
Cartoon – Doctors without borders, meet patient without insurance



A complete financial recovery for many organizations is still far away, findings from Kaufman Hall indicate.
For the past three years, Kaufman Hall has released annual healthcare performance reports illustrating how hospitals and health systems are managing, both financially and operationally.
This year, however, with the pandemic altering the industry so broadly, the report took a different approach: to see how COVID-19 impacted hospitals and health systems across the country. The report’s findings deal with finances, patient volumes and recovery.
The report includes survey answers from respondents almost entirely (96%) from hospitals or health systems. Most of the respondents were in executive leadership (55%) or financial roles (39%). Survey responses were collected in August 2020.
FINANCIAL IMPACT
Findings from the report indicate that a complete financial recovery for many organizations is still far away. Almost three-quarters of the respondents said they were either moderately or extremely concerned about their organization’s financial viability in 2021 without an effective vaccine or treatment.
Looking back on the operating margins for the second quarter of the year, 33% of respondents saw their operating margins decline by more than 100% compared to the same time last year.
Revenue cycles have taken a hit from COVID-19, according to the report. Survey respondents said they are seeing increases in bad debt and uncompensated care (48%), higher percentages of uninsured or self-pay patients (44%), more Medicaid patients (41%) and lower percentages of commercially insured patients (38%).
Organizations also noted that increases in expenses, especially for personal protective equipment and labor, have impacted their finances. For 22% of respondents, their expenses increased by more than 50%.
IMPACT ON PATIENT VOLUMES
Although volumes did increase over the summer, most of the improvement occurred in areas where it is difficult to delay care, such as oncology and cardiology. For example, oncology was the only field where more than half of respondents (60%) saw their volumes recover to more than 90% of pre-pandemic levels.
More than 40% of respondents said that cardiology volumes are operating at more than 90% of pre-pandemic levels. Only 37% of respondents can say the same for orthopedics, neurology and radiology, and 22% for pediatrics.
Emergency department usage is also down as a result of the pandemic, according to the report. The respondents expect that this trend will persist beyond COVID-19 and that systems may need to reshape their business model to account for a drop in emergency department utilization.
Most respondents also said they expect to see overall volumes remain low through the summer of 2021, with some planning for suppressed volumes for the next three years.
RECOVERY MEASURES
Hospitals and health systems have taken a number of approaches to reduce costs and mitigate future revenue declines. The most common practices implemented are supply reprocessing, furloughs and salary reductions, according to the report.
Executives are considering other tactics such as restructuring physician contracts, making permanent labor reductions, changing employee health plan benefits and retirement plan contributions, or merging with another health system as additional cost reduction measures.
THE LARGER TREND
Kaufman Hall has been documenting the impact of COVID-19 hospitals since the beginning of the pandemic. In its July report, hospital operating margins were down 96% since the start of the year.
As a result of these losses, hospitals, health systems and advocacy groups continue to push Congress to deliver another round of relief measures.
Earlier this month, the House passed a $2.2 trillion stimulus bill called the HEROES Act, 2.0. The bill has yet to pass the Senate, and the chances of that happening are slim, with Republicans in favor of a much smaller, $500 billion package. Nothing is expected to happen prior to the presidential election.
The Department of Health and Human Services also recently announced the third phase of general distribution for the Provider Relief Fund. Applications are currently open and will close on Friday, November 6.
https://mailchi.mp/burroughshealthcare/april-16-3240709?e=7d3f834d2f
Less than three months from now, either Donald Trump will begin his second term as President, or Joe Biden will begin his first. What the U.S. healthcare system on that date and moving forward could be starkly different depending on who is sworn in.
The policy differences between the two men are essentially on opposite poles. If fully enacted, Trump’s policies could potentially cause tens of millions of Americans to lose their healthcare coverage. Biden’s policies would likely provide healthcare access to tens of millions more Americans compared to today.
In November, the U.S. Supreme Court will hear arguments in a case called California v. Texas. It stems from the 2017 tax bill that zeroed out the penalty individuals paid if they did not obtain health insurance. The argument put forth by the 20 Republican state attorney generals in that case is if the individual mandate no longer has taxing power, the entire law should be declared unconstitutional based upon a lack of severability of the entire law.
Many legal scholars have noted that this case is premised on a shaky argument. But with a 6-3 majority of conservative justices now on the high court, many bets are off as to the ACA’s survival. And President Trump just said in an interview with “60 Minutes” he fervently hoped the ACA is eliminated. He put forth no alternatives to the ACA in that interview.
Should the ACA be declared unconstitutional, health insurance for some 23 million people would be imperiled. That includes some 12 million Americans who are eligible for Medicaid under the ACA’s expanded income guidelines, and another 11 million who purchase insurance on the state and federal health insurance exchanges – roughly 85% of whom receive premium subsidies that make it more affordable. Moreover, another 14 million Americans who are estimated to have lost their employer-based health plans during the COVID-19 pandemic may not have another place to turn for coverage.
Before the ACA case, the Trump administration also promoted so-called “off-exchange” health plans, and health sharing ministries. The first is often a form of short-term health insurance, the second operates as a cooperative serving those of the same religious stripe. Both offer health coverage that is potentially cheaper that what is offered on the exchanges, but both also tend to cap it at low dollar levels. Many also bar applicants for a variety of claims, such as for maternity or cancer care, or if they have pre-existing medical conditions – practices prohibited for ACA plans.
Should Trump be re-elected and the ACA survives constitutional muster, expect to see many states apply for more waivers from that law. Georgia just received approval to modestly expand Medicaid eligibility, primarily for those poor already working 80 hours or more a month. The state is also on the cusp of being able to opt out of the healthcare.gov exchange entirely and have consumers work directly with insurance brokers to purchase coverage. However, there is nothing in the pending waiver to prevent those brokers from offering stripped-down coverage without the ACA protections that the Trump administration is already promoting.
There could also be more block grants to states for their Medicaid budgets, which most experts have concluded would reduce the number of enrollees in that program.
If Biden is elected and both incoming houses of Congress are also Democratic, the entire Supreme Court case can be mooted simply by reattaching a financial penalty to the individual mandate. That hasn’t been mentioned at all during the campaign, presumably because Biden does not want to discuss what would essentially be a promise to raise taxes. But it is the most direct way to skirt the risk of an adverse Supreme Court decision.
Biden’s campaign has also put forth numerous proposals to enlarge the ACA and the Medicare program. They include expanded premium subsidies for individuals and families to purchase coverage, and a public health plan option – which would allow those who live in the states that have yet to expand Medicaid to obtain coverage. Biden has also proposed a buy-in to Medicare at age 60.
The estimates are that an expanded ACA and other Biden plans could net another 20 to 25 million Americans healthcare coverage. That would leave fewer than 10 million – 2% to 3% of the population – without access to coverage. It would probably be as close to universal healthcare as the United States could get given its current political realities.
The two different approaches will either lead to a country where virtually everyone has access to healthcare coverage and services, or one where 50 million or more people could potentially be uninsured. It’s a shift that could impact a minimum of 45 million people – and that’s not even counting those who lost their coverage during the current public health crisis.
Elections have consequences. Less than three months from now, this one will determine whether the U.S. healthcare system will take one consequential path over another.

https://mailchi.mp/f2794551febb/the-weekly-gist-october-23-2020?e=d1e747d2d8

The upcoming election has huge implications for healthcare, far beyond how COVID is managed, ranging from how care is covered to how it’s delivered. The graphic above shows a continuum of potential policy outcomes of the November 3rd vote.
If President Trump wins a second term and Republicans control at least one house of Congress, there will likely be more attempts to dismantle the ACA, as well as continued privatization of Medicare coverage.
If Democrats win the presidency and sweep Congress, actions to expand the Affordable Care Act (ACA), or even create a national public option, are on the table—although major healthcare reform seems unlikely to occur until the second half of a Biden term.
In the short term, we’d expect to see more policy activity in areas of bipartisan agreement, like improving price transparency, ending surprise billing and lowering the cost of prescription drugs, regardless of who lands in the White House.
While healthcare emerged as the most important issue for voters in the 2018 midterm elections, the COVID pandemic has overshadowed the broader healthcare reform platforms of both Presidential candidates heading into the election. As shown in the gray box, many Americans view the election as a referendum on the Trump administration’s COVID response. Managing the pandemic is one of the most important issues for voters, especially Democrats, who now rank the issue above reducing the cost of healthcare or lowering the cost of drugs.
In many aspects, the COVID policies of Biden and Trump are almost diametrically opposed, especially concerning the role of the federal government in organizing the nation’s pandemic response.
The next administration’s actions to prevent future COVID-19 surges, ensure safe a return to work and school, accelerate therapies, and coordinate vaccine delivery will remain the most important aspect of healthcare policy well into 2021.
https://mailchi.mp/f2794551febb/the-weekly-gist-october-23-2020?e=d1e747d2d8
This week Nebraska became the latest state to receive waiver authority from the Trump administration to implement work requirements as part of its Medicaid expansion program.
The program, called “Heritage Health Adult”, will be a two-tiered system, with expansion-eligible adults choosing between “Basic” and “Prime” coverage levels. The lower tier will provide coverage for physical and behavioral health services, with a prescription drug benefit, and is open to adults not eligible for traditional Medicaid with incomes under 138 percent of the federal poverty line.
“Prime” enrollees will get additional dental, vision, and over-the-counter drug benefits, in exchange for agreeing to 80 hours per month of work, volunteering, or active job seeking, which must be reported to the state.
Nebraska voters approved the Medicaid expansion two years ago, although enrollment only began this August, and the work-linked demonstration project is slated to start next year. An estimated 90,000 additional Nebraskans are expected to enroll in Medicaid under the expanded program.
The approval of Nebraska’s Medicaid work requirement comes a week after the Trump administration approved a partial expansion of Medicaid in Georgia, called “Pathways to Coverage”, which is also tied to a requirement to seek or engage in employment or education activities.
The Georgia program also requires premium payments by eligible adults who make between 50 and 100 percent of the federal poverty line. Court challenges will inevitably ensue for both the Nebraska and Georgia programs—only Utah has successfully implemented Medicaid work requirements, with 16 other state programs either pending approval, held up in court, or awaiting implementation. We continue to be deeply skeptical of Medicaid work requirements, and believe they only serve to deter those who would otherwise qualify for coverage from enrolling, and that the expense of their implementation and ongoing operation often outweighs any savings to the state.
The argument that “work encourages health”, often advanced by proponents of work requirements, gets it exactly backwards—rather, health security encourages work, a reality that has become ever more urgent as the COVID pandemic has drawn on.
As the economy continues to falter, Medicaid’s importance as a safety net program grows ever greater, and work requirements create an unhelpful obstacle to basic healthcare access.
https://www.axios.com/trump-biden-debate-coronavirus-14b6e962-e968-4547-933d-6d7105df24b9.html

President Trump repeated baseless claims at the final presidential debate that the coronavirus “will go away” and that the U.S. is “rounding the turn,” while Joe Biden argued that any president that has allowed 220,000 Americans to die on his watch should not be re-elected.
Why it matters: The U.S. is now averaging about 59,000 new coronavirus infections a day, and added another 73,000 cases on Thursday, according to the Covid Tracking Project. The country recorded 1,038 deaths due to the virus Thursday, the highest since late September.
What they’re saying: “More and more people are getting better,” Trump said. We have a problem that’s a worldwide problem. This is a worldwide problem. But I’ve been congratulated by the heads of many countries on what we’ve been able to do … It will go away and as I say, we’re rounding the turn. We’re rounding the corner. It’s going away.”
Biden responded: “Anyone responsible for that many deaths should not remain as president of the United States of America.”
The bottom line: Biden and Trump are living in two different pandemic realities, but Biden’s is the only one supported by health experts.
Go deeper: The pandemic is getting worse again
https://www.commonwealthfund.org/blog/2020/health-care-2020-presidential-election-whats-stake
As the presidential election draws near, we reflect on the meaningful differences in health policy priorities and platforms between the two candidates, which we’ve described more fully in our recent blog series.
While similarities exist in some areas — most notably prescription drug pricing and proposals to control health care costs — the most striking differences between the positions taken by President Donald Trump and those of former Vice President Joe Biden are on safeguarding access to affordable health care coverage, advancing health equity for those who have been historically disadvantaged by the current system, and managing the novel coronavirus pandemic.
The importance of maintaining or expanding access to affordable health care in the midst of a pandemic cannot be understated. Going into the crisis, 30 million Americans lacked health coverage, with many more potentially at risk as a result of the current economic downturn. And even for many with coverage, costs are a barrier to receiving care. Moreover, despite efforts by Congress and the Trump administration to ease the financial burden of COVID-19 testing and treatment, many people remain concerned about costs; examples of charges for COVID-related medical expenses are not uncommon.
In this context, President Trump’s efforts to repeal the Affordable Care Act (ACA) is the most important signal of his position on health care. The administration’s legal challenge of the law will be considered by the Supreme Court this fall. With no Trump proposal for a replacement to the ACA, if the Court strikes the law in its entirety or in part, many voters cannot be certain that their health coverage will be secure. By undermining the ACA — the vast law that protects Americans with preexisting health conditions and makes health coverage more affordable through a system of premium subsidies and cost-sharing assistance — the president has put coverage for millions at risk.
Trump issued an executive order to preserve preexisting condition protections. If the ACA remains intact, the order is redundant. But if the ACA is repealed by the Court, the order is meaningless because it lacks the legal underpinning and legislative framework to take effect.
In contrast, Vice President Biden has proposed expanding coverage through the ACA by adding a public option, enhancing subsidies to make health care more affordable, filling the gap for low-income families living in states that did not expand Medicaid, and giving people with employer health plans the option to enroll in marketplace coverage and take advantage of premium subsidies. For sure, if Biden is elected, many policy details must be ironed out; passing legislation in a deeply divided Congress is never easy. Despite these challenges, Biden proposes expanding health coverage rather than revoking it.
Just as COVID-19 has exposed gaps in health coverage and affordability, it also has highlighted the poor health outcomes stemming from racial and ethnic inequities in the U.S. health system. Communities of color — Black, Hispanic, and American Indian and Alaska Native people — have higher rates of COVID cases, hospitalizations, and deaths compared to white people. These disparities are a result of myriad factors, many of which are deeply rooted in structural racism. The candidates’ plans to address health disparities and advance health equity set them apart.
The ACA has played a critical role in reducing disparities in access to health care and narrowed the uninsured rate among Black and Hispanic people compared to white people. Medicaid expansion has been key to improving racial equity. Repealing the ACA, as President Trump has sought to do, would reverse these gains. Even beyond repealing the ACA, this administration has pursued policies intended to limit Medicaid eligibility — for example, by permitting states to impose work requirements and other restrictions that would lead to fewer people covered. These measures and others are already having an impact; coverage gains achieved through the ACA have eroded since 2016. Health care for legal immigrants also has declined as a result of policies like the recently finalized “public charge” rule, which seems also to have caused an increase in uninsurance among children. The administration has further revoked ACA antidiscrimination and civil rights protections for LGBTQ people.
In addition to restoring and expanding coverage under the ACA, Vice President Biden has pledged to address health disparities and reinstate antidiscrimination protections. He has a proposal to advance racial equity not just in health care but across the economy. If successful, his plan could address underlying factors contributing to higher rates of COVID-19 cases and deaths among people of color, as well as their higher rates of heart disease, diabetes, and other health conditions tied to social determinants of health.
Finally, the candidates differ deeply in their approaches to the coronavirus pandemic. President Trump has failed to orchestrate a national strategy for combating coronavirus and has routinely undermined accepted public health advice with respect to mask-wearing and social distancing. He has delegated to the states responsibility for controlling the pandemic when it is clear that the virus travels freely across the country, regardless of state borders. Lax states can negate the efforts of those states sacrificing to bring the pandemic under control. Vice President Biden has strongly signaled, though his personal conduct and rhetoric, that he intends more aggressive federal leadership in fighting the virus.
In a recent Commonwealth Fund survey of likely voters, control of the pandemic and covering preexisting conditions were very important factors in choosing a president. In seven battleground states, protections for preexisting conditions outweighed COVID-19 and health costs as the leading health care issue voters are considering. In all 10 battleground states included in the survey, Vice President Biden was viewed as the more likely candidate to address these critical health care issues.
Perhaps since the Civil War, the United States has never faced starker choices in a presidential election. In health and other areas, there are profound differences in the positions of President Trump and former Vice President Biden. Voting this November is literally a matter of life and death for the American people.
Overall approach: Repeal the ACA and replace it with market-driven coverage options aimed at lowering premiums and increasing choice of plans tailored to individual preferences; give states more flexibility in designing coverage options; require more accountability for people with low incomes enrolled in public programs; protect preexisting conditions.
Medicaid: Repeal the ACA Medicaid expansion for adults; provide block grants to states to design their own programs; increase accountability through work requirements.
Individual market and marketplaces: Has promoted weaker regulations on plans that don’t comply with the ACA’s preexisting condition protections and other requirements; elimination of advertising and enrollment assistance during open enrollment; elimination of payments to insurers to offer lower-deductible plans.
Employer coverage: Has promoted weaker regulations on association health plans that don’t comply with the ACA and allowed employers to fund accounts for employees to buy health plans on their own, including products that don’t comply with the ACA.
Overall approach: Protect insurance for people with preexisting conditions by supporting and building on the ACA; expand insurance coverage and reduce consumers’ health care costs by enhancing the ACA’s marketplace subsidies, covering people currently eligible for Medicaid in nonexpansion states, and giving more people in employer plans the option to enroll in marketplace plans with subsidies.
Medicaid: Expand enrollment by allowing eligible people in 12 states without Medicaid expansion to enroll in a public plan through the marketplaces with no premiums; make enrollment easier with autoenrollment.
Individual market and marketplaces: Expand enrollment through enhanced subsidies, greater advertising and enrollment assistance: no one pays more than 8.5 percent of income on marketplace coverage; change the benchmark plan from silver to gold to reduce deductibles and cost-sharing.
Employer coverage: Allows anyone with employer coverage to enroll in a public plan through the marketplaces and be eligible for subsidies.
Medicare: Would allow people ages 60 to 65 to enroll in a Medicare-like heath plan.
Trump: The number of people without health insurance has increased under the president’s watch in part because of policies that have eliminated the promotion and advertising of marketplace open-enrollment periods, enrollment restrictions in Medicaid, and immigration policies that have had a chilling effect on enrollment of legal immigrants and their children. Trump supports a lawsuit now before the Supreme Court that argues for repeal of the ACA, which would eliminate coverage for as many as 20 million people. Says he will come up with a replacement but has yet to do so.
Biden: Has introduced proposals to build on the ACA by covering people in the 12 states that haven’t expanded Medicaid and enhance subsidies for marketplace plans. This would provide new options for people who are currently uninsured and increase coverage over time.
Trump: The ACA currently provides this protection. Trump supports the lawsuit before the Supreme Court that argues for repeal of the ACA and its preexisting conditions provision. Trump issued an executive order that said preexisting conditions are protected, but without the ACA or new legislation the order has no effect and is purely symbolic.
Biden: The vice president pledges to support and build on the ACA, retaining its preexisting condition protections.
Trump: The president eliminated payments to insurers to reimburse them for offering lower-deductible plans in the ACA marketplaces to people with lower incomes, as required by the law. This had the effect of increasing premiums for people not eligible for subsidies. He has promoted the sale of non-ACA-compliant health plans, like short-term plans. These plans have lower premiums for healthy people but screen for preexisting conditions and often provide little cost protection if someone becomes sick. He has loosened regulations for association health plans, although that was turned back under legal challenge. The repeal of the ACA would mean the loss of marketplace subsidies and preexisting-condition protections, making coverage unavailable or unaffordable for people with low and moderate incomes and those with health problems.
Biden: The vice president’s proposal to enhance marketplace subsidies will cap the amount of premiums people pay at 8.5 percent of income, including people in employer plans who would have the option to enroll in the marketplaces. By linking subsidies to gold plans, deductibles would also fall for those who choose those plans.
Trump: Uninsured rates among Hispanic people have risen under the president’s watch. Repealing the ACA would further eliminate coverage gains made by Hispanics, as well as Black people and Asian Americans, widening racial disparities in coverage and access.
Biden: The vice president’s proposals to expand coverage under the ACA will particularly benefit people of color. This is because people living in the 12 states that have not yet expanded Medicaid are disproportionately Black and Hispanic.
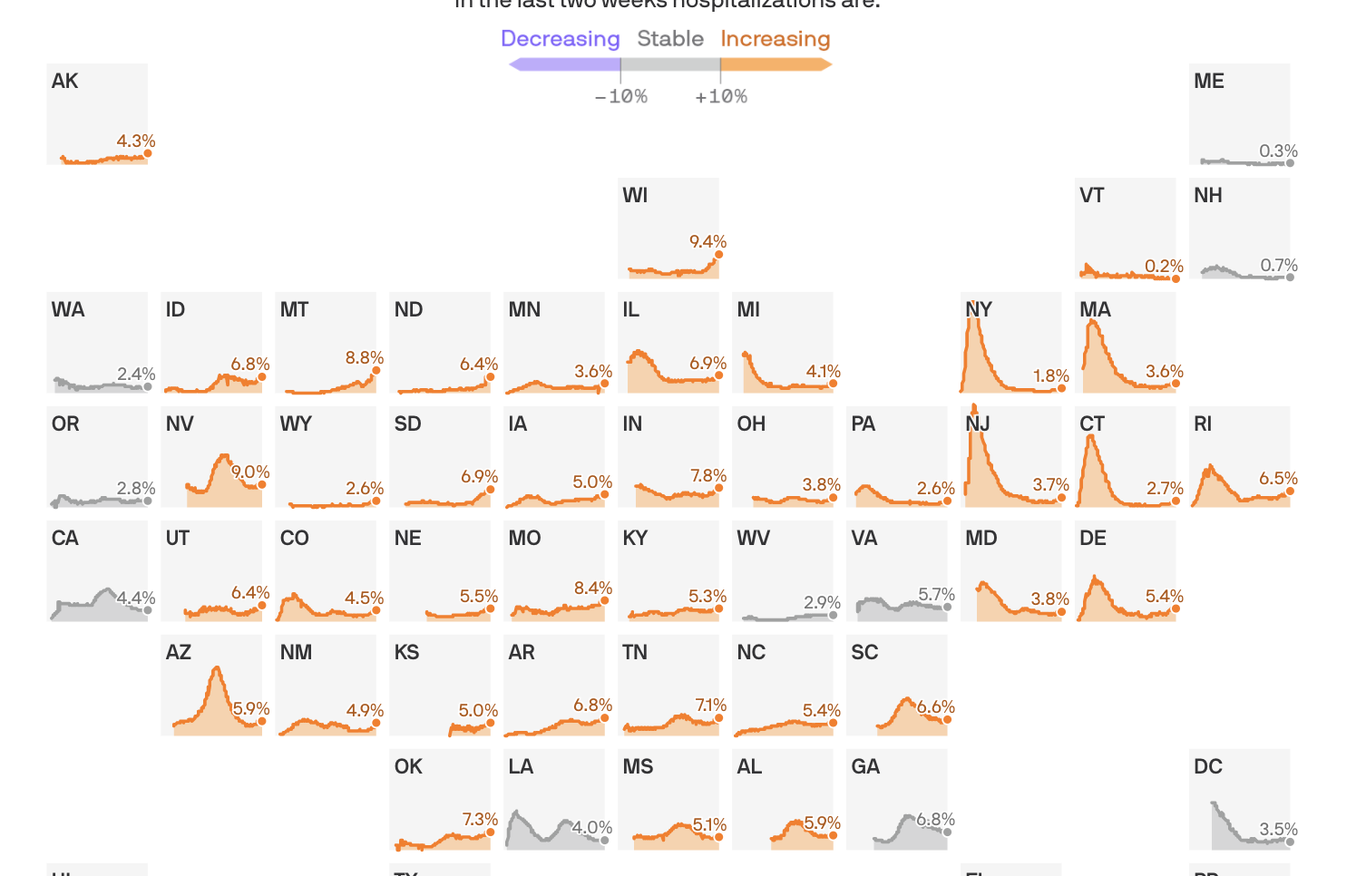
Coronavirus hospitalizations are increasing in 39 states, and are at or near their all-time peak in 16.
The big picture: No state is anywhere near the worst-case situation of not having enough capacity to handle its COVID-19 outbreak. But rising hospitalization rates are a sign that things are getting worse, at a dangerous time, and a reminder that this virus can do serious harm.
By the numbers: 39 states saw an increase over the past two weeks in the percentage of available hospital beds occupied by coronavirus patients.
Yes, but: The all-time peak of coronavirus hospitalizations happened in the spring, when 40% of New Jersey’s beds were occupied by COVID patients. Thankfully, even the the worst-performing states today are still a far cry from that.
Between the lines: These numbers, combined with the nationwide surge in new infections, confirm that the pandemic in the U.S. is getting worse — just as cold weather begins to set in in some parts of the country, which experts have long seen as a potentially dangerous inflection point.