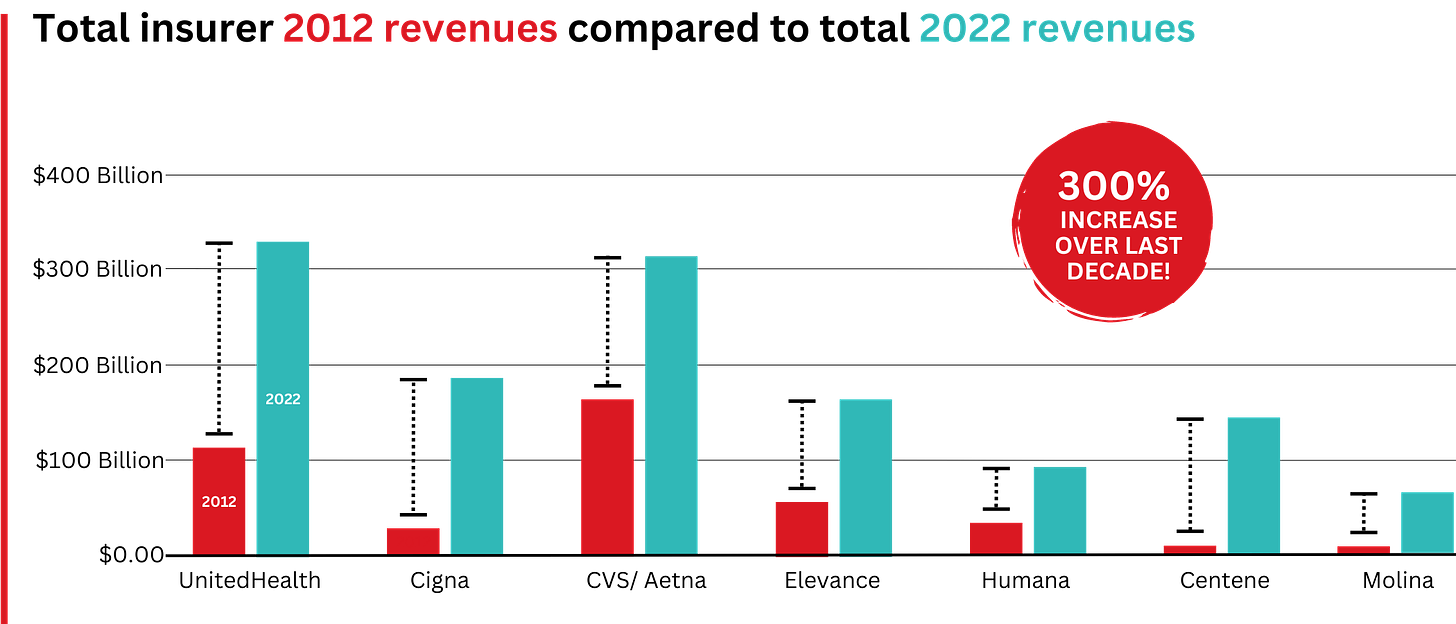
In 2022, Big Insurance revenues reached $1.25 trillion and profits soared to $69.3 billion.
That’s a 300% increase in revenue and a 287% increase in profits from 2012, when revenue was $412.9 billion and profits were $24 billion.
Sucking billions out of the pharmacy supply chain – and taxpayers’ pockets
What has changed dramatically over the decade is that the big insurers are now getting far more of their revenues from the pharmaceutical supply chain and from taxpayers as they have moved aggressively into government programs. This is especially true of Humana, Centene, and Molina, which now get, respectively, 85%, 88%, and 94% of their health-plan revenues from government programs.
The two biggest drivers are their fast-growing pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), the relatively new and little-known middleman between patients and pharmaceutical drug manufacturers, and the privately owned and operated Medicare replacement plans they market as Medicare Advantage.
With the exception of Humana, Centene, and Molina, most of the companies that constitute Big Insurance continue to make substantial amounts of money selling policies and services in what they refer to as their commercial businesses – to individuals, families, and employers – but the seven companies’ commercial revenue grew just 260%, or $176 billion, over 10 years (from $110.4 billion to $287.1 billion). While that’s significant, profitable growth in the commercial sector has become a major challenge for big insurers – so much so that Humana just last week announced it is exiting the employer-sponsored health-insurance marketplace entirely.
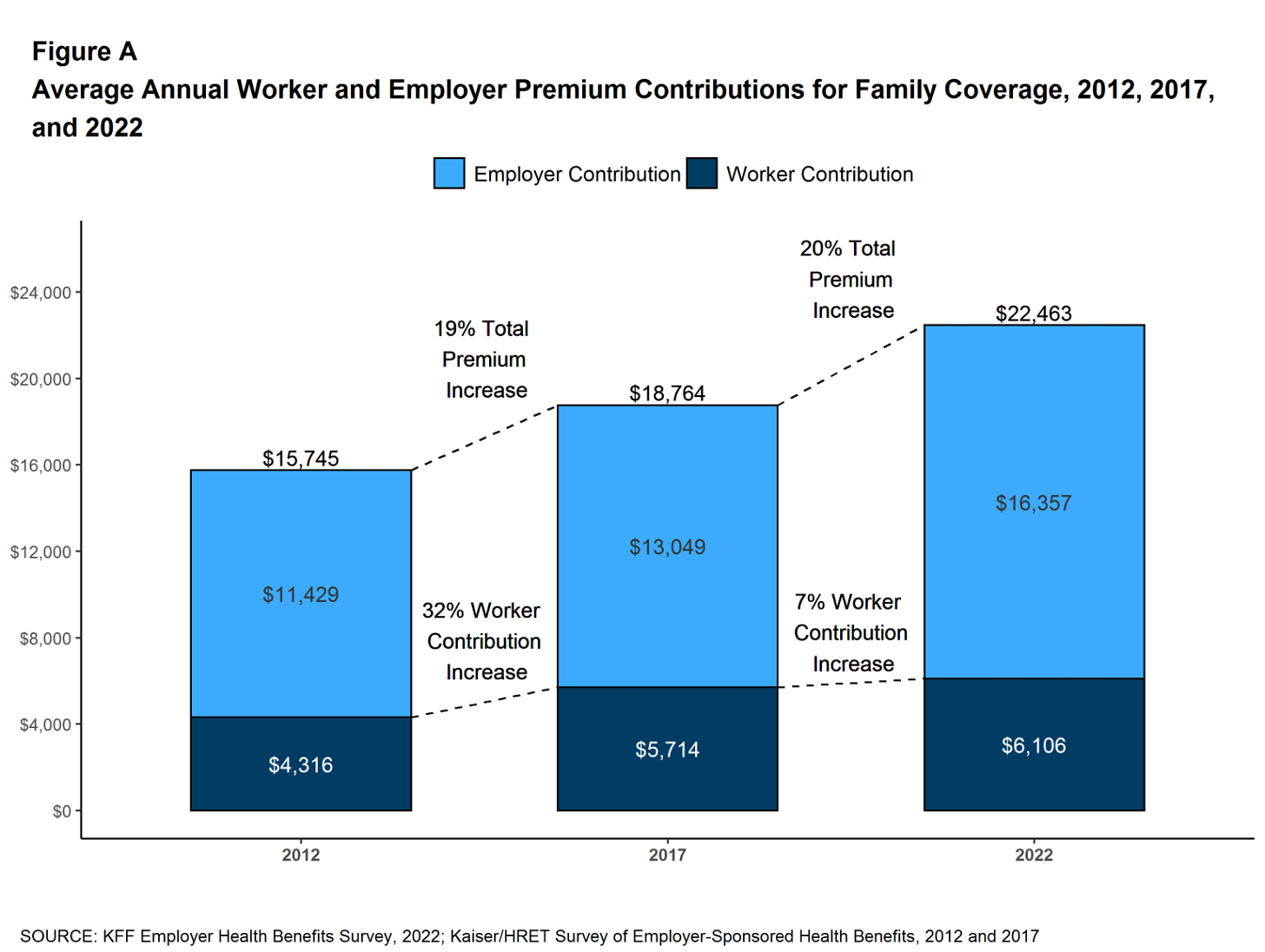
The insurers’ commercial businesses have stagnated because small businesses – which employ nearly half of the nation’s workers – are increasingly being priced out of the health insurance market. Most small businesses can no longer afford the premiums. The average premium for an employer-sponsored family plan – not including out-of-pocket requirements – was $22,463 in 2022, up 43% since 2012, which has contributed to the decades-long decline in the percentage of U.S. employers offering coverage to their workers.
The percentage of U.S. employers providing some level of health benefits to their workers dropped from 69% to 51% between 1999 and 2022 – including a dramatic 8% decrease last year alone. Growth in this category is largely the result of insurers “stealing market share” from each other or from smaller competitors.
As a consequence of this segment’s relative stagnation, PBMs and government programs have become the new cash cows for Big Insurance.
Spectacular PBM Growth
PBM HIGHLIGHTS
- Cigna now gets far more revenue from its PBM than from its health plans. CVS gets more revenue from its PBM than from either Aetna’s health plans or its nearly 10,000 retail stores.
- UnitedHealth has the biggest share of both the PBM and Medicare markets and, through numerous acquisitions of physician practices, is now the largest U.S. employer of doctors.
PBMs are middlemen companies that manage prescription drug benefits for health insurers, Medicare Part D drug plans, employers, and, in some cases, unions. As the Commonwealth Fund has noted:
PBMs have a significant behind-the-scenes impact in determining total drug costs for insurers, shaping patients’ access to medications, and determining how much pharmacies are paid.
The Commonwealth Fund went on to say that PBMs have faced growing scrutiny about their role in rising prescription drug costs and spending. A big reason for the scrutiny – by Congress, state lawmakers and now also by the FTC – is that the biggest PBMs are now owned by Big Insurance.
Through mergers and acquisitions in recent years, three of the seven for-profit insurers – Cigna, CVS/Aetna, and UnitedHealth – now control 80% of the U.S. pharmacy benefits market.
They determine which drugs will be listed in each of their formularies (lists of drugs they will “cover” based on secret deals they negotiate with pharmaceutical companies) and how much patients will have to pay out of their own pockets at the pharmacy counter – in many cases hundreds or thousands of dollars – before their coverage kicks in. The PBMs also “steer” health-plan enrollees to their preferred or owned pharmacies (and, increasingly, away from independent pharmacists), thereby capturing even more of what we spend on our prescription medications.

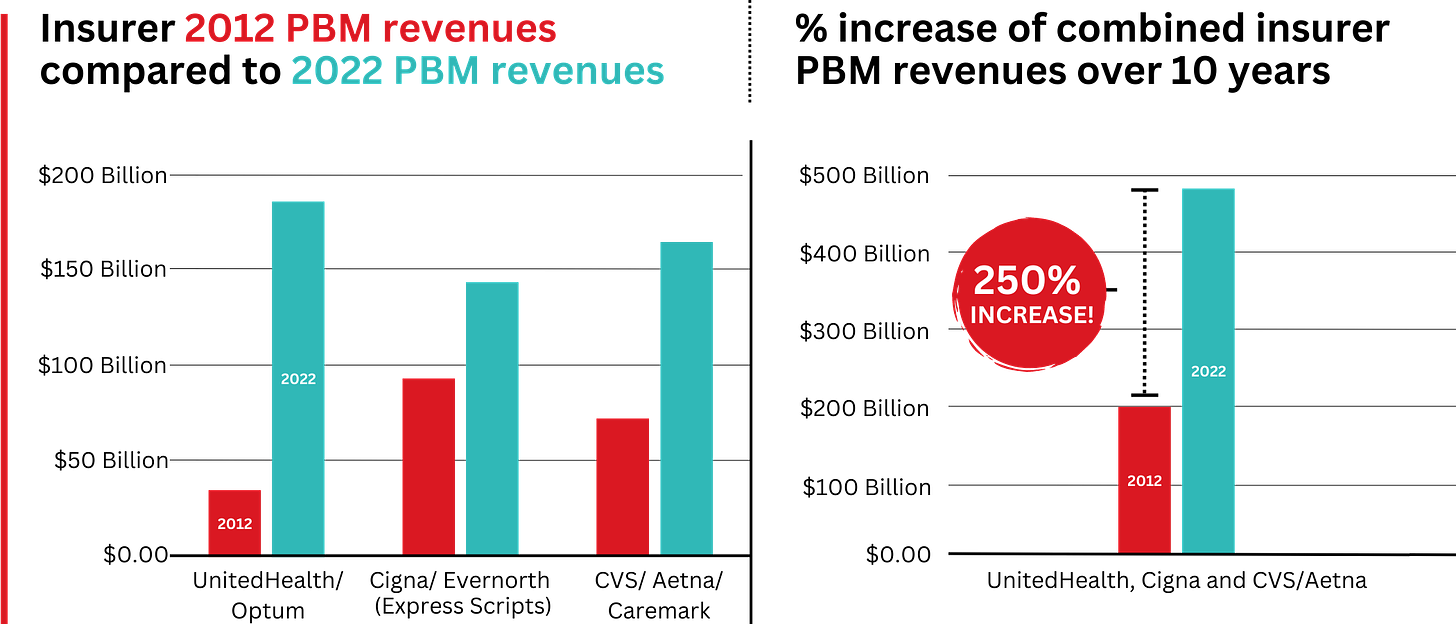
Ten years ago, PBMs contributed relatively little to the three companies’ revenues and profits. But since then, the rapid growth of PBMs has transformed all of the companies. The combined revenues from their PBM business units increased 250% between 2012 and 2022, from $196.7 billion to $492.4 billion.
PBM Profit Generation
The PBM profit growth at the three companies over the past decade was even more dramatic than revenue growth. Collectively, their PBM profits increased 438%, from $6.3 billion in 2012 to $27.6 billion in 2022.
As a result of this fast growth, more than half (52%) of three companies’ profits in 2022 came from their PBM business units: Cigna’s Evernorth, CVS/Aetna’s Caremark, and UnitedHealth’s Optum. Cigna now gets far more revenue and profits from its PBM than from its health plans. And CVS gets more revenue from its PBM than from either Aetna’s health plans or its nearly 10,000 retail stores. (The companies’ business units that include their PBMs have also moved aggressively in recent years into health-care delivery through acquisitions of physician practices, clinics, dialysis centers, and other facilities. Notably, UnitedHealth Group is now the largest U.S. employer of physicians.)
Huge strides in privatizing both Medicare and Medicaid
GOVERNMENT PROGRAMS HIGHLIGHTS
- More than 90% of health-plan revenues at three of the companies come from government programs as they continue to privatize both Medicare and Medicaid, through Medicare Advantage in particular.
- Enrollment in government-funded programs increased by 261% in 10 years; by contrast commercial enrollment increased by just 10% over the past decade.
- Commercial enrollment actually declined at both UnitedHealth and Humana.
- 85% of Humana’s health-plan members are in government-funded programs; at Centene, it is 88%, and at Molina, it is 94%.
The big insurers now manage most states’ Medicaid programs – and make billions of dollars for shareholders doing so – but most of the insurers have found that selling their privately operated Medicare replacement plans is even more financially rewarding for their shareholders.
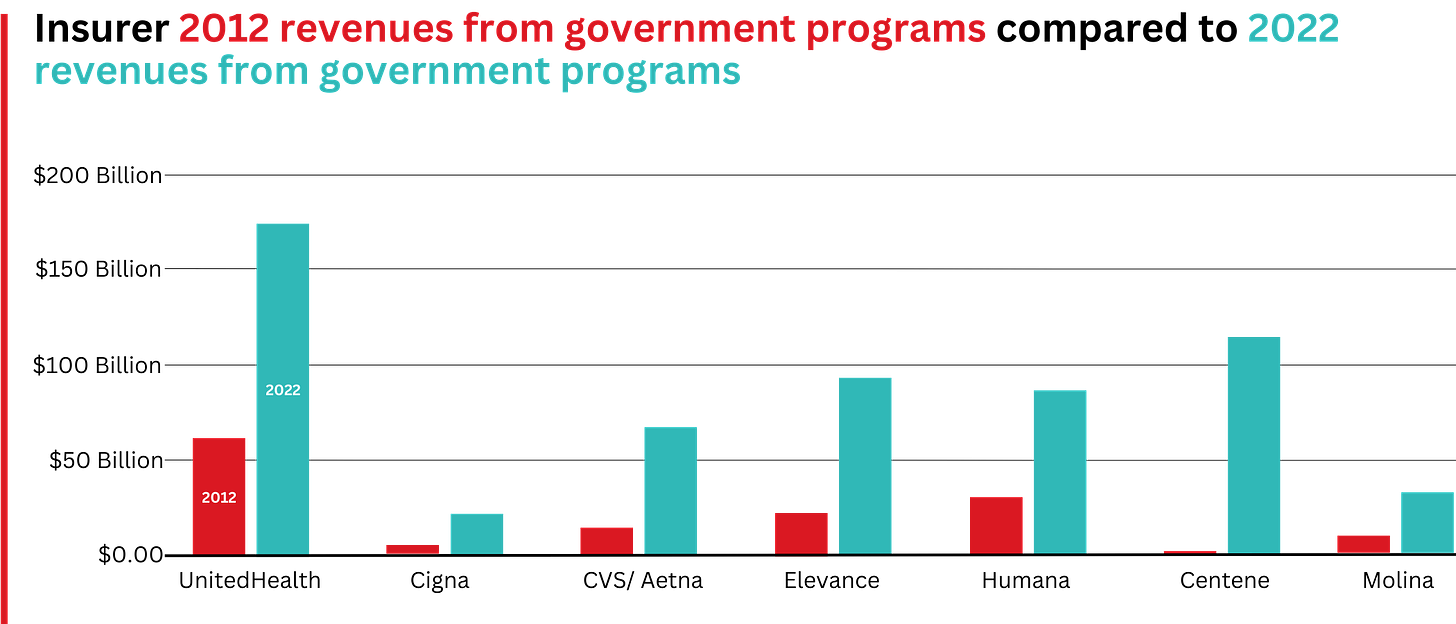
This is especially apparent when you see that the Big Seven’s combined revenues from taxpayer-supported programs grew 500%, from $116.3 billion in 2012 to $577 billion in 2022.
These numbers should be of interest to the Biden administration and members of Congress, many of whom are calling for much greater scrutiny of the Medicare Advantage program. Numerous media and government reports have shown that the federal government is overpaying private insurers billions of dollars a year, largely because of loopholes in laws and regulations that enable them to get more taxpayer dollars by claiming their enrollees are sicker than they really are. The companies also make aggressive use of prior authorization, largely unknown in traditional Medicare, to avoid paying for doctor-ordered care and medications.
In addition to their focus on Medicare and Medicaid, the companies also profit from the generous subsidies the government pays insurers to reduce the premiums they charge individuals and families who do not qualify for either Medicare or Medicaid or who work for an employer that does not offer subsidized coverage. But many people enrolled in those types of plans – primarily through the health insurance “marketplaces” established by the Affordable Care Act – cannot afford the deductibles and other out-of-pocket requirements they must pay before their insurers will begin paying their medical claims.
Dramatic Enrollment Shifts
Changes in health-plan enrollment over the past decade show how dramatic this shift has been. Between 2012 and 2022, enrollment in the companies’ private commercial plans increased by 10%, from 85.1 million in 2012 to 93.8 million in 2022.
By comparison, growth in enrollment in taxpayer-supported government programs increased 261%, from 27 million in 2012 to 70.4 million in 2022.
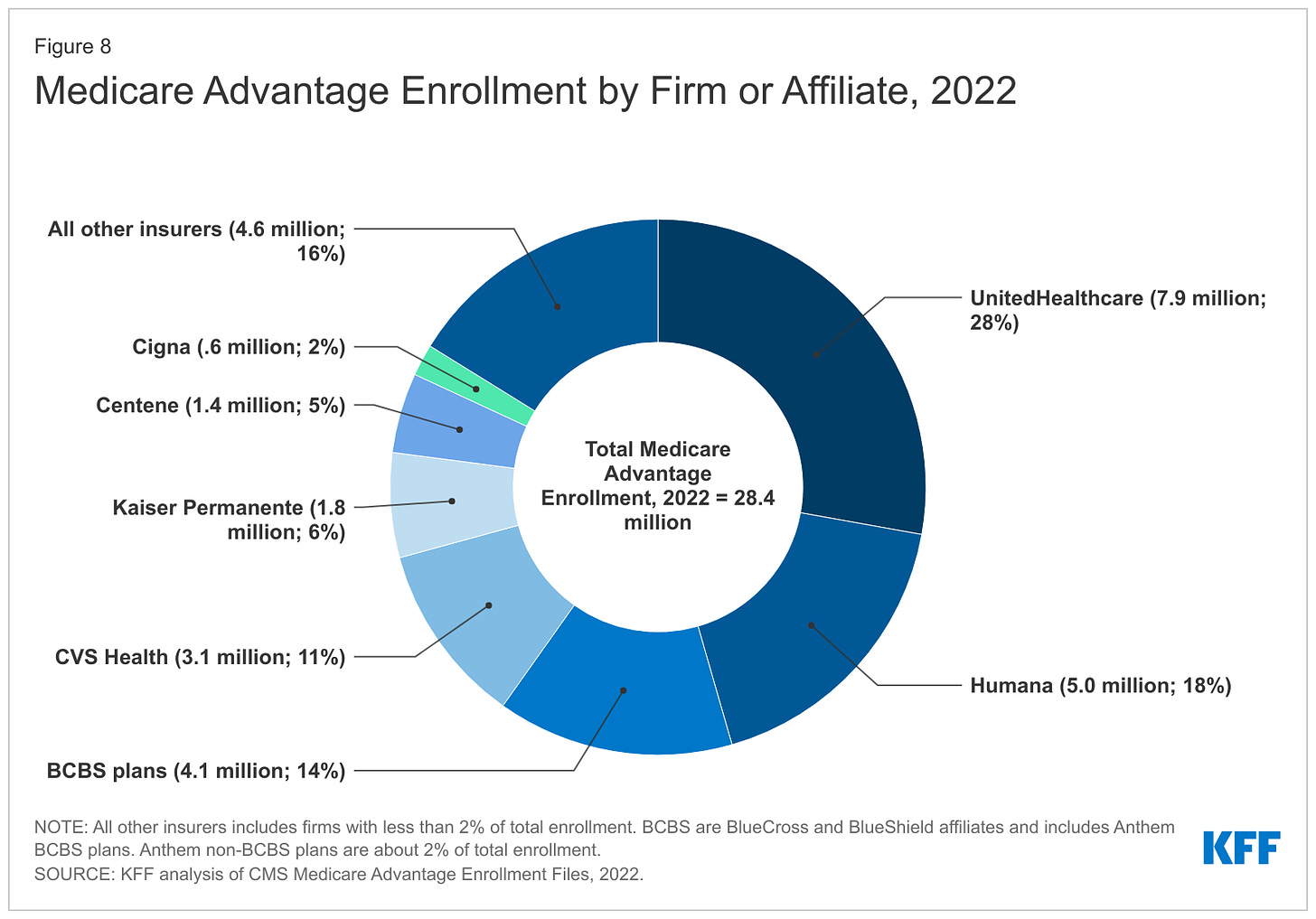
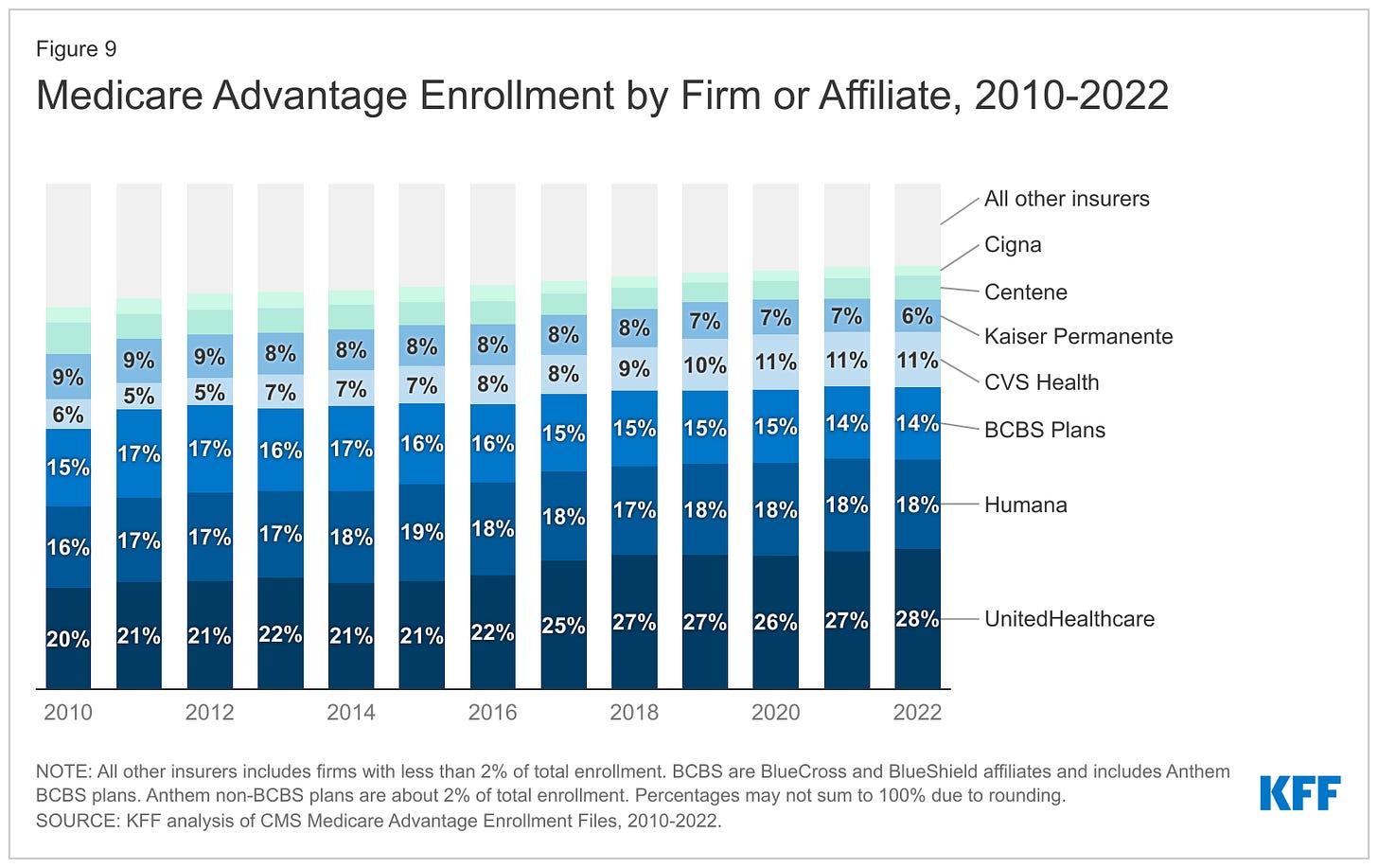
Within that category, Medicare Advantage enrollment among the Big Seven increased 252%, from 7.8 million in 2012 to 19.7 million in 2022.
Nationwide, enrollment in Medicare Advantage plans increased to 28.4 million in 2022 (and to 30 million this year). That means that the Big Seven for-profit companies control more than 70% of the Medicare Advantage market.
The remaining growth in the government segment occurred in the Medicaid programs that a subset of the Big Seven (UnitedHealth, Elevance, Centene, and Molina in particular) manages for several states.
A few other facts and figures to keep in mind as Big Insurance thrives:
- 27.5 million people remain uninsured in the United States. Up to 14 million more will lose their Medicaid coverage once the pandemic emergency period ends later this year.
- 100 million of us – almost one of every three people in this country – now have medical debt.
- In 2023, U.S. families can be on the hook for up to $18,200 in out-of-pocket requirements before their coverage kicks in, up 43% since 2014 when it was $12,700.The Affordable Care Act allows the out-of-pocket maximum to increase annually – 43% since the maximum limit went into effect in 2014.
- 44% of people in the United States who purchased coverage through the individual market and (ACA) marketplaces were underinsured or functionally uninsured.
- 46% of those surveyed said they had skipped or delayed care because of the cost.
- 42% said they had problems paying medical bills or were paying off medical debt.
- Half (49%) said they would be unable to pay an unexpected medical bill within 30 days, including 68% of adults with low income, 69% of Black adults, and 63% of Latino/Hispanic adults.
- In 2021, about $650 million, or about one-third of all funds raised by GoFundMe, went to medical campaigns. That’s not surprising when you realize that in the United States, even people with insurance all too often feel they have no choice but to beg for money from strangers to get the care they or a loved one needs.
- 62% of bankruptcies are related to medical costs.
- Even as we spend about $4.5 trillion on health care a year, Americans are now dying younger than people in other wealthy countries. Life expectancy in the United States actually decreased by 2.8 years between 2014 and 2021, erasing all gains since 1996, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
BOTTOM LINE:
The companies that comprise Big Insurance are vastly different from what they were just 10 years ago, but policymakers, regulators, employers, and the media have so far shown scant interest in putting their business practices under the microscope.
Changes in federal law, including the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003, which created the lucrative Medicare Advantage market, and the Affordable Care Act of 2010, which gave insurers the green light to increase out-of-pocket requirements annually and restrict access to care in other ways, opened the Treasury and Medicare Trust Fund to Big Insurance. In addition, regulators have allowed almost all of their proposed acquisitions to go forward, which has created the behemoths they are today.
CVS/Health is now the 4th largest company on the Fortune 500 list of American companies. UnitedHealth Group is now No. 5 – and all the others are climbing toward the top 10.










