To help Californians and state policymakers understand evolving demands on the state’s health care system during the COVID-19 pandemic, CHCF is working with survey firms on two fronts. CHCF and global survey firm Ipsos are assessing residents’ desire for COVID-19 testing and their access to health care services. CHCF and Truth on Call, a physician market-research firm, are surveying hospital-based critical care, emergency department, and infectious disease physicians about staffing and the availability of testing, personal protective equipment (PPE), intensive care unit beds, and ventilators. Download the charts and data for your own presentations and analyses.
Californians’ support for sheltering in place to curb the spread of coronavirus remains strong, according to a new tracking poll from CHCF and survey firm Ipsos.
For the second time in two weeks, Californians were asked which of the following statements came “closest to your opinion” of the state’s pandemic response:
- Californians should continue to shelter in place for as long as is needed to curb the spread of coronavirus, even if it means continued damage to the economy.
- Californians should stop sheltering in place to stimulate the economy even if it means increasing the spread of coronavirus.
This week, 71% of Californians want to continue the statewide order, compared to 75% two weeks ago. The change is within the statistical margin of error. This week, 17% say to stop sheltering in place, and 12% say they don’t know or have no opinion. Seventy-three percent of Californians with incomes at or below 138% of the federal poverty guidelines (PDF) support the stay-at-home orders.
Support for sheltering in place is strong among Californians no matter the setting in which they live. Seventy-three percent of urban residents support continuing to stay at home compared to 72% of rural Californians, and 68% of suburban residents.
As public officials plan greater use of “contact tracing” in future phases of COVID-19 containment efforts, Californians were asked which of the following came closest to their opinion about sharing personal information with public health officials:
- I am willing to share personal information about my health, movements, and contacts with local and state public health officials in order to help them understand and combat the spread of coronavirus.
- I am not willing to share personal information about my health, movements, and contacts with local and state public health officials under any circumstances.
Sixty percent of state residents are willing to share personal information to help stop the spread of the coronavirus, while 21% are unwilling to share information under any circumstances, and 18% don’t know or have no opinion. These results have changed little in two weeks. Forty-nine percent of Black Californians (not shown) and 50% of Californians with low incomes are willing to share information.
Public officials are discussing moving from broad shelter-in-place strategies to more targeted quarantine-and-isolate approaches to COVID-19 containment. In this week’s tracking survey, CHCF and Ipsos asked Californians who live with at least one other person about their capacity to physically separate themselves from others in their home. According to the most recent US Census data, 11% of Californians live alone.
Eighty-one percent of those who live with at least one other person say they have access to a separate bedroom at home, and 58% say they have access to both a separate bedroom and a separate bathroom. Among Californians with low incomes, 74% of those who live with at least one other person have access to a separate bedroom, and 38% have access to a separate bedroom and a separate bathroom. Sixteen percent of all Californians surveyed and 22% of Californians with low incomes do not have access to a separate bedroom.
Californians say they continue to engage in recommended behaviors to slow the spread of the new coronavirus. Eighty-four percent say they avoid unnecessary trips out of the home “all of the time” or “most of the time.” With regard to other public health behaviors:
- 81% of Californians say they routinely wear a mask in public spaces all or most of the time.
- 93% say they stay at least six feet away from others in public spaces all or most of the time.
- 93% say they wash their hands frequently with soap and water all or most of the time.
Compared with previous editions of the tracking survey, the percentage of Californians who would like to get tested increased. This week, 17% of those surveyed say they haven’t sought a test but would like to get one, up from 11% in the first survey in March.
As in findings in previous rounds of the tracking survey, 2.7% of Californians report they were tested in the preceding seven days. More Californians with low incomes report trying and failing to get tested than those overall (5.8% vs. 2.4%).
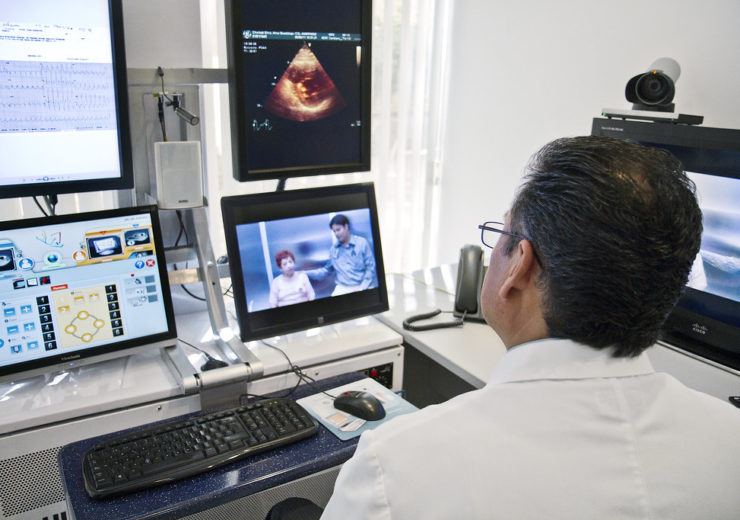
The share of Californians seeing health care providers by phone or video continues to rise. This week, 8% of Californians report seeing a provider by phone or video. The portion of Californians seeing a health care provider in person in the previous week has fallen by half, from 10% to 5% since this poll began in March.
The growth in telehealth appointments is more pronounced for Californians with low incomes, with 11% reporting that they saw a provider by phone or video in the previous seven days compared to 1.7% in late March.
Over the previous seven days, 70% of Californians say their mental health is “about the same” as before. This response is unchanged from two weeks ago. The percentage of respondents saying their mental health has gotten “a little” or “a lot” worse declined from 22% to 18%. This change is within the margin of error.
Less than 1% of Californians say they have lost health insurance coverage in the last month. Fifteen percent are “very” or “somewhat” worried about losing coverage, and among Californians with low incomes, 27% are worried about losing health insurance coverage.