https://www.healthcaredive.com/news/presidential-election-2020-trump-biden-different-healthcare-policies-ACA-coronavirus/585184/?utm_source=Sailthru&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=Issue:%202020-10-01%20Healthcare%20Dive%20%5Bissue:29992%5D&utm_term=Healthcare%20Dive

Spoiler: the 2 nominees differ on almost everything.
President Donald Trump and Democrat nominee Joe Biden’s starkly contrasting views on healthcare were laid bare during this week’s chaotic debate. But some major industry executives noted at a recent conference they’ve done relatively well under Trump and could likely weather a Biden presidency, given his moderate stance and rejection of liberal dreams of “Medicare for All.”
The former vice president stresses incremental measures to shore up President Barack Obama’s landmark Affordable Care Act. Trump’s campaign website has no list of healthcare priorities, making his record even more relevant to attempts to forecast his future policies.
“I think a lot of the president’s second term agenda will be extensions of things he’s done in his first term,” Lanhee Chen, domestic policy director at Stanford University’s Public Policy program, said at AHIP in September.
Either way, the impact of whoever lands in the White House next year still matters for the industry’s future.
And 33 seats in the Senate are also up for grabs in November, complicating the outlook. Two scenarios would likely lead to health policy gridlock, according to analysts and DC experts: Trump wins regardless of Senate outcome, or Biden wins and Republicans maintain control of the Senate. A third scenario, where Biden wins and Democrats retake the Senate, would be the most negative for healthcare stocks, Jefferies analysts say, while the other two outcomes would be a net positive or mostly neutral.
Here’s a look at where the candidates stand on the biggest healthcare issues: the coronavirus pandemic, the Affordable Care Act, changes to Medicare and Medicaid and lowering skyrocketing healthcare costs.
COVID-19 response
Trump
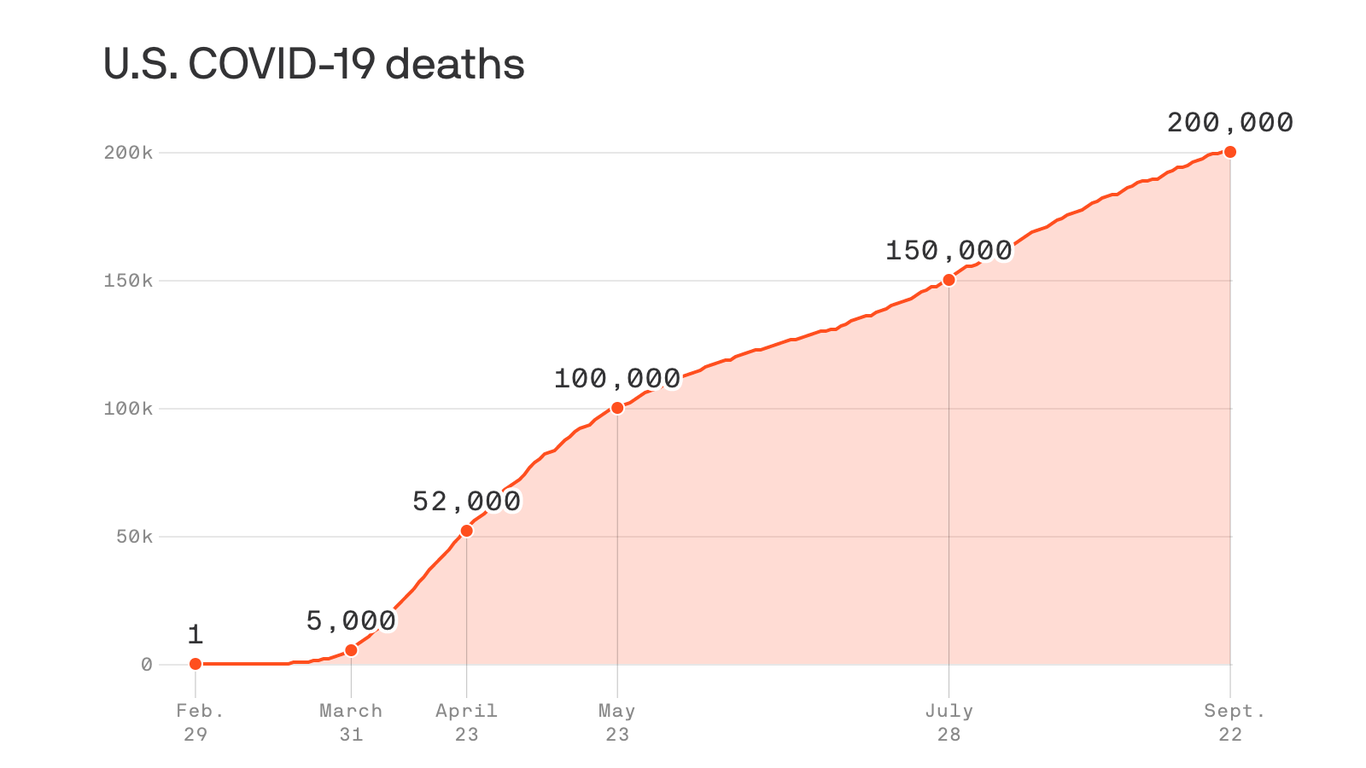
Of all wealthy nations, the U.S. has been particularly unsuccessful in mitigating the pandemic. The U.S. makes up 4% of the global population, but accounted for 23% of all COVID-19 cases and 21% of all deaths as of early September.
Public health experts assign the majority of the blame to an uncoordinated federal response, with the president electing to take a largely hands-off approach to the virus that’s killed nearly 207,000 people in the U.S. to date. That backseat stance is unlikely to change if Trump is elected to a second term.
In March, Trump said a final COVID-19 death toll in the range of 100,000 to 200,000 Americans would mean he’s “done a very good job.”
Critics blame shortages of supplies like test materials, personal protective equipment and ventilators, especially in the crucial early days of the pandemic, on Trump’s approach. States and healthcare companies have also reported challenges with shifting federal guidelines on topics from risk of infection to hospital requirements for reporting COVID-19 caseloads.
Trump has also pushed unproven treatments for COVID-19, giving rise to concerns about political influence on traditionally nonpartisan agencies like the Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
These concerns have colored Operation Warp Speed, the administration’s public-private partnership to fast-track viable vaccines. The operation received $10 billion in funds from Congress, but administration officials have also pulled $700 million from the CDC, even as top health officials face accusations of trying to manipulate CDC scientific research publications.
Fears that political motivations, not clinical rigor, are driving the historically speedy timeline could lower public trust in a vaccine once it’s eventually approved.
Trump has also repeatedly refused to endorse basic protections like widespread mask wearing, often eschewing the face covering himself in public appearances. He’s consistently downplayed the severity of the pandemic, saying it’ll go away on its own while suggesting falsely that rising COVID-19 cases were solely due to increased testing.
While Trump’s list of priorities for his second term include “eradicating COVID-19,” the plan is short on details. His most aggressive promise has been approval of a vaccine by the end of this year and creating all “critical medicines and supplies for healthcare workers” for a planned return to normal in 2021, along with refilling stockpiles to prepare for future pandemics.
Biden
Biden, for his part, would likely work to enact COVID-19 legislation and dramatically change the role of the federal government in pandemic response first thing if elected.
The Democratic candidate says he would re-assume primary responsibility for the pandemic. He plans to “dramatically scale up testing” and “giving states and local governments the resources they need to open schools and businesses safely,” per an August speech in Wilmington, Delaware.
Biden says he’d take a backseat to scientists and allow FDA to unilaterally make decisions on emergency authorizations and approvals.
The candidate supports reopening an ACA enrollment period for the uninsured, eliminating out-of-pocket costs for COVID-19 treatment, enacting additional pay and protective equipment for essential workers, increasing the federal match rate for Medicaid by at least 10%, covering COBRA with 100% premium subsidies during the emergency, expanding unemployment insurance and sick leave, reimbursing employers for sick leave and giving them tax credits for COVID-19 healthcare costs.
Trump opposes most of these measures, though he did sign COVID-19 relief legislation that upped the Medicaid match rate by 6.2% and extended the COBRA election period, though without subsidies.
Biden has said he’d be willing to use executive power for a national mask mandate, though ensuring compliance would be difficult. He’d also rejoin the World Health Organization, which Trump pulled the U.S. out of in May.
Affordable Care Act
Trump
On his first day in office, Trump issued an executive order saying: “It is the policy of my Administration to seek the prompt repeal of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act.” But after the Republican repeal-and-replace effort floundered in 2017, the administration began steadily chipping away at key tenets of the decade-old law through regulatory avenues.
Trump has maintained he’ll protect the 150 million people with preexisting conditions in the U.S. But despite publicly promising a comprehensive replacement plan on the 2015 campaign trail (and at least five times this year alone), Trump has yet to make one public. The president did in September sign a largely symbolic executive order that it’s the stance of his administration to protect patients with preexisting conditions.
The president doesn’t mention the ACA in his list of second term priorities. The omission could have been intentional, as Trump is backing a Republican state-led lawsuit seeking to overturn the sweeping law, now pending in front of the U.S. Supreme Court and scheduled for oral arguments one week after the election.
The death of liberal justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg puts the law in an even more precarious position.
And Trump’s health agencies have enacted myriad policies keeping the law from functioning as designed.
The president signed legislation zeroing out the individual mandate penalty requiring people to be insured in 2017. The same year, he ended cost-sharing reduction payments to insurers, suggesting that would cause the ACA to become “dead.” But the marketplace generally stabilized.
The administration has also increased access to skimpier but cheaper coverage that doesn’t have to comply with the 10 essential health benefits under the ACA. The short-term insurance plans widely discriminate against people with pre-existing health conditions, even as a growing number of Americans, facing rising healthcare costs, enrolled, according to a probe conducted by House Democrats this year.
Trump has also encouraged state waivers that promote non-ACA plans, cut funding for consumer enrollment assistance and outreach, shortened the open enrollment period and limited mid-year special enrollments.
Despite his efforts, the ACA has grown in popularity among voters on both sides of the aisle, mostly due to provisions like shoring up pre-existing conditions and allowing young adults to stay on their parent’s insurance until age 26.
Biden
If elected, Biden would likely roll back Trump-era policies that allowed short-term insurance to proliferate, and restore funding for consumer outreach and assistance, political consultants say.
Building on the law is the linchpin of Biden’s healthcare plan. The nominee has pledged to increase marketplace subsidies to help more people afford ACA plans through a number of policy tweaks, including lowering the share of income subsidized households pay for their coverage; determining subsidies by setting the benchmark plan at the pricier “gold” level; and removing the current cap limiting subsidies to people making 400% of the federal poverty level or below.
Biden maintains as a result of these changes, no Americans would have to pay more than 8.5% of their annual income toward premiums. They could save millions of people hundreds of dollars a month, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation analysis. Commercial payers mostly support these efforts, hoping they’ll stabilize the exchanges.
But a second prong of Biden’s health strategy is deeply unpopular with private insurers: the public option. Biden’s called for a Medicare-like alternative to commercial coverage, available to anyone, including people who can’t afford private coverage or those living in a state that hasn’t expanded Medicaid.
The rationale of the public plan is that it can directly negotiate prices with hospitals and other providers, lowering costs across the board. However, market clout will depend on enrollment, which is still to-be-determined.
Critics see the plan, which by Biden’s estimate would cost $750 billion over 10 years, as a down payment on Medicare for All. And the private sector worries it could threaten the very profitable healthcare industry, which makes up about a fifth of the U.S. economy.
Medicare
Trump
Neither Trump nor Biden supports Medicare for All, dashing the hopes of supporters of the sweeping insurance scheme for at least another four years.
“It has a pulse — it’s not dead — I just don’t see it happening in any near term,” John Cipriani, vice president at public affairs firm Global Strategy Group, said at AHIP.
Trump has promised to protect Medicare if elected to a second term, and it’s unlikely he’d make any major changes to the program’s structure or eligibility requirements, experts say.
But Medicare is quickly running out of money, and neither Trump nor Biden has issued a complete plan to ensure it survives beyond 2024. Political consultants think it’ll teeter right up to the edge of insolvency before lawmakers feel compelled to act.
The president’s administration has allowed Medicare to pay for telehealth and expanding supplemental benefits in privately run Medicare Advantage programs, efforts that would likely bleed into his second term — or Biden’s first, given general bipartisan support on both, experts say.
Under Trump, HHS did pass a site-neutral payment policy, cutting Medicare payments for hospital outpatient visits in a bid to save money. But Democratic lawmakers have argued Trump’s calls to get rid of the federal payroll tax, which partially funds Medicare, could throw the future of the cash-strapped program in jeopardy.
The president has also signed legislation experts say accelerated insolvency, including the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 and the Further Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2020, which repealed the ACA’s Cadillac tax — a tax on job-based insurance premiums above a certain level.
Nixing that tax lowered payroll tax revenue, also dinging Medicare’s shrinking trust fund.
Trump’s proposed budget for the 2021 fiscal year floated culling about $450 billion in Medicare spending over a decade. And repealing the ACA would also nix provisions that closed the Medicare prescription drug “donut hole,” that added free coverage of preventive services and reduced spending to strengthen Medicare’s winnowing Hospital Insurance Trust Fund.
Biden
Biden has proposed lowering the Medicare age of eligibility to 60 years, with the option for people aged 60-64 to keep their coverage if they like it. The idea is popular politically, though providers oppose it, fearful of losing more lucrative commercial revenue.
It would make about 20 million more people eligible for the insurance, but could also add even more stress onto the program, experts say. Biden’s campaign says it would be financed separately from the current Medicare program, with dollars from regular tax revenues, and will reduce hospital costs.
Biden also says he’d add hearing, vision and dental benefits to Medicare.
Medicaid
Trump
Trump’s tenure has also been defined by repeated efforts to prune Medicaid. The president has consistently backed major cuts to the safety net insurance program, along with stricter rules for who can receive coverage. That’s likely to continue.
Republican lawmakers maintain the program costs too much and discourages low-income Americans from getting job-based coverage, and have enacted policies trying to privatize Medicaid. The Trump administration took a step toward a long-held conservative dream earlier this year, when CMS invited state waivers that would allow states to deviate from federal standards in program design and oversight, in exchange for capped funding.
So far, no states have enacted the block grants.
The administration also aggressively encouraged states to adopt work requirements, programs tying Medicaid coverage to work or volunteering hours. A handful of states followed suit, but all halted implementation or rolled back the idea following fierce public backlash and legal ramifications.
And repealing the ACA would ax Medicaid expansion, which saved some 20,000 lives between 2014 and 2017, according to the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Biden
Biden, however, wants to preserve expansion, and would take a number of other steps to bolster the program, including increasing federal Medicaid funding for home- and community-based services. The roughly 4.8 million adults in states that elected not to expand Medicaid would be automatically enrolled into his public option, with no premium and full Medicaid benefits.
Additionally, states that have expanded Medicaid could elect to move their enrollees into the public option, with a maintenance-of-effort payment.
Lowering costs of drugs and services
Trump
Efforts to lower prescription drug costs have defined Trump’s healthcare agenda in his first term, and been a major talking point for the president. That’s more than likely to continue into a second term, experts say, despite a lack of results.
Trump did cap insulin costs for some Medicare enrollees, effective 2021. He also signed legislation in 2018 banning gag clauses preventing pharmacists from telling customers about cheaper options.
But despite fiery rhetoric and a litany of executive orders, Trump has made little if any concrete progress on actually lowering prices. One week into 2020, drugmakers had announced price hikes for almost 450 drugs, despite small price drops earlier in Trump’s tenure.
Trump has proposed several ideas either dropped later or challenged successfully by drugmakers in court, including allowing patients to import drugs from countries like Canada, banning rebates paid to pharmacy benefit manufacturers in Medicare and forcing drugmakers to disclose the list prices of drugs in TV ads.
The president has signed recent executive orders to lower costs largely viewed as pre-election gambits, including one tying drug prices in Medicare to other developed nations and another directing his agencies to end surprise billing. Implementation on both is months away. Trump has also promised to send Medicare beneficiaries $200 in drug discount cards before the election, an effort slammed as vote-buying that would cost Medicare at least $6.6 billion.
Both Trump and Biden support eliminating surprise bills but haven’t provided any details how. That “how” is important, as hospitals and payers support wildly different solutions.
Biden
Biden also has a long list of proposals to curb drug costs, including allowing the federal government to negotiate directly with drug manufacturers on behalf of Medicare and some other public and private purchasers, with prices capped at the level paid by other wealthy countries. Trump actually supported this proposal in his 2016 campaign, but quickly dropped it amid fierce opposition from drugmakers and free market Republican allies.
Biden would also cap out-of-pocket drug costs in Medicare Part D — but wouldn’t ban rebates, as of his current plan, allow consumers to import drugs (subject to safeguards) and eliminate tax breaks for drug advertising expenses.
He would also prohibit prices for all brand-name and some generic drugs from rising faster than inflation under Medicare and his novel public option. Biden would create a board to assess the value of new drugs and recommend a market-based price, in a model that’s shown some efficacy in other wealthy countries like Germany.
Both Biden and Trump say they support developing alternative payment models to lower costs. But they diverge on the role of competition versus transparency in making healthcare more affordable. In a rule currently being challenged in court, Trump’s HHS required hospitals to disclose private negotiated prices between hospitals and insurers, with the hope price transparency will allow consumers to shop between different care sites and shame companies into lowering their prices.
Biden, by comparison, says he would enforce antitrust laws to prevent anti-competitive healthcare consolidations, and other business practices that jack up spending. Trump has been mum on the role of M&A in driving healthcare costs, and inherited a complacent Federal Trade Commission that’s done little to reduce provider consolidation. Until a contentious hospital merger in February this year, the FTC hadn’t opposed a hospital merger since 2016.