Of all frightening ways that the SARS-COV-2 virus affects the body, one of the more insidious is the effect of COVID-19 on the brain.
It is now clear that many patients suffering from COVID-19 exhibit neurological symptoms, from loss of smell, to delirium, to an increased risk of stroke. There are also longer-lasting consequences for the brain, including myalgic encephalomyelitis /chronic fatigue syndrome and Guillain-Barre syndrome.
These effects may be caused by direct viral infection of brain tissue. But growing evidence suggests additional indirect actions triggered via the virus’s infection of epithelial cells and the cardiovascular system, or through the immune system and inflammation, contribute to lasting neurological changes after COVID-19.
I am a neuroscientist specializing in how memories are formed, the role of immune cells in the brain and how memory is persistently disrupted after illness and immune activation. As I survey the emerging scientific literature, my question is: Will there be a COVID-19-related wave of memory deficits, cognitive decline and dementia cases in the future?
The immune system and the brain
Many of the symptoms we attribute to an infection are really due to the protective responses of the immune system. A runny nose during a cold is not a direct effect of the virus, but a result of the immune system’s response to the cold virus. This is also true when it comes to feeling sick. The general malaise, tiredness, fever and social withdrawal are caused by activation of specialized immune cells in the brain, called neuroimmune cells, and signals in the brain.
These changes in brain and behavior, although annoying for our everyday lives, are highly adaptive and immensely beneficial. By resting, you allow the energy-demanding immune response to do its thing. A fever makes the body less hospitable to viruses and increases the efficiency of the immune system. Social withdrawal may help decrease spread of the virus.
In addition to changing behavior and regulating physiological responses during illness, the specialized immune system in the brain also plays a number of other roles. It has recently become clear that the neuroimmune cells that sit at the connections between brain cells (synapses), which provide energy and minute quantities of inflammatory signals, are essential for normal memory formation.
Unfortunately, this also provides a way in which illnesses like COVID-19 can cause both acute neurological symptoms and long-lasting issues in the brain.
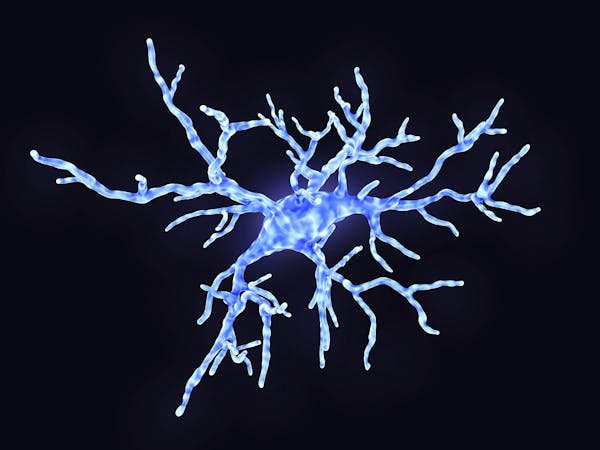
Microglia are specialized immune cells in the brain. In healthy states, they use their arms to test the environment. During an immune response, microglia change shape to engulf pathogens. But they can also damage neurons and their connections that store memory.
During illness and inflammation, the specialized immune cells in the brain become activated, spewing vast quantities of inflammatory signals, and modifying how they communicate with neurons. For one type of cell, microglia, this means changing shape, withdrawing the spindly arms and becoming blobby, mobile cells that envelop potential pathogens or cell debris in their path. But, in doing so, they also destroy and eat the neuronal connections that are so important for memory storage.
Another type of neuroimmune cell called an astrocyte, typically wraps around the connection between neurons during illness-evoked activation and dumps inflammatory signals on these junctions, effectively preventing the changes in connections between neurons that store memories.
Because COVID-19 involves a massive release of inflammatory signals, the impact of this disease on memory is particularly interesting to me. That is because there are both short-term effects on cognition (delirium), and the potential for long-lasting changes in memory, attention and cognition. There is also an increased risk for cognitive decline and dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, during aging.
How does inflammation exert long-lasting effects on memory?
If activation of neuroimmune cells is limited to the duration of the illness, then how can inflammation cause long-lasting memory deficits or increase the risk of cognitive decline?
Both the brain and the immune system have specifically evolved to change as a consequence of experience, in order to neutralize danger and maximize survival. In the brain, changes in connections between neurons allows us to store memories and rapidly change behavior to escape threat, or seek food or social opportunities. The immune system has evolved to fine-tune the inflammatory response and antibody production against previously encountered pathogens.
Yet long-lasting changes in the brain after illness are also closely linked to increased risk for age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. The disruptive and destructive actions of neuroimmune cells and inflammatory signaling can permanently impair memory. This can occur through permanent damage to the neuronal connections or neurons themselves and also via more subtle changes in how neurons function.
The potential connection between COVID-19 and persistent effects on memory are based on observations of other illnesses. For example, many patients who recover from heart attack or bypass surgery report lasting cognitive deficits that become exaggerated during aging.
Another major illness with a similar cognitive complications is sepsis – multi-organ dysfunction triggered by inflammation. In animal models of these diseases, we also see impairments of memory, and changes in neuroimmune and neuronal function that persist weeks and months after illness.
Even mild inflammation, including chronic stress, are now recognized as risk factors for dementias and cognitive decline during aging.
In my own laboratory, I and my colleagues have also observed that even without bacterial or viral infection, triggering inflammatory signaling over a short-term period results in long-lasting changes in neuronal function in memory-related brain regions and memory impairments.
Does COVID-19 increase risk for cognitive decline?
It will be many years before we know whether the COVID-19 infection causes an increased risk for cognitive decline or Alzheimer’s disease. But this risk may be decreased or mitigated through prevention and treatment of COVID-19.
Prevention and treatment both rely on the ability to decrease the severity and duration of illness and inflammation. Intriguingly, very new research suggests that common vaccines, including the flu shot and pneumonia vaccines, may reduce risk for Alzheimer’s.
Additionally, several emerging treatments for COVID-19 are drugs that suppress excessive immune activation and inflammatory state. Potentially, these treatments will also reduce the impact of inflammation on the brain, and decrease the impact on long-term brain health.
COVID-19 will continue to impact health and well-being long after the pandemic is over. As such, it will be critical to continue to assess the effects of COVID-19 illness in vulnerability to later cognitive decline and dementias.
In doing so, researchers will likely gain critical new insight into the role of inflammation across the life-span in age-related cognitive decline. This will aid in the development of more effective strategies for prevention and treatment of these debilitating illnesses.