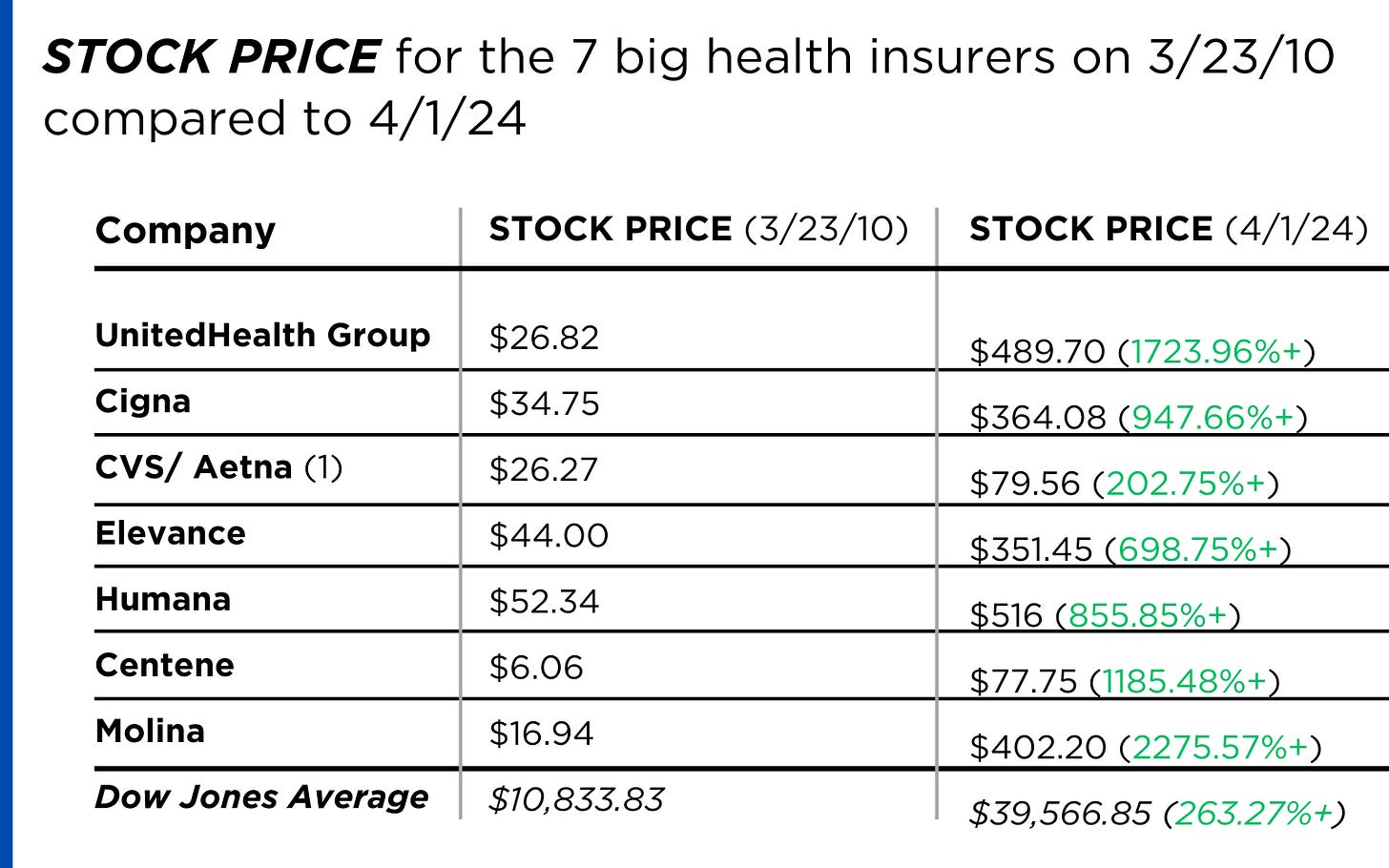
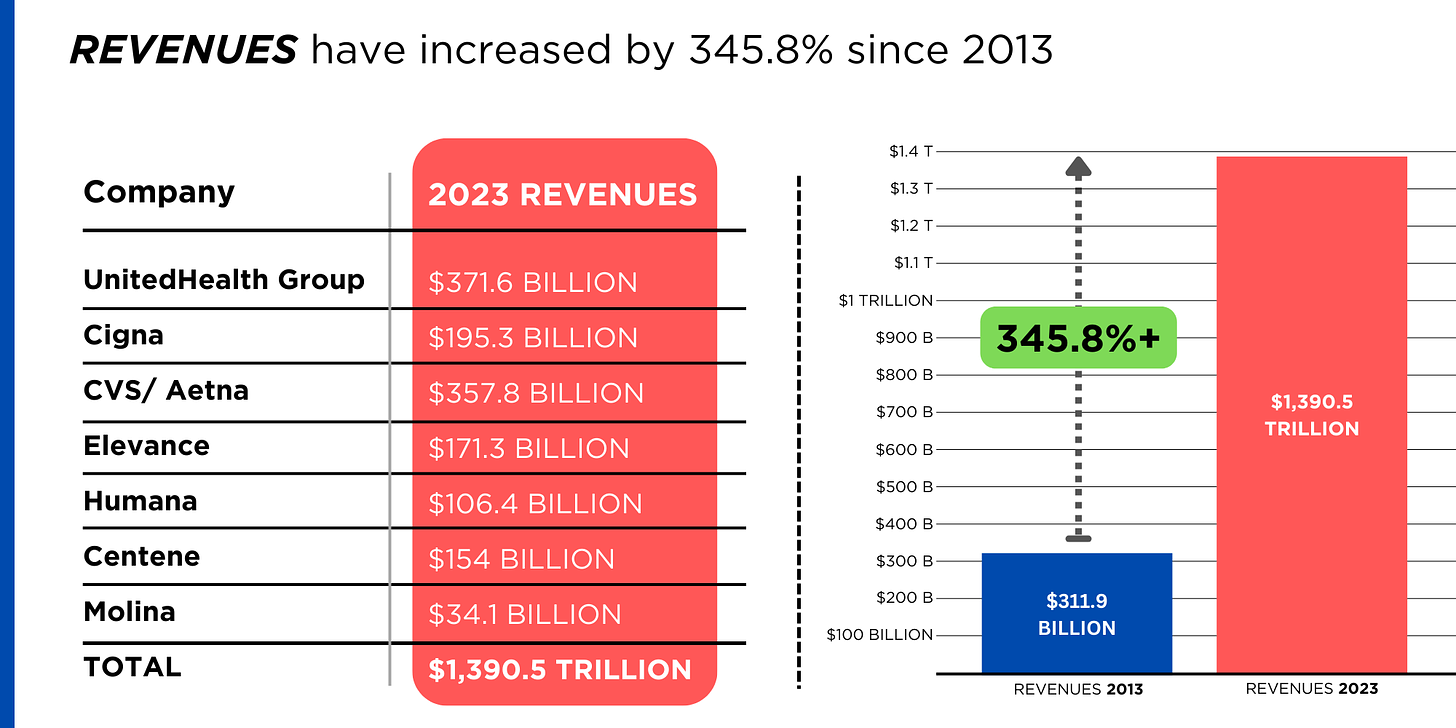
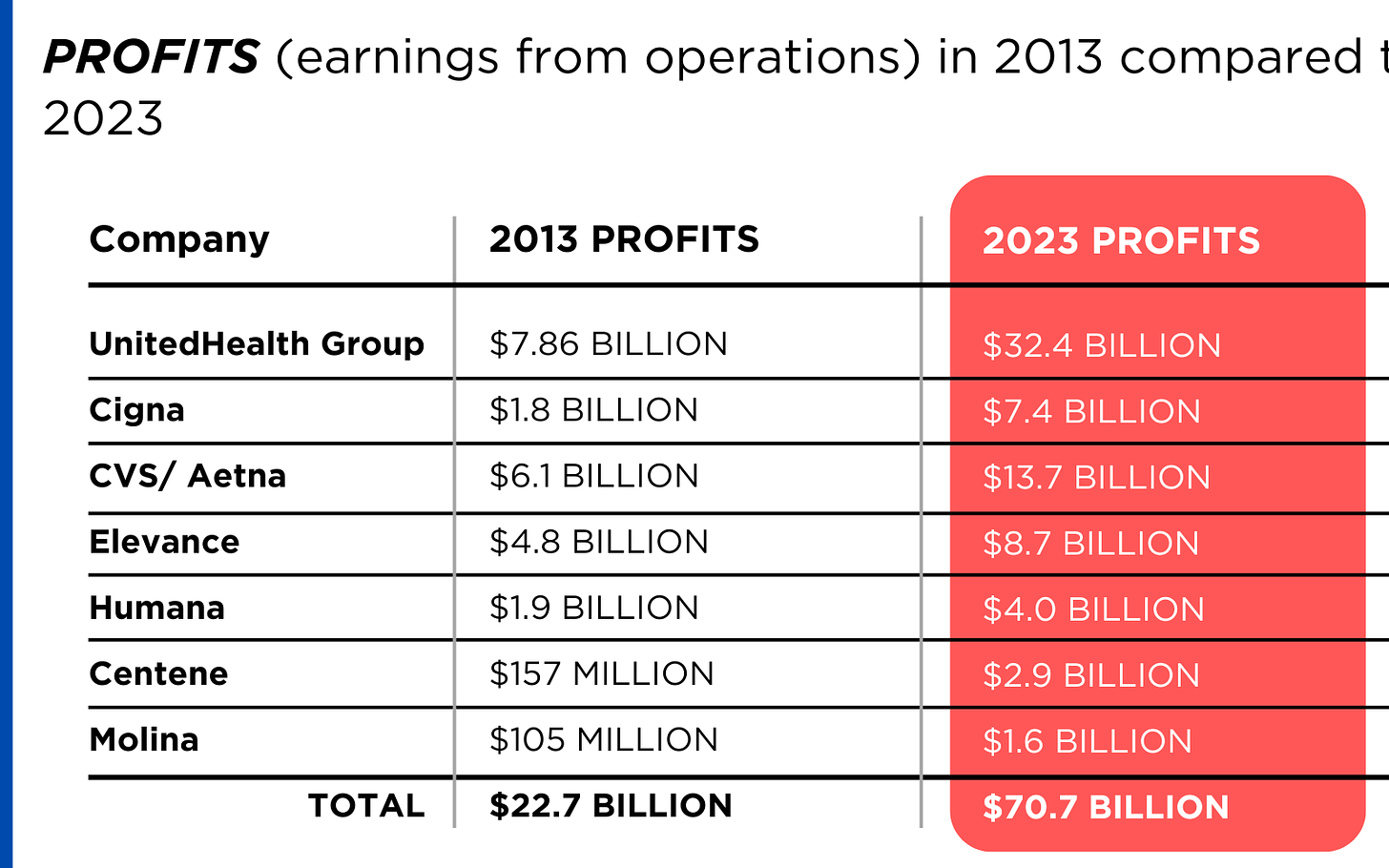
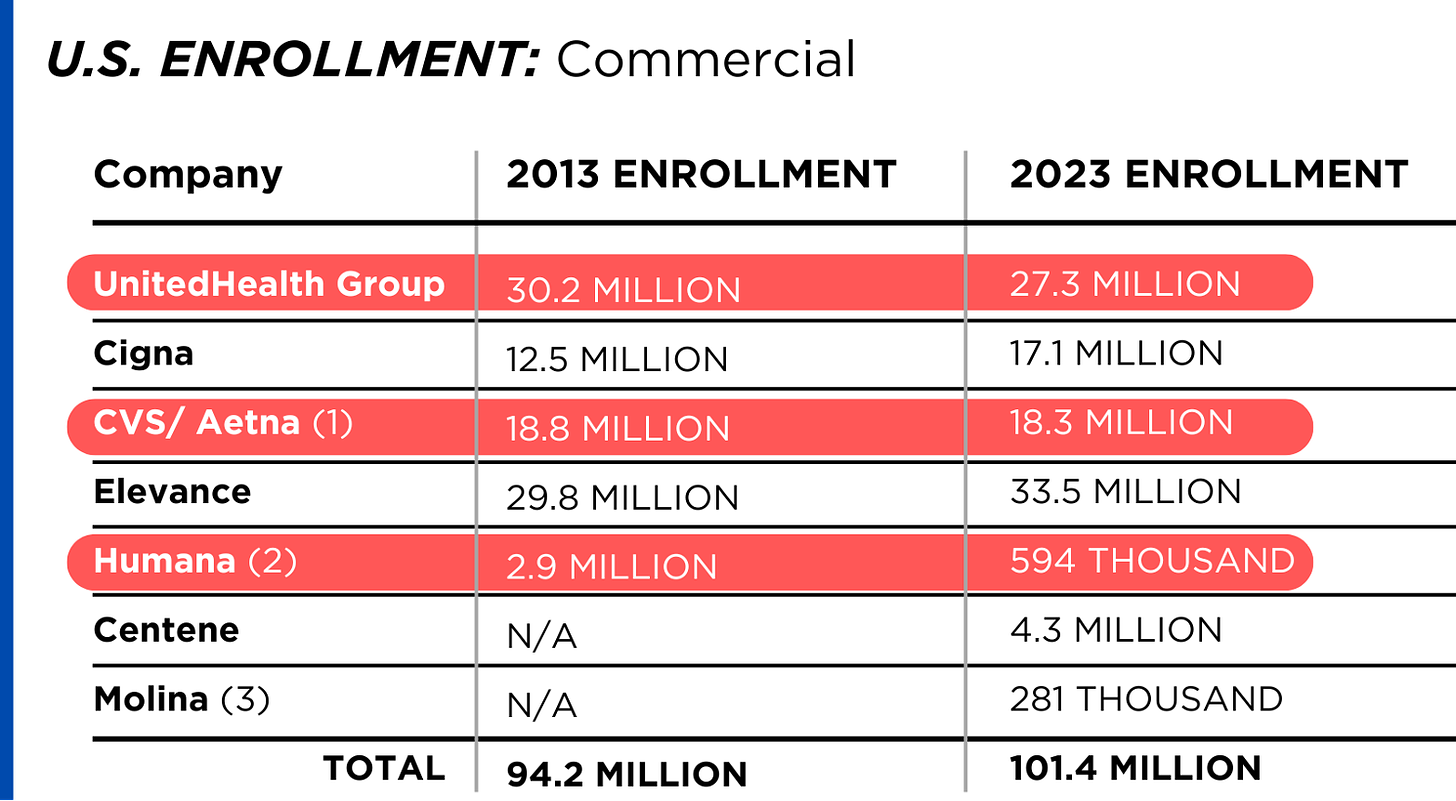
In 126 days, U.S. voters will settle Campaign 2024 choosing the winners for 435 House seats, 34 Senate seats, 13 Governors and the White House. When final votes are counted, the last week of June, 2024 will be seen as the tipping point when much about politics and policy was re-set as the result of two events:
1-The ‘Great Debate’:
Thursday’s standoff between President Biden and former President Trump drew 51.3 million viewers across 17 networks that carried it. That’s well below previous head-to-head debate match-ups i.e. 84 million for Clinton-Trump in 2016, 73 million for Trump and Biden in 2020. Perhaps more telling, only 3.9 million of these were adults 18-34– 7.6% of debate viewers but 22.9% of U.S. population.
While pundits debated the fitness of the President to continue and speculated about alternative candidates over the weekend, the majority of Americans paid no attention—especially young adults. They think both candidates are old.
In 2020, 57% of 18–34-year-olds voted for a Presidential candidate vs. 69% of 35–64-year-olds and 74% of voters 65+.
Polls show young adults think the political system is fundamentally flawed and partisanship harmful to policies that advance the well-being of the population. They also show their declining trust and confidence in America’s institutions—the press, big business, Congress, organized religion and the medical system.
Young adults get their information from social media and friends and they’re tuning out spin in politics.
2-Supreme Court decisions impacting healthcare:
As is customary for the high court, many of its rulings are handed down in the last week of June before it adjourns for the summer. Only one case remains in limbo: Presidential immunity with a decision expected today. Of the 61 cases SCOTUS has heard in its 2023-2024 term, these four decisions are the most significant to the health industry:
- Power of federal agencies (Loper Bright Enterprises v. Raimondo and Relentless, Inc. v. Dept. of Commerce): By a vote of 6-3, SCOTUS ruled that judges no longer have to defer to agency officials when interpreting ambiguous federal statutes about the environment, the workplace, public health and other aspects of American life overturning a 40-year-old legal precedent known as “Chevron deference.” The court’s decision will significantly curtail the power federal agencies have to regulate thousands of private companies, products, industries and the environment.
- Emergency room abortions (Idaho v. U.S): SCOTUS ruled 6-3 that hospitals in Idaho that receive federal fundsmust allow emergency abortion care to stabilize patients — even though the state strictly bans the procedure.
- Opioid lawsuit settlement (Harrington v. Purdue Pharma): By a vote of 5-4, the justices blocked a controversialPurdue Pharma bankruptcy plan that would have provided billions of dollars to address the nation’s opioid crisis in exchange for protecting the family that owns the company from future lawsuits. The majority found that the plan was invalid because all the affected parties had not been consulted on the deal
- Abortion medication restrictions (FDA v. Alliance for Hippocratic Medicine): By a vote of 9-0, the justices maintained broad access to mifepristone, unanimously reversing a lower court decision that would have made the widely used abortion medication more difficult to obtain. The decision was not on the substance of the case, but a procedural ruling that the challengers did not have legal grounds to bring their lawsuit.
Based on these events last week, healthcare organizations and their trade groups making plans for 2025 and beyond should consider:
- Young adults. Out of Sight, Out of Mind: Polling data shows young adults think the health system is broken and alternatives worth considering. Affordability, equitable access and price transparency matter to them. Their finances are stretched as inflation (housing, energy, food et al), their medical debt prevalent and mounting and their employers are cutting their health benefits and forcing them to assume more out-of-pocket responsibility. Hospitals, insurers, physicians and drug companies pay close attention to older working age consumers and seniors. They pay little attention to younger adults, and the reverse is true. But history teaches that social movements originate from disenchanted youth and young adults who feel taken for granted, abused by corporate greed and unheard. Might the healthcare status quo be a target?
- The federal administrative state in flux: The ripple effect of the court’s Chevron decision is equivalent to its decision ending Roe v. Wade (June 2022). The latitude afforded key federal agencies i.e. CDC, CMS, OSHA, CMMI, FDA, HRSA et al will be revisited. States will be forced to step in where federal guidance is in jeopardy. Governors and the White House will face more frequent court challenges on their Executive Orders and agencies for their Administrative Actions as government oversight of healthcare evolves. For investors, safe bets will be targets. For hospitals, insurers and physicians, federal advocacy will require recalibration.
- The administrative state flux means state legislatures and ballot referenda will play a bigger role in healthcare. States already have enormous responsibilities for healthcare:
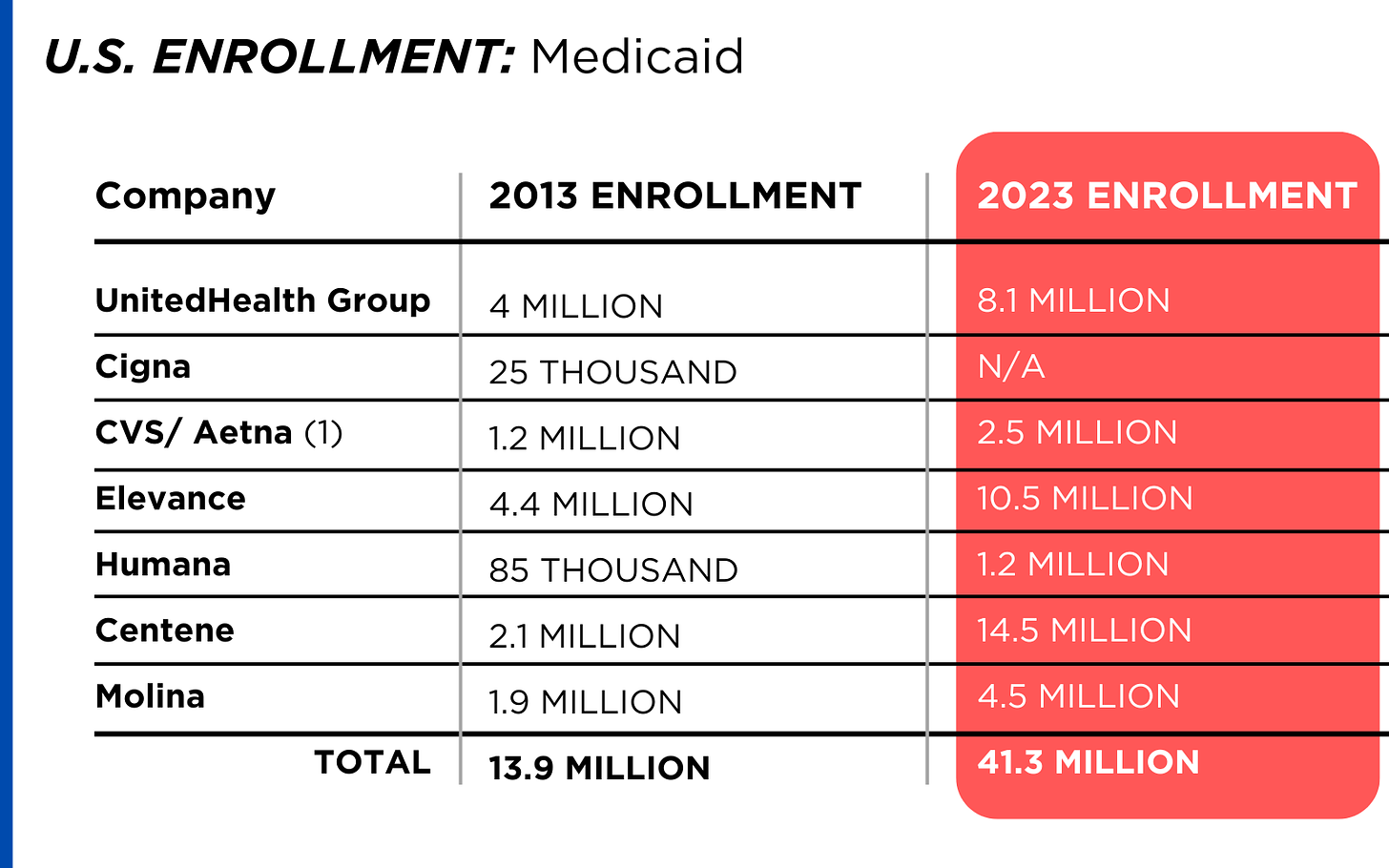
- Medicaid coverage determination
- Retail Health i.e. services (efficacy), truth in advertising, consumer safety et al
- Public health services i.e. STDs, disease surveillance, immunization policies et al.
- Prescription Drug Affordability (in 11 states)
- Health Insurance Marketplaces
- Healthcare workforce scope of practice
- Medical Malpractice and consumer protections
- Abortion Rights: as a result of the 2022 Supreme Court ruling that Roe v. Wade
- Behavioral health, substance abuse workforce adequacy, licensure, scope of practice et al.
- Certificate of Need Programs
- Use Medical Marijuana (Cannabis) for Therapeutics and/or Recreational Use.
- Health Insurer Licensing, Network adequacy and Liquidity
- Quality and patient safety inspection in post-acute & home-based settings.
- Workers’ compensation eligibility, administration use and funding.
- Formulary design and expense control.
- School clinics
- Prison health
- And others
The court decisions last week open the door to additional actions by state agencies and elected officials in areas where federal policies are in limbo:
- Tax exemptions for not-for-profit health systems
- Hospital consolidation and price transparency,
- Accessibility of hospital emergency services for abortion,
- Insurer prior authorization and network adequacy
- Minimum staffing requirements,
- Telehealth use and payment
- Restrictive drug formulary
- And more.
For every healthcare organization and trade group, vigilance about pending legislation/action at the state level will take on added importance.
- The U.S. health system’s future is not a repeat of its past: The week’s events lend to the health industry’s uncertain future. Today, strategic planning in most U.S. healthcare organizations i.e. insurers, hospitals, physician organization, device and drug manufacturers, et al is based on incremental changes forecast 3-5 years out. While consideration is given “transformational” changes 10-15 years out, it is under-studied by planners and rarely included on board agenda dockets. Yet, signal detection of disruptive shifts in financial services, higher education and other industries predict winners and losers. The U.S. system is change-averse because it benefits its self-interests. Outsiders do not share this view. No trade group or organization in healthcare can afford to bet its future on incrementalism in healthcare. These court decisions and the pending election results suggest that healthcare’s future is not a repeat of its past: new rules, new players and new critical success factors are inevitable.
It was a big week for U.S. politics and perhaps a bigger week for healthcare. Stay tuned.