
Cartoon – Health Workers


I’m a nurse in a Covid-19 unit. My hospital’s leaders frighten me more than the virus

I’ve been a nurse for almost 10 years, working mainly on a hospital’s cardiac floor.
One day I was assigned to a makeshift intensive care unit that had previously been an observation unit for highly stable patients waiting for test results. Many of the patients in this new Covid-19 unit were intubated, with ventilators breathing for them.
When I started the shift, a trained intensive care unit nurse was crying in the supply closet. She was overwhelmed and anxious, hadn’t worked on her familiar unit in weeks, and had been told that her next shift would be an overnight one — and she had no choice in the matter.
Many of us don’t have a choice. We are assigned to work in unfamiliar units, with patients who are outside our expertise, without any training. We’re lost.
Most shifts start with nurses crying. Most shifts end that way too.
“It’s out of our hands,” we hear from hospital administrators.
Nurses who typically work in outpatient clinics are being sent to inpatient floors and assigned to care for patients who are acutely ill. Many haven’t worked at the bedside in decades. The number of patients who have fallen in this unit has risen exponentially in the past two weeks due to lack of training of outpatient nurses.
I wonder if the patients know their nurses are overwhelmed, and that many of them are scared they’ll make a deadly mistake.
“Everyone is out of their comfort zone, just hang in there,” we’re told.
Doctors have been instructed not to enter patients’ rooms unless they must as a way to minimize their exposure to the virus that causes Covid-19 while nurses go from one room to the next, medicating, bathing, turning, and comforting their patients without changing their uncomfortable personal protective equipment, since supplies are limited. This work can take hours. It is not uncommon for nurses to go all day without drinking water or eating because that would mean removing our protective gear.
During one of my shifts, a doctor at my hospital posted several TikToks he made while sitting at the nurses’ station of a busy Covid-19 unit as nurses whispered words of encouragement to patients clinging to life supported by ventilators. Over our words and the hum of the ventilators, I wondered if our patients heard music coming from this doctor’s TikToks.
“We hear your concerns, but there’s nothing we can do,” doesn’t reassure or encourage us.
One day as I worked in the makeshift ICU, one of the hospital’s leaders went floor to floor making an important delivery. She approached our nursing station in her crisp professional attire and fresh disposition, and proudly delivered a supply of makeup-removing wipes. She told us to use the wipes to clean our faces before putting on our N95 masks so we could reuse the masks later, then moved on to the next nurses’ station without asking how our staff was doing or if we needed anything. I wonder if she had noticed the nurse crying in the supply closet.
“That’s above us, we don’t make those decisions,” is passing the buck at its worst.
Excuses from hospital administrators seem to have punctuated every shift for the past six weeks. The praise and applause from hospital leadership only go so far.
I can read in my co-workers’ faces and hear from the stories they tell that the biggest danger we face is not Covid-19. It’s the hospital’s administration.
Leadership is failing us, even as we stand firm in not failing our patients. We care for your loved ones, Covid-19 or not, monitor their vital signs, give them medications, rub lotion on their backs, help them to the bathroom, and brush their hair. We FaceTime their families from our personal phones so they can see their loved ones fighting to live. This is important care that nurses are proud to provide.
The narrative is simple. Nursing, and nurses, are not valued. It’s a shame, and maybe even a deadly shame, that hospital leaders don’t care about nurses like we care for our patients.
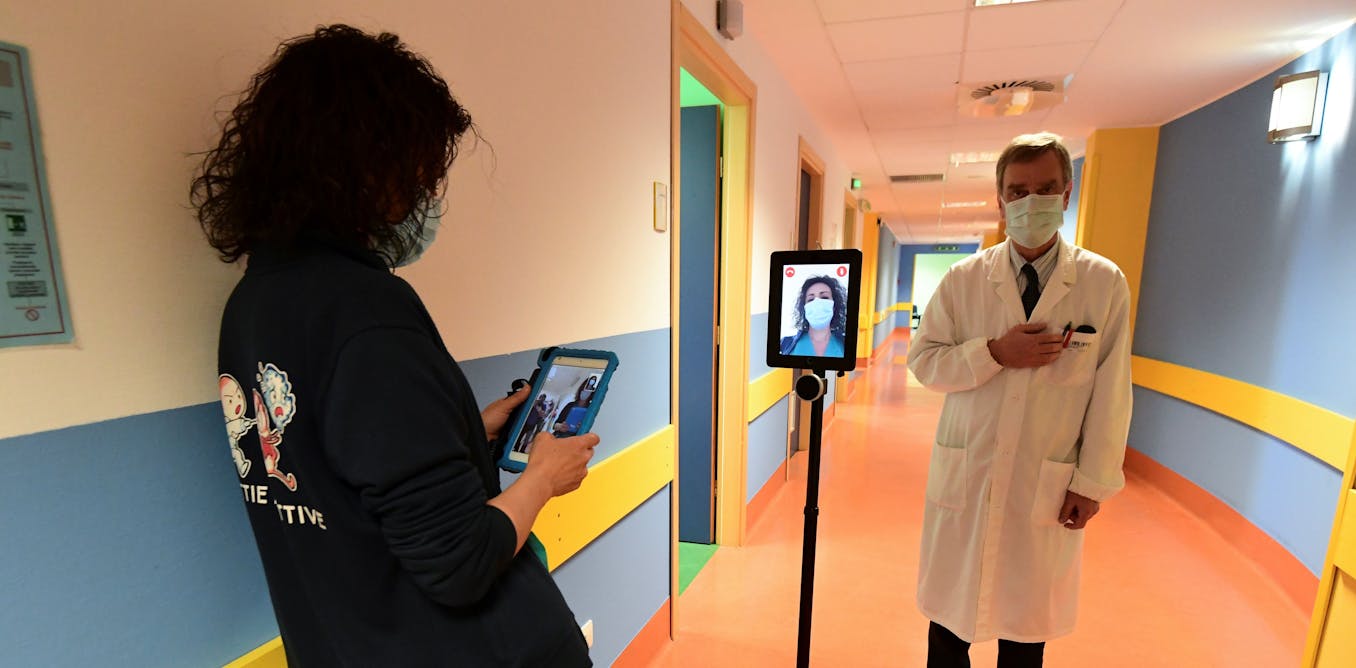




A cylindrical robot rolls into a treatment room to allow health care workers to remotely take temperatures and measure blood pressure and oxygen saturation from patients hooked up to a ventilator. Another robot that looks like a pair of large fluorescent lights rotated vertically travels throughout a hospital disinfecting with ultraviolet light. Meanwhile a cart-like robot brings food to people quarantined in a 16-story hotel. Outside, quadcopter drones ferry test samples to laboratories and watch for violations of stay-at-home restrictions.
These are just a few of the two dozen ways robots have been used during the COVID-19 pandemic, from health care in and out of hospitals, automation of testing, supporting public safety and public works, to continuing daily work and life.
The lessons they’re teaching for the future are the same lessons learned at previous disasters but quickly forgotten as interest and funding faded. The best robots for a disaster are the robots, like those in these examples, that already exist in the health care and public safety sectors.
Research laboratories and startups are creating new robots, including one designed to allow health care workers to remotely take blood samples and perform mouth swabs. These prototypes are unlikely to make a difference now. However, the robots under development could make a difference in future disasters if momentum for robotics research continues.
As roboticists at Texas A&M University and the Center for Robot-Assisted Search and Rescue, we examined over 120 press and social media reports from China, the U.S. and 19 other countries about how robots are being used during the COVID-19 pandemic. We found that ground and aerial robots are playing a notable role in almost every aspect of managing the crisis.
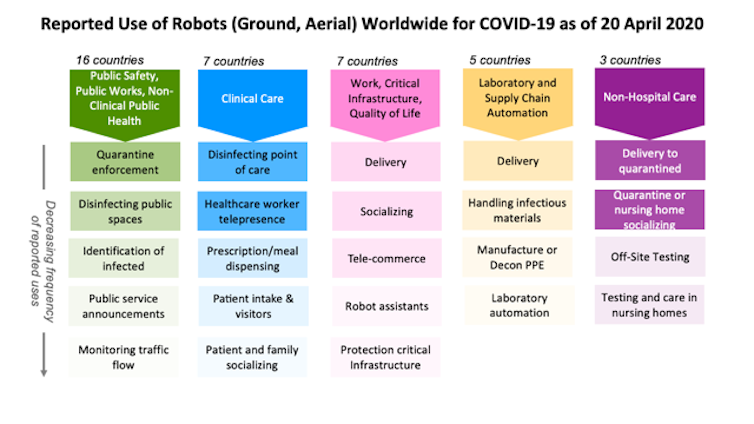
In hospitals, doctors and nurses, family members and even receptionists are using robots to interact in real time with patients from a safe distance. Specialized robots are disinfecting rooms and delivering meals or prescriptions, handling the hidden extra work associated with a surge in patients. Delivery robots are transporting infectious samples to laboratories for testing.
Outside of hospitals, public works and public safety departments are using robots to spray disinfectant throughout public spaces. Drones are providing thermal imagery to help identify infected citizens and enforce quarantines and social distancing restrictions. Robots are even rolling through crowds, broadcasting public service messages about the virus and social distancing.
At work and home, robots are assisting in surprising ways. Realtors are teleoperating robots to show properties from the safety of their own homes. Workers building a new hospital in China were able work through the night because drones carried lighting. In Japan, students used robots to walk the stage for graduation, and in Cyprus, a person used a drone to walk his dog without violating stay-at-home restrictions.
Every disaster is different, but the experience of using robots for the COVID-19 pandemic presents an opportunity to finally learn three lessons documented over the past 20 years. One important lesson is that during a disaster robots do not replace people. They either perform tasks that a person could not do or do safely, or take on tasks that free up responders to handle the increased workload.
The majority of robots being used in hospitals treating COVID-19 patients have not replaced health care professionals. These robots are teleoperated, enabling the health care workers to apply their expertise and compassion to sick and isolated patients remotely.
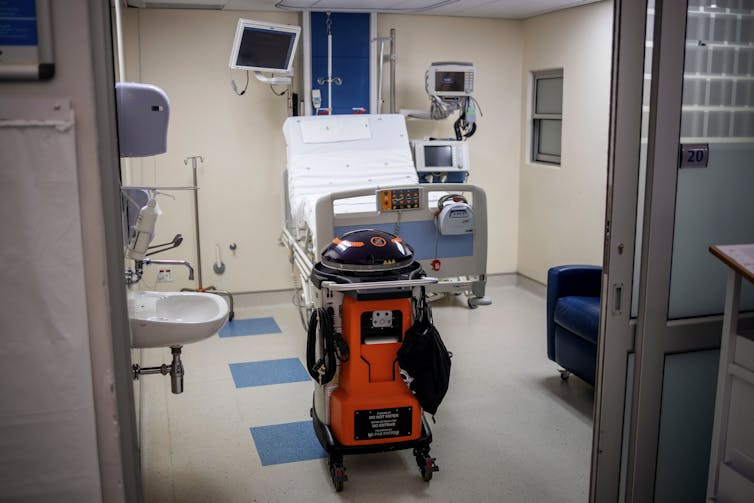
A small number of robots are autonomous, such as the popular UVD decontamination robots and meal and prescription carts. But the reports indicate that the robots are not displacing workers. Instead, the robots are helping the existing hospital staff cope with the surge in infectious patients. The decontamination robots disinfect better and faster than human cleaners, while the carts reduce the amount of time and personal protective equipment nurses and aides must spend on ancillary tasks.
The second lesson is the robots used during an emergency are usually already in common use before the disaster. Technologists often rush out well-intentioned prototypes, but during an emergency, responders – health care workers and search-and-rescue teams – are too busy and stressed to learn to use something new and unfamiliar. They typically can’t absorb the unanticipated tasks and procedures, like having to frequently reboot or change batteries, that usually accompany new technology.
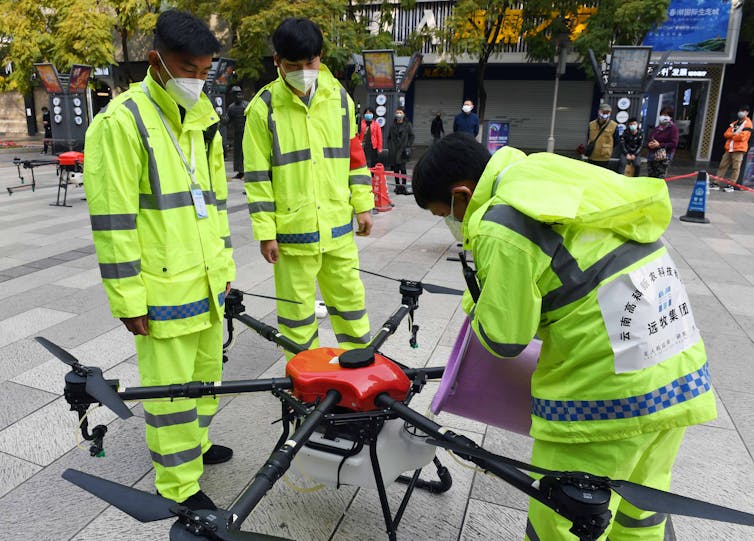
Fortunately, responders adopt technologies that their peers have used extensively and shown to work. For example, decontamination robots were already in daily use at many locations for preventing hospital-acquired infections. Sometimes responders also adapt existing robots. For example, agricultural drones designed for spraying pesticides in open fields are being adapted for spraying disinfectants in crowded urban cityscapes in China and India.

A third lesson follows from the second. Repurposing existing robots is generally more effective than building specialized prototypes. Building a new, specialized robot for a task takes years. Imagine trying to build a new kind of automobile from scratch. Even if such a car could be quickly designed and manufactured, only a few cars would be produced at first and they would likely lack the reliability, ease of use and safety that comes from months or years of feedback from continuous use.
Alternatively, a faster and more scalable approach is to modify existing cars or trucks. This is how robots are being configured for COVID-19 applications. For example, responders began using the thermal cameras already on bomb squad robots and drones – common in most large cities – to detect infected citizens running a high fever. While the jury is still out on whether thermal imaging is effective, the point is that existing public safety robots were rapidly repurposed for public health.
The broad use of robots for COVID-19 is a strong indication that the health care system needed more robots, just like it needed more of everyday items such as personal protective equipment and ventilators. But while storing caches of hospital supplies makes sense, storing a cache of specialized robots for use in a future emergency does not.
This was the strategy of the nuclear power industry, and it failed during the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident. The robots stored by the Japanese Atomic Energy Agency for an emergency were outdated, and the operators were rusty or no longer employed. Instead, the Tokyo Electric Power Company lost valuable time acquiring and deploying commercial off-the-shelf bomb squad robots, which were in routine use throughout the world. While the commercial robots were not perfect for dealing with a radiological emergency, they were good enough and cheap enough for dozens of robots to be used throughout the facility.
Hopefully, COVID-19 will accelerate the adoption of existing robots and their adaptation to new niches, but it might also lead to new robots. Laboratory and supply chain automation is emerging as an overlooked opportunity. Automating the slow COVID-19 test processing that relies on a small set of labs and specially trained workers would eliminate some of the delays currently being experienced in many parts of the U.S.
Automation is not particularly exciting, but just like the unglamorous disinfecting robots in use now, it is a valuable application. If government and industry have finally learned the lessons from previous disasters, more mundane robots will be ready to work side by side with the health care workers on the front lines when the next pandemic arrives.
https://www.axios.com/coronavirus-west-virginia-first-case-ac32ce6d-5523-4310-a219-7d1d1dcb6b44.html

The pandemic is a long way from over, and its impact on our daily lives, information ecosystem, politics, cities and health care will last even longer.
The big picture: The novel coronavirus has infected more than 939,000 people and killed over 54,000 in the U.S., Johns Hopkins data shows. More than 105,000 Americans have recovered from the virus as of Sunday.
Lockdown measures: Demonstrators gathered in Florida, Texas and Louisiana Saturday to protest stay-at-home orders designed to protect against the spread of COVID-19, following a week of similar rallies across the U.S.
Catch up quick: Deborah Birx said Sunday that it “bothers” her that the news cycle is still focused on Trump’s comments about disinfectants possibly treating coronavirus, arguing that “we’re missing the bigger pieces” about how Americans can defeat the virus.

Bill Gates is a co-chair of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. This article is adapted from his blog post “Pandemic I: the First Modern Pandemic,” available at gatesnotes.com.
It’s entirely understandable that the national conversation has turned to a single question: “When can we get back to normal?” The shutdown has caused immeasurable pain in jobs lost, people isolated and worsening inequity. People are ready to get going again.
Unfortunately, although we have the will, we don’t have the way — not yet. Before the United States and other countries can return to business and life as usual, we will need some innovative new tools that help us detect, treat and prevent covid-19.
It begins with testing. We can’t defeat an enemy if we don’t know where it is. To reopen the economy, we need to be testing enough people that we can quickly detect emerging hotspots and intervene early. We don’t want to wait until the hospitals start to fill up and more people die.
Innovation can help us get the numbers up. The current coronavirus tests require that health-care workers perform nasal swabs, which means they have to change their protective gear before every test. But our foundation supported research showing that having patients do the swab themselves produces results that are just as accurate. This self-swab approach is faster and safer, since regulators should be able to approve swabbing at home or in other locations rather than having people risk additional contact.
Another diagnostic test under development would work much like an at-home pregnancy test. You would swab your nose, but instead of sending it into a processing center, you’d put it in a liquid and then pour that liquid onto a strip of paper, which would change color if the virus was present. This test may be available in a few months.
We need one other advance in testing, but it’s social, not technical: consistent standards about who can get tested. If the country doesn’t test the right people — essential workers, people who are symptomatic and those who have been in contact with someone who tested positive — then we’re wasting a precious resource and potentially missing big reserves of the virus. Asymptomatic people who aren’t in one of those three groups should not be tested until there are enough for everyone else.
The second area where we need innovation is contact tracing. Once someone tests positive, public-health officials need to know who else that person might have infected.
For now, the United States can follow Germany’s example: interview everyone who tests positive and use a database to make sure someone follows up with all their contacts. This approach is far from perfect, because it relies on the infected person to report their contacts accurately and requires a lot of staff to follow up with everyone in person. But it would be an improvement over the sporadic way that contact tracing is being done across the United States now.
An even better solution would be the broad, voluntary adoption of digital tools. For example, there are apps that will help you remember where you have been; if you ever test positive, you can review the history or choose to share it with whoever comes to interview you about your contacts. And some people have proposed allowing phones to detect other phones that are near them by using Bluetooth and emitting sounds that humans can’t hear. If someone tested positive, their phone would send a message to the other phones, and their owners could get tested. If most people chose to install this kind of application, it would probably help some.
Naturally, anyone who tests positive will immediately want to know about treatment options. Yet, right now, there is no treatment for covid-19. Hydroxychloroquine, which works by changing the way the human body reacts to a virus, has received a lot of attention. Our foundation is funding a clinical trial that will give an indication whether it works on covid-19 by the end of May, and it appears the benefits will be modest at best.
But several more-promising candidates are on the horizon. One involves drawing blood from patients who have recovered from covid-19, making sure it is free of the coronavirus and other infections, and giving the plasma (and the antibodies it contains) to sick people. Several major companies are working together to see whether this succeeds.
Another type of drug candidate involves identifying the antibodies that are most effective against the novel coronavirus, and then manufacturing them in a lab. If this works, it is not yet clear how many doses could be produced; it depends on how much antibody material is needed per dose. In 2021, manufacturers may be able to make as few as 100,000 treatments or many millions.
If, a year from now, people are going to big public events — such as games or concerts in a stadium — it will be because researchers have discovered an extremely effective treatment that makes everyone feel safe to go out again. Unfortunately, based on the evidence I’ve seen, they’ll likely find a good treatment, but not one that virtually guarantees you’ll recover.
That’s why we need to invest in a fourth area of innovation: making a vaccine. Every additional month that it takes to produce a vaccine is a month in which the economy cannot completely return to normal.
The new approach I’m most excited about is known as an RNA vaccine. (The first covid-19 vaccine to start human trials is an RNA vaccine.) Unlike a flu shot, which contains fragments of the influenza virus so your immune system can learn to attack them, an RNA vaccine gives your body the genetic code needed to produce viral fragments on its own. When the immune system sees these fragments, it learns how to attack them. An RNA vaccine essentially turns your body into its own vaccine manufacturing unit.
There are at least five other efforts that look promising. But because no one knows which approach will work, a number of them need to be funded so they can all advance at full speed simultaneously.
Even before there’s a safe, effective vaccine, governments need to work out how to distribute it. The countries that provide the funding, the countries where the trials are run, and the ones that are hardest-hit will all have a good case that they should receive priority. Ideally, there would be global agreement about who should get the vaccine first, but given how many competing interests there are, this is unlikely to happen. Whoever solves this problem equitably will have made a major breakthrough.
World War II was the defining moment of my parents’ generation. Similarly, the coronavirus pandemic — the first in a century — will define this era. But there is one big difference between a world war and a pandemic: All of humanity can work together to learn about the disease and develop the capacity to fight it. With the right tools in hand, and smart implementation, we will eventually be able to declare an end to this pandemic — and turn our attention to how to prevent and contain the next one.

The names came from all over the country — New York and Alabama, Puerto Rico and Nevada, California and Michigan, Florida and Maryland, New Jersey and the District.
A man in blue scrubs stood behind Jones as she read, holding a metallic gold sign painted with the message: “20 seconds won’t scrub ‘hero’ blood off your hands.”
“Let us remember and honor the ultimate sacrifice these nurses paid,” Jones said. “We commit ourselves to fight like hell for the living.”
The protest stood in stark contrast to demonstrations in recent days in some parts of the country in which protesters have demanded the reopening of nonessential businesses. Nurses have been spotted at those gatherings, too, standing arms crossed, in opposition to demonstrators, many of whom are unmasked and milling in crowds.
More than 9,000 health-care workers in the United States have tested positive for the novel coronavirus, according to figures from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Those numbers are believed to be an undercount of infections due to a lack of tests in many areas.
The nurses said Tuesday that they wanted to bring their demands for more personal protective equipment directly to President Trump’s doorstep.
Health-care providers in hospitals, clinics, nursing homes, assisted-living facilities and rehabilitation centers have for weeks asked lawmakers and government agencies for more protective equipment to shield themselves and their vulnerable patients from the spread of covid-19.
National Nurses United last month petitioned the Occupational Safety and Health Administration to institute an emergency safety standard that would provide nurses with more protective gear, including N95 respirator masks, face shields, gowns, gloves and shoe coverings.
Health-care workers, governors and other officials have for weeks demanded that Trump enforce the Defense Production Act to order mass production of those materials. Many have also petitioned Congress to mandate Trump use his authority to help boost the production of such gear.
Last week, a protest in the shadow of the Capitol displayed the faces of health-care workers demanding better protection on 1,000 signs. The sign represented protesters that organizers said would not have been safe if gathered together on the Capitol lawn.

Today I stood with some of my fellow nurses and faced a tidal wave of ignorance, fear, and abuse.
I was mocked. I was called more names than I can remember. I was told I was ignorant, unintelligent, and compassionless. I was accused of being a fake nurse, a paid protester, a fraud. I was told I was nothing. I had cigarette smoke blown in my face. I was sexually harassed. A few times, I was surrounded on all sides by multiple people yelling at me.
Desperation and fear bring out the worst in people. I will admit, I cried a bit. How could I not in the face of so much hate?
But I when I did, I was crying for my fellow healthcare workers on the front lines, who are working their asses off fighting this illness, who are being put at worse risk because of the lack of essential protective equipment in this country. I cried for those who have left their families behind to go help where the situation is most dire. I cried for those who have died and will continue to die, after working their hardest to help those who needed them.
I cried for every protester who doesn’t know how they are going to make ends meet, that are afraid for their businesses, their jobs, their homes, and their lives. I cried for every American who has received less than adequate help from the government, who felt like this is the only way for them to get the resources they need, and who have been failed by our president who has not implemented the measures required to help and protect our most vulnerable people.
I cried for every person at this protest that will inevitably get sick, and increase the spread in our state when we had been doing a pretty good job of flattening the curve and delaying the spread of covid-19 in Arizona. I cried for every person who will be infected by those that contracted the disease today.
But more important than the few tears I shed today, was that I stood strong for what is right.
I stood for using science, not feelings, to make important decisions in a pandemic. I stood for the healthcare workers who are going to keep working our hardest to help heal the sick, whether they appreciate it or not. I stood for those who couldn’t. I stood for the lives we have lost, many unnecessarily, to this virus. I stood strong and looked every protester fighting to open Arizona in the eye, so they would have to stare into the face of some of the individuals they are hurting with their ignorance. My hands cramped up from standing in this position so long, but I kept standing until everything died down.
And I will keep standing.
https://nowthisnews.com/news/health-care-workers-stand-up-to-people-protesting-stay-at-home-orders
Remarkable scene at 12th and Grant, where two healthcare workers from a Denver-area hospital — they declined to say which or give their names — are standing in the crosswalk during red lights as a “reminder,” they say, of why shutdown measures are in place.
Two health care workers blocked a parade of protesters in Denver, Colorado on Sunday, who were storming the capitol to protest the state’s stay-at-home order.
Powerful images and videos of the standoff were widely shared on social media of the two unidentified people wearing scrubs and N95 masks, standing in a crosswalk blocking protesters’ vehicles. The two were identified as health care workers by photographers on the scene.
One video shared by Twitter user Marc Zenn, captured cars lined up and beeping their horns at the two medical workers, with a woman hanging out of her vehicle’s window shouting “Go to China if you want communism. Go to China,” and “You get to go to work, why can’t we?”
They say they’ve been treating COVID patients for weeks. Today most of the people driving by have been “very aggressive,” they say. I’ve been standing here for a few minutes and already seen two people get in their faces.
Hundreds of people showed up on foot and in their vehicles for two separate protests in Colorado’s capitol on Sunday. The protests were reportedly planned by ReOpen Colorado and “various Libertarian parties,” according to a local Denver news outlet. People attending the march were shown carrying American flags, “Don’t Tread on Me” flags, and signs about reopening businesses and schools.
“Coloradans have a first amendment right to protest and to free speech, and the Governor hopes that they are using social distancing and staying safe,” Colorado Gov. Jared Polis’ office said in a statement. “No one wants to reopen Colorado businesses and lift these restrictions more than the Governor, but in order to do that, Coloradans have to stay home as much as possible during this critical period, wear masks and wash their hands regularly to slow the spread of this deadly virus.”
As of Monday morning, Colorado has more than 9,700 cases of COVID-19, leading to at least 420 deaths, according to the Johns Hopkins coronavirus tracker. The state of Colorado is set to continue its stay-at-home order until at least April 26, to slow the transmission of the virus.
Colorado isn’t the only state where protesters are demonstrating against their government’s stay-at-home orders—Several other states held protests over the weekend including Utah, Idaho, and Washington state. Last week, parts of Michigan, New York, Ohio, Virginia, North Carolina, and others also saw a wave of demonstrators.
President Trump encouraged the protesters last week during his Friday press briefing and in tweets which said to “liberate” multiple states holding protests.
In a Politico poll, 81% of Americans agreed we “should continue to social distance for as long as is needed to curb the spread of coronavirus, even if it means continued damage to the economy.” An NBC News poll found that 60% of responders agreed with keeping at-home restrictions.