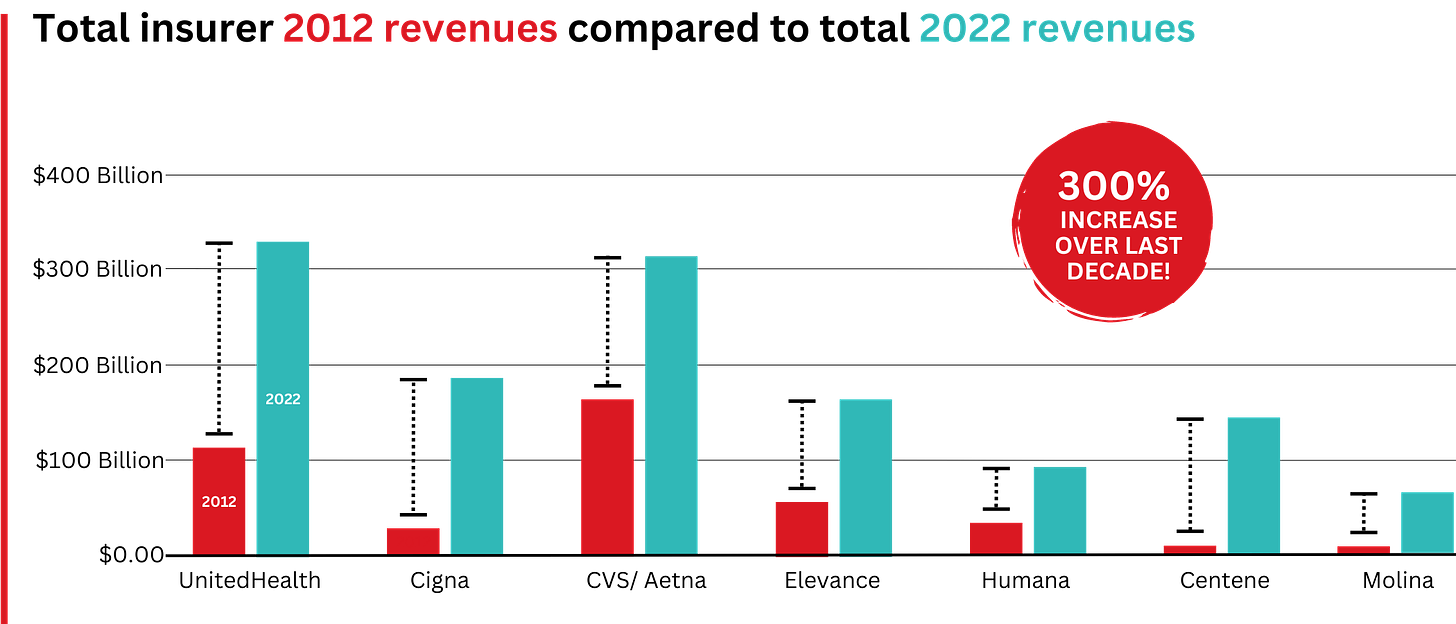
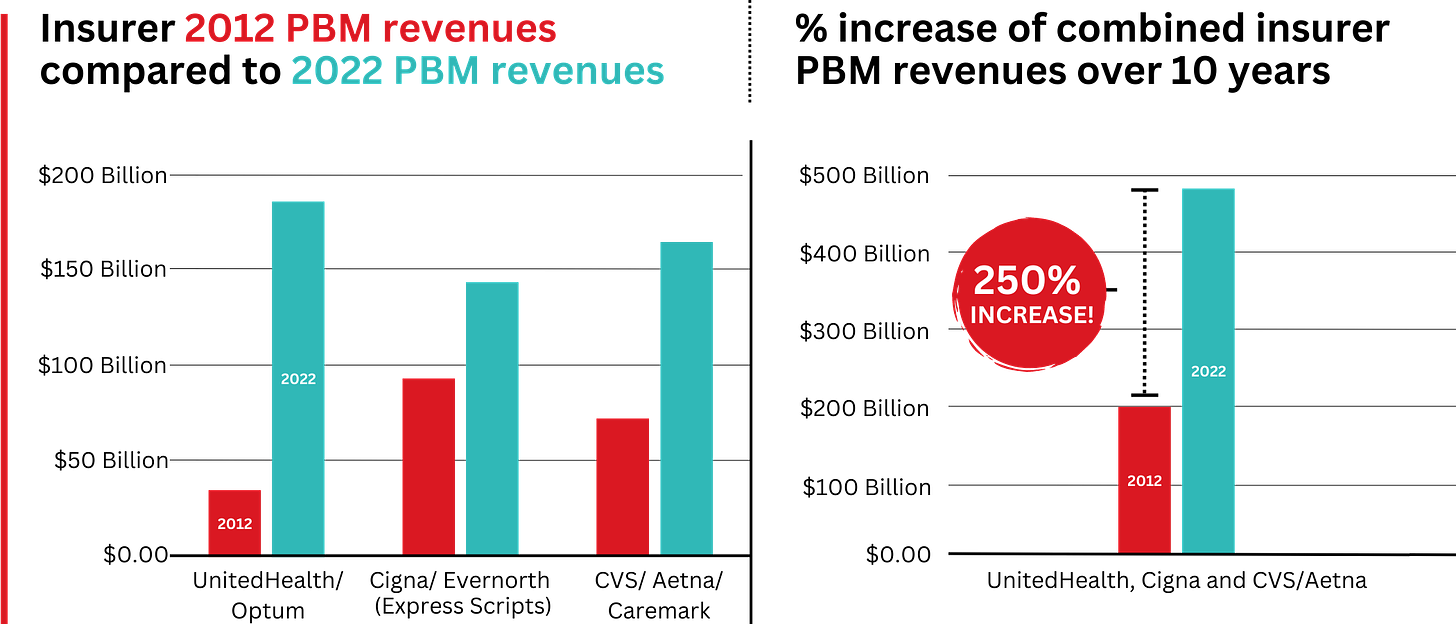
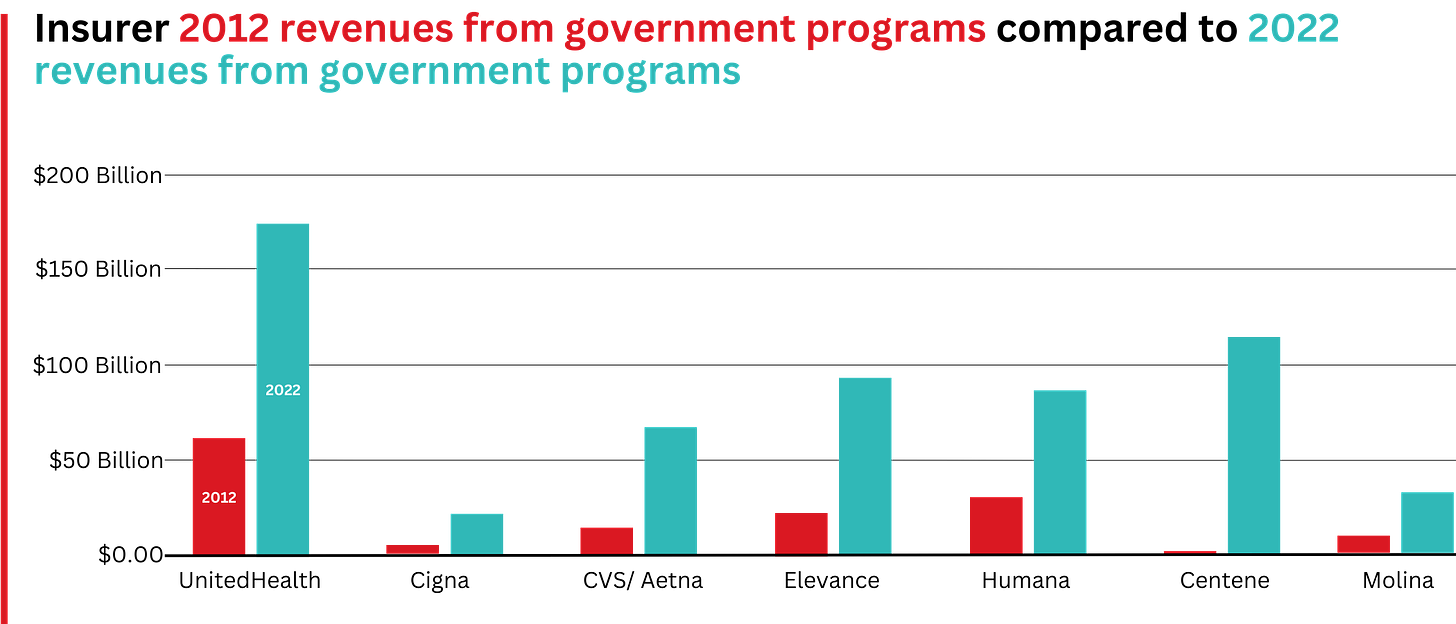
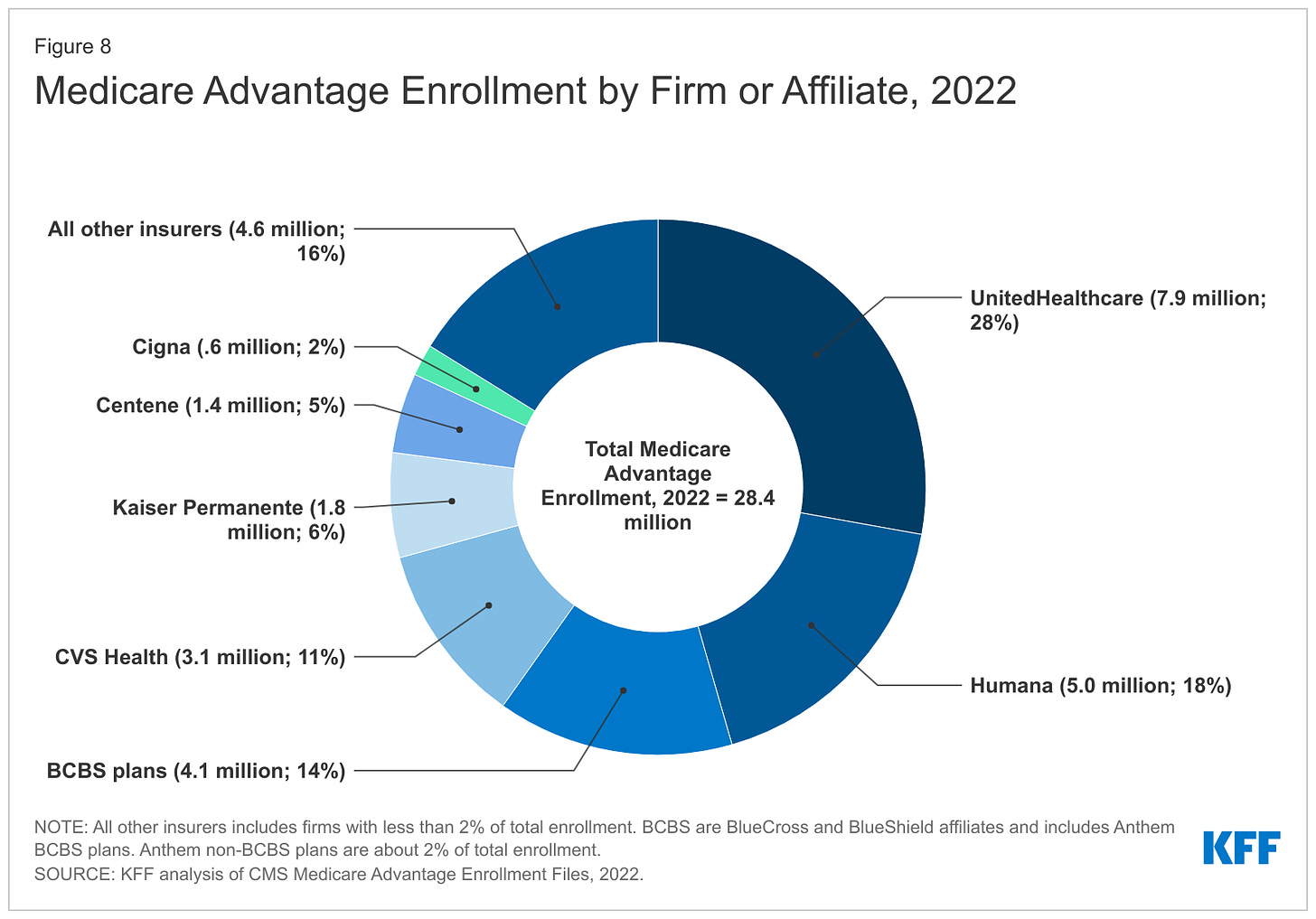
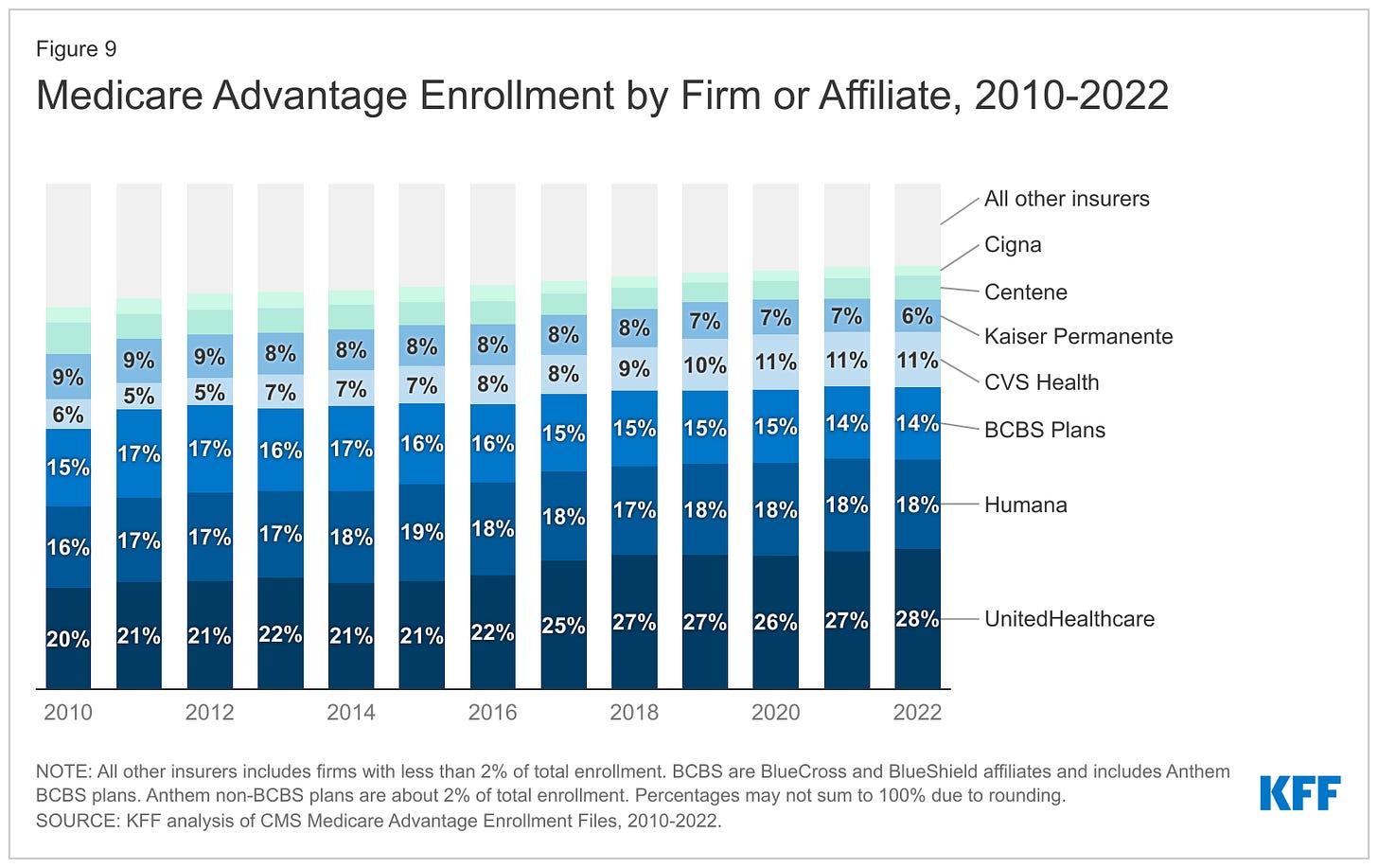
Elevance, which owns Blue Cross plans, is now reeling from Wall Street losses thanks to its Medicare Advantage business.
The company now known as Elevance, which owns Blue Cross plans in 14 states, took a drubbing on Wall Street yesterday after executives told shareholders that it had to pay out way more in medical claims during the second quarter than expected, especially in its Medicare Advantage business. As a reminder, Wall Street hates to hear such news, so much so that investors rushed to sell their shares in the company, sending the stock price to $296.39 – a 52-week low – before closing at $302.45 yesterday afternoon. That’s down 47% from the all-time high of $567.36 it reached last September.
The news was so distressing for people who still have investments in for-profit health insurers that many of them finally bailed, getting the message that the entire sector is likely not the best place to make money these days. All seven of the companies (Centene, Cigna, CVS/Aetna, Elevance, Humana, Molina and UnitedHealth) saw big drops in their stock price with two others (Centene and Molina) also falling to 52-week lows. The companies’ stock is continuing to tank today as I write this.
When Denial Becomes a Liability
UnitedHealth has historically been the first of the companies to release quarterly earnings, but it stepped back as leader of the pack this quarter after that giant’s recent troubles on Wall Street. UnitedHealth missed financial analysts’ profit expectations last quarter and withdrew its profit guidance for the year, an unprecedented move for that company, which terrified its shareholders. UnitedHealth’s stock price has lost nearly 55% of its value since reaching a high of $630.73 last November.
Like UnitedHealth, Elevance had been a Wall Street darling until a business practice common in the health insurance game – refusing to pay for patients’ medically necessary care – finally caught up with it.
I’m talking about prior authorization, the benign sounding term that covers a number of ways a health insurer banks money by saying no to a doctor’s plea to cover a patient’s treatment or medications. The fundamental problem is that by refusing to pay for care a patient needs, that patient likely will get sicker and wind up needing even more expensive care down the road. Insurance company beancounters know that can happen, but they also know there is a decent chance that that potentially high-cost patients will not even be enrolled in one of the company’s health plans when the day finally arrives that they have to go to the hospital, which, of course, might have been avoided if the initial treatment had been approved in the first place.
We’re not just talking about a stay in the hospital. One permutation of prior auth is called step therapy in which an insurer demands that a patient try other medications on the insurer’s list of preferred drugs (its “formulary”) before approving the drug a doctor believes will work best. Sometimes it’s called “fail first.” In other words, a patient must endure pain and suffering for weeks or months taking an ineffective drug on an insurer’s formulary – the price of which the insurer has negotiated to its financial advantage with a drug maker – before the insurer will agree to cover the medication the doctor believes will be more effective. The doctor will then have to persuade the insurer that the insurer’s preferred drug failed. We’ll dive deeper into that insurer-induced nightmare in a future post, but know for now that it is a big and expensive time-suck that doctors have to endure while insurers can keep unused premium dollars in their investment accounts.
The Conversion That Changed Everything
But let’s go back to Elevance, which until recently was called Anthem and before that WellPoint. Many of its subsidiaries still use the term Anthem in its branding, like the biggest under its corporate umbrella, Anthem Blue Cross of California. All of those Blues plans operated on a nonprofit basis until a savvy executive named Leonard Schaeffer, who was CEO of Anthem of California back when it was still a nonprofit, pulled off a deal that would put him on the path to considerable fame and fortune, a first-of-its-kind “conversion” that would prove to be a major reason why the U.S. has the most complex, expensive and inefficient health care system on the planet.
According to his official bio on the website of the Leonard D. Schaffer Fellows in Government Service, which is affiliated with some of the country’s most prestigious universities, Schaeffer was recruited as CEO of Blue Cross of California in 1986 when, we are told, it was near bankruptcy. We’re also told that Schaeffer “managed the turnaround of Blue Cross of California and the IPO (initial public offering, i.e., converting it to for-profit status) creating WellPoint in 1993. During his tenure, WellPoint made 17 acquisitions and endowed four charitable foundations with assets of over $6 billion. Under Schaeffer’s leadership, WellPoint’s value grew from $11 million to over $49 billion.”
One might think from reading that last sentence that Schaeffer himself wrote big personal checks to endow those foundations, but establishing those nonprofit foundations (which includes the California Endowment, the California Health Care Foundation and the California Wellness Foundation) was demanded by California regulators as a condition of their approval of the IPO. The money was referred to as a conversion fund (converting from nonprofit to for-profit status), and it came from the proceeds of the IPO.
But Schaffer did indeed make a ton of money from the deal and WellPoint’s subsequent acquisition by a rival company that also owned recently converted Blues plans, Anthem, in 2004.
One of the organizations that opposed the WellPoint-Anthem deal, Consumer Watchdog, wrote at the time that:
Payments to WellPoint executives after the company’s buyout by Anthem Inc. could top $600 million if regulators and shareholders do not modify the acquisition terms, according to documents received from California regulators by the Foundation for Taxpayer and Consumer rights under a Public Records Act Request late Tuesday.
The documents detail potential payments in excess of those estimated by the company to shareholders at $200 million in a recent proxy. Executives will receive cash bonuses worth between $146 million and $365 million under the proposed terms of the company buyout by Anthem, in addition to over $251 million in stock options. WellPoint CEO Leonard Schaeffer has already begun exercising his stock options as of June 1st at sweetheart prices – earning him $16 million on that one day alone and increasing the size of his shares by hundreds of thousands.
When we look back at the history of health insurance in this country, we can thank this one man for the rapid shifting of Americans out of what historically had been nonprofit health insurance plans that initially were community-rated, meaning they charged everybody the same premium, regardless of gender, health status, occupation or address, and did not use gimmicks like prior authorization to boost profits. Being nonprofits, they couldn’t even book profits, although many of them did amass millions more in “reserves” than regulators required for solvency reasons.
I was working at Cigna when WellPoint joined the club of big for-profit insurers in 1993, along with Aetna, Humana (where I also previously worked), UnitedHealth, which was a relatively small player back then, and giant “multiline” insurers like MetLife, Prudential and Travelers. All of those last three decided to sell their health insurance operations to UnitedHealth and Aetna, putting those companies on the path to becoming the behemoths they are today.
And Schaeffer would wind up being one of America’s richest men, and, to his credit, he has been personally philanthropic. We know that because his name shows up all over the place in U.S. health care think-tank world. Indeed, his name is now associated far more with groups and institutions engaged in public policy than the “platinum parachute,” to use Consumer Watchdog’s term, he got when he and a few colleagues engineered the sale of WellPoint to Anthem. As his bio notes:
In 2009, Schaeffer established the Schaeffer Center for Health Policy and Economics at the University of Southern California, which emphasizes the interdisciplinary approach to research and analysis to support evidence-based health policy. In 2015, he established the Schaeffer Fellows in Government Service program which has supported 418 undergraduates to date in high-level, summer government internships. In 2004, he established the Schaeffer Institute for Public Policy & Government Service. He has also endowed chairs in health care financing and policy at the Brookings Institution, Harvard Medical School, the National Academy of Medicine, UC Berkeley and USC.
If Schaeffer still owns shares in Elevance, he is a bit poorer today than he was yesterday morning, but he’s probably still doing OK. Shares of Elevance’s stock have increased 1731% in value since they started trading on the New York Stock Exchange in October 2001, even with the company’s very bad Thursday on the Street.